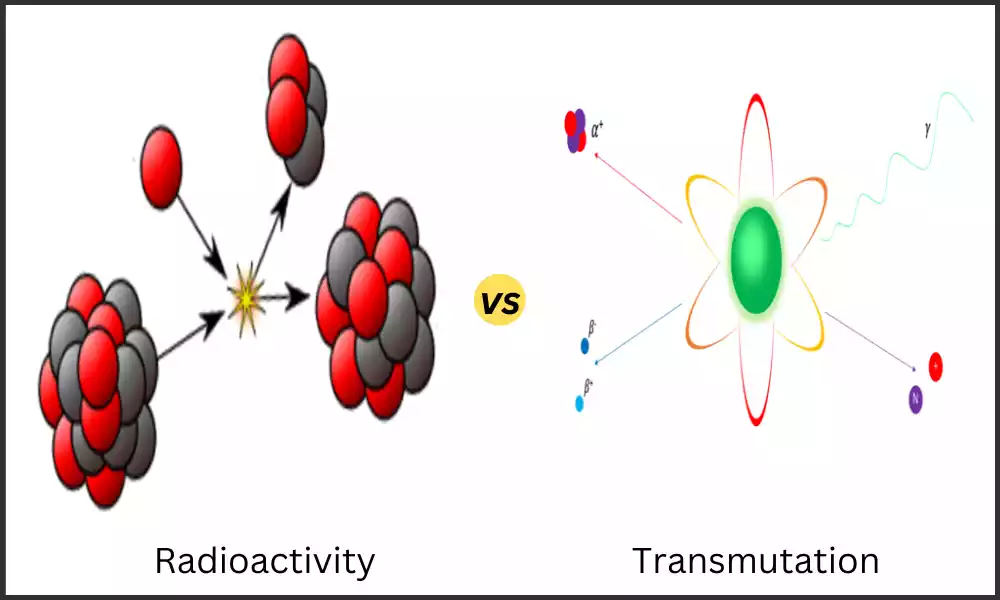
Atomic Nuclei are composed of Protons and Neutrons, Which are held together by a strong force. Changes to atomic Nuclei can result in the formation of different elements and the release of energy. Radioactivity and Transmutation are two ways in which atomic Nuclei can change.
What is Radioactivity?
Radioactivity, or spontaneous nuclear Transformation, involves creating new elements. Radioactivity refers to any ability of substances and materials to release radiation into space.
Nature offers us many varieties of radioactive elements, while some synthetic ones exist as well. Most normal (non-radioactive) atoms tend to possess stable nuclei; in radioactive elements however, their nucleus contains an imbalanced ratio of neutrons to protons which makes their nucleus unstable and subject them to radioactivity.
Radioactive decay occurs when nuclei emit particles to become stable; this process is commonly known as radioactive decay.
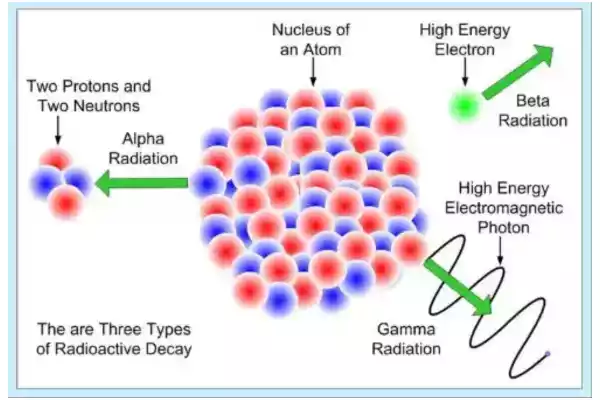
Radioactive elements usually decay at an exponential rate called the half-life, which indicates how quickly their original quantity declines to half its initial amount.
Transformations that result include Alpha particle emission, Beta particle emission, and orbital electron capture. Alpha particles are released when the neutron-to-proton ratio drops below an acceptable limit; by contrast, beta particle emissions occur due to too few protons available to react with electrons in orbitals of an atom’s nucleus and orbitals can capture orbitals electrons for capture by orbits around it.
Th-228 is a radioactive element capable of emitting alpha particles with various energies and emitting beta particles when neutrons inside nuclei change into protons by emitting these beta particles; P-32, H-3, and C-14 are pure emitters; radioactivity measurement units include Becquerel or Curie units.
Radioactivity found naturally is known as natural radioactivity. Uranium is one of the heaviest naturally occurring elements, boasting an atomic number 92.
Artificial radioactivity occurs when unstable nuclei are created artificially in laboratories by bombarding them with slow-moving neutrons; we call this form of production artificial radioactivity.
Artificial radioactivity refers to creating Transuranium elements capable of radioactive decay through artificial means. While there may already be radioactive isotopes present within natural materials like Thorium and Uranium, Artificial Radioactivity involves creating such elements deliberately.
What is Transmutation?
Transmutation is the process by which one element is Transformed into another element by changing the number of protons in the Nucleus.
This can occur naturally through radioactive decay or artificially through nuclear reactions. The process of transmutation can release energy in the form of radiation and is a fundamental process in nuclear physics.
In artificial Transmutation, A nucleus is bombarded with High-Energy particles such as Protons, Neutrons, or Alpha particles to induce a nuclear reaction that changes the identity of the Nucleus.
This process is used in Nuclear power plants to produce energy in Nuclear weapons to release large amounts of energy in an Explosion, and in Medical applications to produce isotopes for diagnostic imaging and Radiation Therapy.
In natural Transmutation, A Radioactive nucleus Spontaneously decays, emits particles or Radiation, and Transforms into a different nucleus with a different number of protons. This process occurs in nature and can result in the formation of new elements over time.
Transmutation is a complex process with important applications in various fields including Nuclear physics, energy Production, Medicine, and Materials Science.
Differences Between Radioactivity and Transmutation
Radioactivity and transmutation are related concepts, but they have some crucial differences:
1. Definition: Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of particles or energy from the nucleus of an atom as it undergoes a decay process, resulting in the formation of a different Nucleus. Transmutation is the process by which one element is Transformed into another element by changing the number of protons in the Nucleus.
2. Cause: Radioactivity occurs naturally or artificially due to the instability of the nucleus, while transmutation can occur naturally through radioactive decay or artificially through nuclear reactions.
3. Energy release: Radioactivity releases energy in the form of radiation during decay, while transmutation can release energy through the nuclear reactions that cause the change in the nucleus.
4. Products: Radioactivity results in the formation of a different nucleus, which may or may not be a different element. Transmutation, on the other hand, always results in the formation of a different element.
5. Application: Radioactivity has many applications, including power generation, medical imaging, and radiation therapy. Transmutation is mainly used in nuclear reactors to produce Energy and in Research to study the properties of Elements and their Isotopes.
Radioactivity and Transmutation are related but distinct concepts with important differences in their causes, energy release, products, and applications.
Summary – Radioactivity vs Transmutation
Radioactivity and Transmutation are chemical processes that involve changing atomic nuclei to form new chemical elements from existing elements.
One key distinction between Radioactivity and Transmutation lies within natural Transmutation compared with that which happens through artificial means such as nuclear fission. Radioactivity only refers to natural transmutation while transmutation encompasses either method.