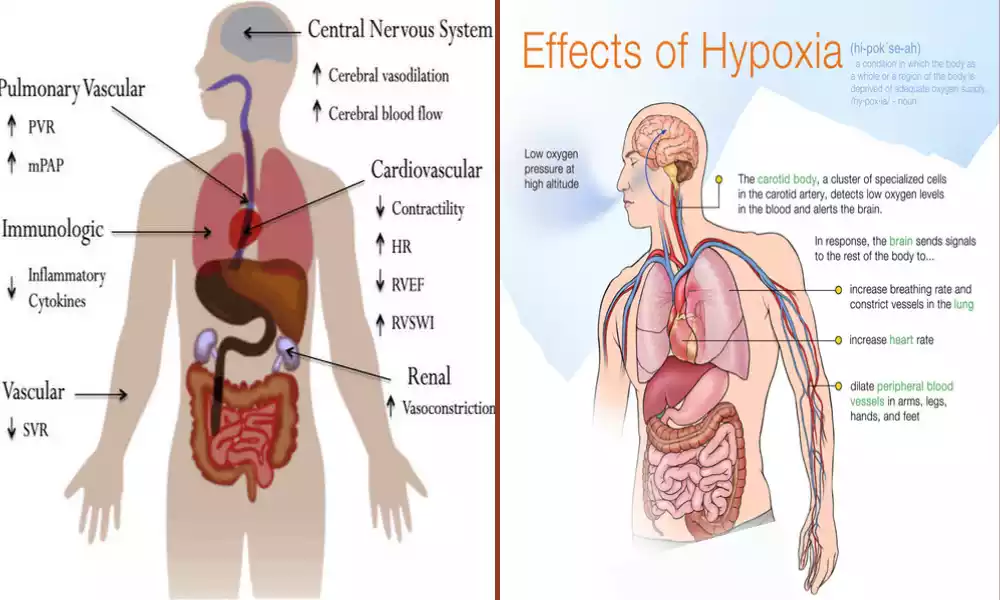
Hypoxia is a medical condition characterized by an inadequate supply of oxygen to tissues and organs in the body. It occurs when the oxygen levels in the blood or the environment are insufficient to meet the metabolic demands of the cells, resulting in potential damage or dysfunction of vital organs.
Hypoxia can have various causes, including respiratory disorders, circulatory problems, high altitudes, or exposure to environments with reduced oxygen levels. The severity of hypoxia can range from mild, with minimal symptoms, to severe, leading to organ failure and life-threatening situations if left untreated.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms and signs of hypoxia and hypercapnia can vary depending on the severity of the condition and its underlying cause.
Here, I’ll outline the typical symptoms and signs associated with each of these respiratory conditions:
- Shortness of Breath: Individuals with hypoxia often experience difficulty breathing and a sensation of not getting enough air.
- Cyanosis: This is a bluish discoloration of the skin, lips, and nail beds, which occurs due to insufficient oxygen in the bloodstream.
- Rapid Heart Rate (Tachycardia): The heart may beat faster in an attempt to pump more oxygenated blood to the body’s tissues.
- Confusion and Cognitive Impairment: As the brain receives inadequate oxygen, cognitive functions can be affected, leading to confusion, memory problems, and impaired judgment.
- Headache: Some people with hypoxia may experience headaches, often described as throbbing and severe.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Insufficient oxygen can lead to a feeling of dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Fatigue: Individuals may feel unusually tired and weak.
- Chest Pain: In severe cases, chest pain may occur, especially if there’s an underlying heart condition.
- Changes in Breathing Pattern: Breathing may become rapid and shallow, or, in some cases, slow and irregular.
- Loss of Consciousness: In extreme cases, hypoxia can lead to unconsciousness and, if left untreated, may be life-threatening.
It’s important to note that the severity of symptoms and signs can vary widely, and some individuals may experience a combination of these symptoms. Additionally, the underlying causes of hypoxia can influence the specific clinical presentation.
Definition of hypercapnia
Hypercapnia is a medical condition characterized by an elevated level of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the bloodstream. It occurs when the body is unable to effectively remove excess CO2, leading to an imbalance between oxygen and carbon dioxide levels.
Normally, the body maintains a relatively constant level of CO2 through the respiratory system’s ventilation process, where CO2 is exhaled from the lungs. However, in cases of hypercapnia, there is an accumulation of CO2 due to factors such as inadequate ventilation, lung diseases, or other underlying medical conditions.
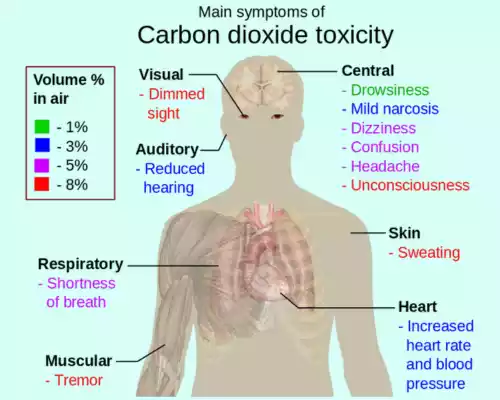
This condition can result in various symptoms, including rapid breathing, and confusion, and can be associated with respiratory distress. Severe or prolonged hypercapnia can be life-threatening and requires prompt medical attention and intervention to correct the underlying cause and restore proper gas exchange in the body.
Symptoms and signs
Hypercapnia Symptoms and Signs:
- Rapid Breathing (Tachypnea): The body attempts to eliminate excess carbon dioxide by increasing the breathing rate.
- Flushing of the Skin: The skin may become reddened due to the vasodilatory effects of high carbon dioxide levels.
- Confusion and Dizziness: Elevated CO2 can affect brain function, leading to confusion, difficulty concentrating, and dizziness.
- Headache: Similar to hypoxia, individuals with hypercapnia may experience headaches.
- Muscle Twitching: Increased CO2 levels can lead to muscle twitching, particularly in the extremities.
- Fatigue: Patients may feel tired and weak.
- Increased Heart Rate (Tachycardia): The heart rate may increase as the body attempts to compensate for the high CO2 levels.
- Severe Symptoms: In severe cases, hypercapnia can lead to respiratory distress, coma, or loss of consciousness.
Important to keep in mind is that symptoms and signs can vary widely in severity; individuals may even experience multiple of them at once. Furthermore, the root causes of hypercapnia can impact its specific clinical presentation.
Importance of understanding the differences between the two conditions
Understanding the differences between hypoxia and hypercapnia is crucial for several reasons, especially in the fields of healthcare and emergency medicine:
- Accurate Diagnosis and Treatment: Recognizing the specific condition a patient is experiencing is essential for providing the appropriate medical care. Hypoxia and hypercapnia have distinct causes and treatments, so misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective or potentially harmful interventions.
- Different Underlying Causes: Hypoxia is primarily caused by a lack of oxygen, often due to issues with the respiratory or circulatory systems, while hypercapnia results from an excess of carbon dioxide, often due to problems with ventilation or lung function. Understanding these distinctions helps healthcare professionals pinpoint the root cause.
- Symptom Recognition: Hypoxia and hypercapnia have different sets of symptoms. Knowing these differences aids in the early identification of these conditions, potentially preventing complications or deterioration of a patient’s health.
- Treatment Strategies: Treatment approaches for hypoxia and hypercapnia vary significantly. For example, hypoxia is typically treated with oxygen therapy, while hypercapnia may require strategies to improve ventilation or treat underlying lung diseases. Understanding these distinctions ensures that healthcare providers implement the most effective treatments.
- Preventative Measures: In certain settings, such as high-altitude environments or industrial workplaces, understanding the differences between these conditions can help individuals and organizations implement preventive measures to reduce the risk of exposure and mitigate potential health hazards.
- Emergency Response: In emergency situations, such as natural disasters, accidents, or medical emergencies, first responders must quickly assess and address potential respiratory issues. Knowing whether a patient is experiencing hypoxia or hypercapnia can guide their immediate actions and decisions.
- Critical Care: In intensive care units and critical care settings, patients with respiratory distress may present with various symptoms. Accurate differentiation between hypoxia and hypercapnia is vital for tailoring treatments and monitoring patient progress.
- Research and Education: For healthcare professionals, researchers, and educators, understanding the differences between these conditions is fundamental for advancing medical knowledge, improving patient care, and training future healthcare providers.
Differentiating between hypoxia and hypercapnia is essential for providing the right care, improving patient outcomes, and ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals in various healthcare and emergency settings.
Hypoxia and Hypercapnia comparison chart
Here’s a comparison chart that highlights the key differences between hypoxia and hypercapnia:
| Aspect | Hypoxia | Hypercapnia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inadequate oxygen supply to tissues and organs due to low oxygen levels in the blood or environment. | Elevated carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the blood, result from inadequate CO2 elimination. |
| Primary Cause | Lack of oxygen, often due to respiratory or circulatory issues. | Excess CO2, often due to ventilation problems or lung-related conditions. |
| Symptoms and Signs | – Shortness of breath – Cyanosis (bluish skin and lips) – Rapid heart rate (tachycardia) – Confusion – Headache – Dizziness – Fatigue – Chest pain (in severe cases) – Changes in breathing pattern – Loss of consciousness (in extreme cases) | – Rapid breathing (tachypnea) – Flushing of the skin – Confusion and dizziness – Headache – Muscle twitching – Fatigue – Increased heart rate (tachycardia) – Severe symptoms: respiratory distress, coma, or loss of consciousness. |
| Diagnostic Methods | – Pulse oximetry – Arterial blood gases (ABG) – Imaging tests (e.g., chest X-ray) | – Arterial blood gases (ABG) – Capnography – Imaging (e.g., chest X-ray or CT scan) |
| Treatment and Management | – Oxygen therapy – Treating underlying causes (e.g., addressing respiratory or circulatory issues) – Avoiding high altitudes | – Addressing underlying ventilation problems or lung diseases – Oxygen therapy with caution (as excessive oxygen can worsen hypercapnia) – Mechanical ventilation (in severe cases) |
| Similarities | – Both can lead to respiratory distress. – Both may require medical intervention. – Oxygen therapy may be a component of treatment for both conditions. | – Both can lead to respiratory distress. – Both may require medical intervention. – Oxygen therapy may be a component of treatment for both conditions. |
| Importance of Understanding | – Accurate diagnosis and treatment. – Differentiating causes to target treatment. – Recognizing symptoms for early intervention. – Preventing complications and life-threatening situations. | – Accurate diagnosis and treatment. – Differentiating causes to target treatment. – Recognizing symptoms for early intervention. – Preventing complications and life-threatening situations. |
Understanding these differences is essential for healthcare professionals to provide appropriate care and for individuals to recognize the signs and seek timely medical attention when necessary.
Similarities Between Hypoxia and Hypercapnia
While hypoxia and hypercapnia are distinct respiratory conditions with different underlying causes, there are some similarities between them, particularly in how they can affect the body and their potential consequences:
- Respiratory Distress: Both hypoxia and hypercapnia can lead to respiratory distress, which includes symptoms like rapid breathing, shortness of breath, and an increased respiratory rate. This shared symptomatology can make it challenging to differentiate between the two conditions based solely on clinical presentation.
- Cognitive Impairment: In both hypoxia and hypercapnia, cognitive impairment can occur. Individuals with these conditions may experience confusion, difficulty concentrating, and changes in mental alertness.
- Cardiovascular Effects: Both conditions can affect the cardiovascular system. They may lead to an increased heart rate (tachycardia) as the body attempts to compensate for the imbalance in oxygen and carbon dioxide levels.
- Fatigue: People with both hypoxia and hypercapnia can feel unusually tired and weak.
- Headache: Headaches are a common symptom in both conditions, likely due to the impact on brain function and blood flow.
- Changes in Breathing Pattern: Individuals with hypoxia and hypercapnia often exhibit changes in their breathing patterns. While the specific alterations differ, they both reflect the body’s efforts to correct the underlying imbalance in oxygen and carbon dioxide levels.
- Potential Life-Threatening Consequences: If left untreated, severe cases of both hypoxia and hypercapnia can lead to life-threatening situations, including loss of consciousness, coma, and organ failure.
- Treatment with Oxygen: In clinical practice, both conditions may involve the administration of supplemental oxygen to help alleviate symptoms and correct the underlying imbalance. However, the specifics of oxygen therapy may differ.
It’s important to note that while there are similarities, the key distinction between these two conditions lies in their underlying causes: hypoxia results from insufficient oxygen, while hypercapnia results from an excess of carbon dioxide.
Therefore, the approaches to diagnosis and treatment should be tailored to address the specific cause of the respiratory imbalance. Proper assessment and monitoring by healthcare professionals are essential to differentiate between these conditions accurately and provide appropriate care.
Conclusion
differentiating between hypoxia and hypercapnia is vital for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. While they share some symptoms, their causes and treatment approaches differ significantly. This knowledge is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals in recognizing and addressing these respiratory conditions promptly.