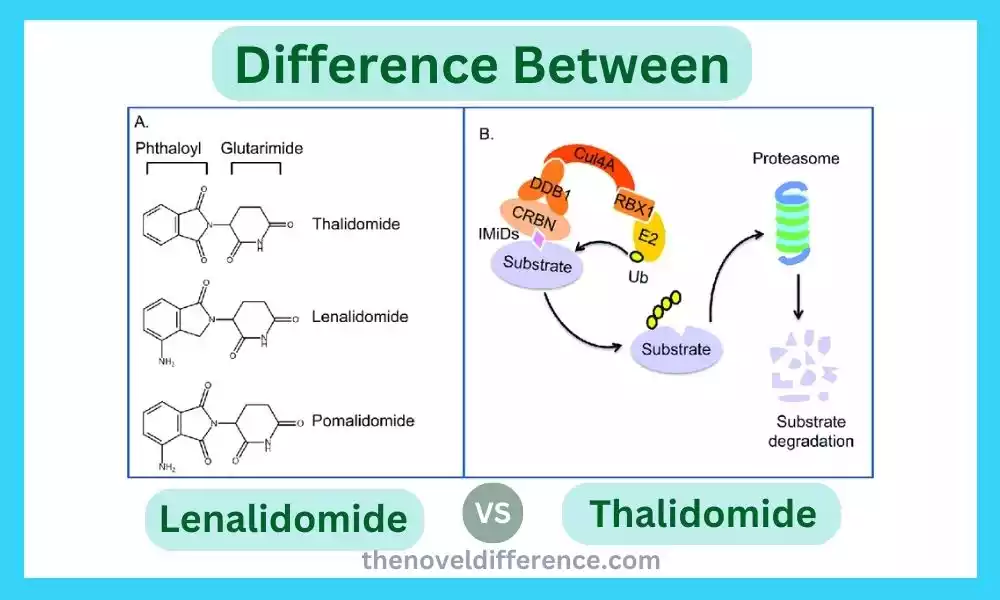
When it comes to pharmaceuticals, it’s fundamental to get the contrasts between different drugs. We’ll investigate the dissimilarities between two drugs Lenalidomide and Thalidomide. While both solutions have been utilized in the treatment of certain conditions, they have particular characteristics and applications. Let’s dive into the details and uncover the key dissimilarities between Lenalidomide and Thalidomide.
Definition of Lenalidomide and Thalidomide
Lenalidomide: Lenalidomide could be a pharmaceutical compound that has a place in the course of drugs known as immunomodulatory operators. It could be a subordinate of thalidomide and exhibits an extent of immunomodulatory, anti-angiogenic, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Lenalidomide is utilized in the treatment of hematological malignancies, including numerous myeloma, myelodysplastic disorders, and mantle cell lymphoma. It works by tweaking the resistant framework and influencing the microenvironment encompassing cancer cells, in this manner repressing tumor development and advancing anti-cancer impacts.
Thalidomide: Thalidomide may be a medicine that was first presented in the late 1950s as a narcotic and antiemetic medication. It gained notoriety due to its severe teratogenic effects, causing birth defects in infants when taken by pregnant women. Despite its disturbed past, thalidomide has found unused helpful employment as an immunomodulatory operator. It exhibits anti-inflammatory properties and affects various components of the immune system.
Thalidomide is essentially utilized within the treatment of numerous myeloma, erythema nodosum leprosum (a complication of sickness), and cutaneous lupus erythematosus. It is also being investigated for its potential in treating other conditions such as graft-versus-host disease and certain inflammatory disorders.
Both lenalidomide and thalidomide have particular components of activity and helpful applications, even though they share likenesses as immunomodulatory specialists. Understanding these differences is crucial for appropriate treatment selection and managing potential risks and side effects associated with each medication.
Mechanism of Action
Lenalidomide: The exact instrument of activity of lenalidomide hasn’t completely caught on, but it is known to have numerous impacts on the resistant framework and the tumor microenvironment.
It is believed to primarily exert its therapeutic effects through the following mechanisms:
1. Immunomodulation: Lenalidomide enhances the activity of certain immune cells, such as natural killer (NK) cells and T-cells, by stimulating their proliferation and activation. This leads to expanded anti-tumor safe reactions and cytotoxicity against cancer cells.
2. Cytokine Modulation: Lenalidomide balances the generation and emission of different cytokines, such as tumor corruption factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-2 (IL-2), and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). This cytokine modulation helps regulate immune responses and promotes anti-inflammatory effects.
3. Anti-angiogenesis: Lenalidomide restrains the arrangement of modern blood vessels (angiogenesis) that are significant for tumor development and survival. It meddles with the signaling pathways included in angiogenesis, such as vascular endothelial development figure (VEGF), subsequently lessening the blood supply to tumors and blocking their movement.
Thalidomide
Thalidomide’s instrument of activity is additionally complex and includes different immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory impacts. Its precise mode of activity isn’t completely explained,
The taking after instruments is thought to contribute to its helpful impacts:
1. Immunomodulation: Thalidomide influences the action and work of resistant cells, counting T-cells, NK cells, and B-cells. It enhances cellular immunity and promotes anti-tumor immune responses.
2. Anti-inflammatory Effects: Thalidomide shows anti-inflammatory properties by repressing the generation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and interleukin-1 (IL-1). By reducing inflammation, it helps alleviate symptoms associated with certain inflammatory conditions.
3. Immunomodulatory Effects: Thalidomide impacts the generation and emission of different cytokines, such as IL-2 and IFN-γ, which are included in resistant reactions. It tweaks the adjustment between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, contributing to its immunomodulatory impacts.
It is critical to note that whereas lenalidomide and thalidomide share a few immunomodulatory properties, they have unmistakable atomic structures and may display distinctive selectivity and power in their intelligence with particular targets within the safe framework and tumor microenvironment.
Thalidomide’s mechanism of action
Thalidomide’s instrument of activity is multifaceted and includes a few atomic pathways.
Even though not completely caught on, the taking after components contribute to its restorative impacts:
1. Immunomodulation: Thalidomide applies immunomodulatory impacts by affecting the action and work of different resistant cells. It upgrades the movement of T-cells, common executioner (NK) cells, and B-cells, which are vital components of the resistant framework included in battling contaminations and cancer. Thalidomide advances the multiplication and actuation of these safe cells, driving improved safe reactions against cancer cells and possibly contributing to its anti-tumor impacts.
2. Anti-inflammatory Effects: Thalidomide shows anti-inflammatory properties by restraining the generation of certain pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor rot factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-1 (IL-1). These cytokines play a part in the fiery reaction, and their intemperate generation is related to different fiery conditions. By lessening the levels of these cytokines, thalidomide makes a difference to hose aggravation and lightens indications related to certain provocative disarranges.
3. Angiogenesis Inhibition: Thalidomide interferes with the process of angiogenesis, which is the formation of new blood vessels. Angiogenesis is basic for tumor development and survival because it gives supplements and oxygen to the developing tumor. Thalidomide restrains the generation of vascular endothelial development calculate (VEGF), a key signaling atom included in angiogenesis. By decreasing VEGF levels, thalidomide disturbs the arrangement of modern blood vessels, subsequently restraining the blood supply to tumors and hindering their development.
4. Immunomodulatory Effects: Thalidomide impacts the generation and discharge of different cytokines, such as interleukin-2 (IL-2) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). These cytokines play imperative parts in controlling safe reactions. Thalidomide balances the adjustment between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, possibly contributing to its immunomodulatory impacts and its capacity to direct safe movement.
It’s critical to note that thalidomide’s correct instruments of activity are still being examined and caught on. Moreover, its impacts may shift depending on the particular condition being treated, highlighting the complexity of its pharmacological activities.
Side Effects and Safety Profile
Lenalidomide: Lenalidomide, like any medication, can cause side effects. It is vital to note that the taking-after list isn’t comprehensive, and not all people will encounter these side impacts.
Common side impacts of lenalidomide may include:
1. Hematologic Toxicity: Lenalidomide can influence the bone marrow, driving a diminish in ruddy blood cells (frailty), white blood cells (neutropenia), and platelets (thrombocytopenia). This may increase the chance of diseases, death, and weakness.
2. Blood Clots: Lenalidomide has been associated with an increased risk of blood clot formation, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Patients with a history of blood clotting disarrange or those at the chance for blood clots ought to be closely observed.
3. Teratogenicity: Lenalidomide is known to cause severe birth defects and fetal harm when taken during pregnancy. It is contraindicated for use in pregnant women or women who may become pregnant unless under strict monitoring and adherence to specific pregnancy prevention programs.
4. Gastrointestinal Effects: Lenalidomide can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. These symptoms are generally manageable with supportive care and dose adjustments.
5. Fatigue: Fatigue is a commonly reported side effect of lenalidomide treatment. It can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life and may require symptom management strategies.
Thalidomide
Thalidomide, as well, has its claim set of potential side impacts. It is vital to talk about these with a healthcare proficient, and not all people will encounter these side impacts.
Common side effects of thalidomide may include:
1. Sedation and Drowsiness: Thalidomide can cause tiredness, sedation, and languor, especially when beginning the pharmaceutical. It is important to exercise caution when engaging in activities that require alertness until the individual’s tolerance to the medication is known.
2. Peripheral Neuropathy: Thalidomide may cause damage to the peripheral nerves, resulting in peripheral neuropathy. This will cause signs such as deadness, shuddering, or torment inside the hands and feet. Regular monitoring and dose adjustments may be necessary to manage this side effect.
3. Constipation: Thalidomide can lead to constipation in some individuals. Maintaining adequate hydration, dietary adjustments, and the use of stool softeners or laxatives can help manage this side effect.
4. Skin Reactions: Thalidomide has been associated with skin reactions, including rash and dry skin. These reactions are generally mild and can be managed with appropriate skincare measures.
5. Birth Defects: Thalidomide is highly teratogenic and can cause severe birth defects if taken during pregnancy. Strict precautions must be taken to avoid pregnancy while on thalidomide treatment, including the use of reliable contraception methods.
It’s important for individuals taking lenalidomide or thalidomide to communicate with their healthcare providers about any side effects experienced during treatment. This allows for timely management and adjustment of the treatment plan to ensure optimal safety and efficacy.
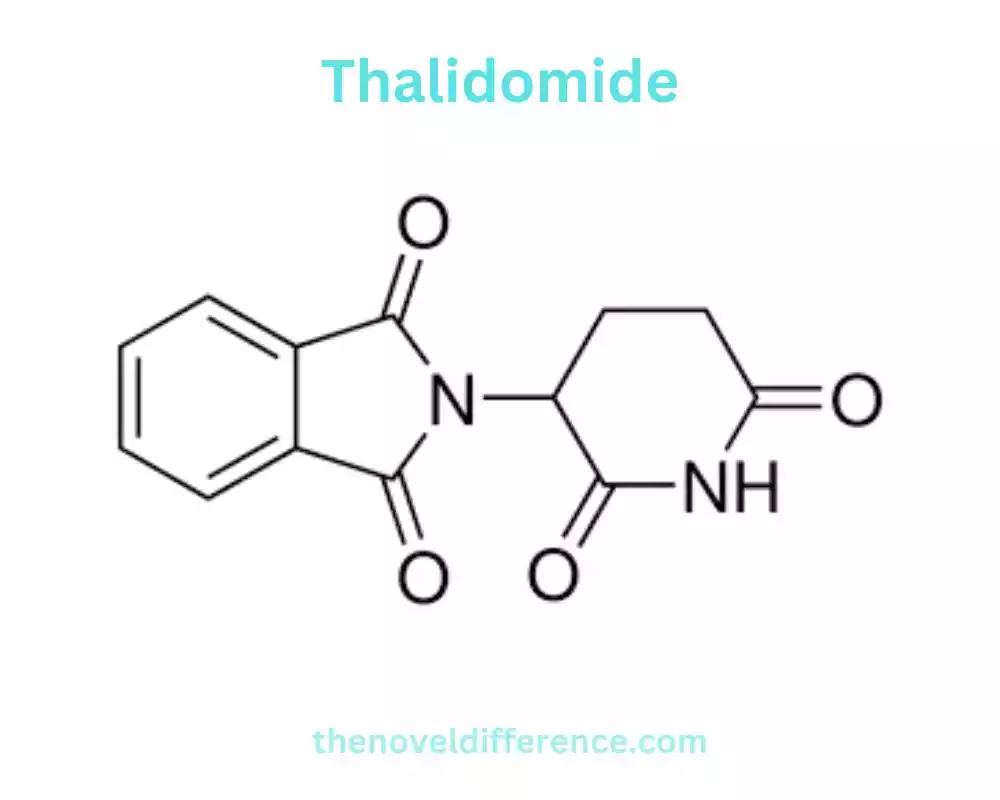
Lenalidomide
Lenalidomide is an oral medication that belongs to the class of drugs known as immunomodulatory agents. It is derived from thalidomide but has been structurally modified to enhance its therapeutic properties. Lenalidomide is utilized within the treatment of certain hematological malignancies and related clutters, counting different myeloma, myelodysplastic disorders, and mantle cell lymphoma.
The instrument of action of lenalidomide hasn’t completely caught on, but it is known to have immunomodulatory, anti-angiogenic, and anti-inflammatory impacts. These properties contribute to its therapeutic efficacy in treating various conditions.
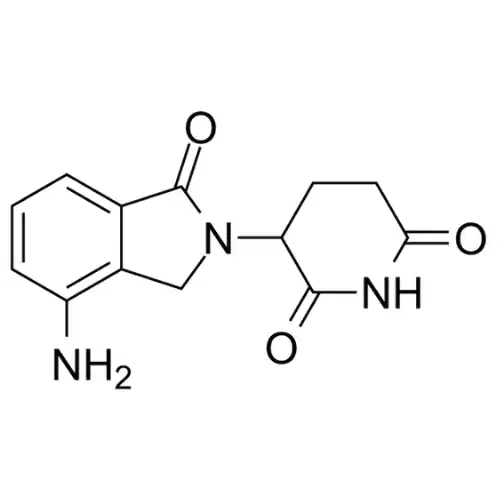
Lenalidomide works by exerting several effects on the immune system and the tumor microenvironment. It upgrades the action and multiplication of resistant cells, such as common executioner (NK) cells and T-cells, driving expanded anti-tumor safe reactions. Lenalidomide moreover balances the generation and emission of cytokines, such as tumor rot factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-2 (IL-2), which play critical parts in resistant control and aggravation.
Moreover, lenalidomide shows anti-angiogenic properties by repressing the arrangement of unused blood vessels. It meddles with the signaling pathways included in angiogenesis, such as vascular endothelial development figure (VEGF), in this manner lessening the blood supply to tumors and hindering their development.
When utilized within the treatment of myelodysplastic disorders, lenalidomide acts by fortifying the generation of sound blood cells and stifling the irregular cells that are characteristic of this clutter.
Lenalidomide is as a rule taken orally once every day, with or without nourishment, as coordinated by a healthcare proficient. The dosage and treatment duration depend on the specific condition being treated and individual patient factors. Regular monitoring of blood counts and other relevant parameters is typically conducted during lenalidomide treatment.
Lenalidomide can cause side effects. Common side impacts incorporate hematologic poisonous quality (such as frailty, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia), the expanded hazard of blood clots, teratogenic impacts (extreme birth abandons if taken amid pregnancy), gastrointestinal side effects (sickness, spewing, loose bowels), and weariness. Patients need to discuss any side effects experienced with their healthcare providers for appropriate management and monitoring.
Lenalidomide has revolutionized the treatment landscape for certain hematological malignancies, providing improved outcomes and extended survival for many patients. However, its use requires careful monitoring and adherence to safety precautions due to its potential risks and side effects.
Comparison Chart
Here’s a comparison chart highlighting the key differences between lenalidomide and thalidomide:
| Aspect | Lenalidomide | Thalidomide |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Derived from thalidomide | Original compound |
| Approved Indications | Multiple myeloma, myelodysplastic syndromes, mantle cell lymphoma | Multiple myeloma, erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL), skin lesions associated with leprosy |
| Mechanism of Action | Immunomodulation, anti-angiogenic | Immunomodulation, anti-angiogenic |
| Potency | More potent | Less potent |
| Selectivity | More selective | Less selective |
| Side Effects | Hematologic toxicity, increased risk of blood clots, gastrointestinal effects, fatigue, teratogenic potential (strict pregnancy prevention programs) | Sedation, peripheral neuropathy, constipation, skin reactions, teratogenicity (severe birth defects) |
| Range of Use | Limited to specific hematological malignancies and related disorders | A broader range of approved indications including hematological malignancies, ENL, and skin lesions associated with leprosy |
Importance of Understanding the Differences between Lenalidomide and Thalidomide
Understanding the distinctions between Lenalidomide and Thalidomide is of significant importance for several reasons. These differences impact their efficacy, safety profile, approved indications, and potential side effects.
Here are some key reasons why understanding these disparities is crucial:
1. Treatment Selection: A clear understanding of the differences between Lenalidomide and Thalidomide helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions when selecting the most appropriate treatment for patients. Each medication has specific indications and effectiveness against certain conditions, and knowing these differences ensures that patients receive the most suitable therapy for their specific medical needs.
2. Safety Considerations: Both Lenalidomide and Thalidomide carry potential risks and side effects. Being aware of the contrasting safety profiles of these drugs is vital for healthcare providers to manage and monitor patients effectively. Understanding the specific adverse events associated with each medication helps in assessing the overall risk-benefit ratio and implementing appropriate safety precautions.
3. Therapeutic Approach: The mechanisms of action of Lenalidomide and Thalidomide differ significantly. Lenalidomide acts by balancing safe reactions and cytokine generation, whereas Thalidomide shows anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory impacts. Recognizing these variances aids in comprehending the distinct therapeutic approaches employed by these drugs, which can influence treatment outcomes and patient responses.
4. Treatment Response and Resistance: Knowing the disparities between Lenalidomide and Thalidomide assists healthcare professionals in evaluating treatment responses and addressing potential resistance. Understanding the unique characteristics of each medication helps in monitoring patient progress and determining appropriate modifications or alternative treatment options if needed.
5. Patient Education: Educating patients about the differences between Lenalidomide and Thalidomide empowers them to be active participants in their care. Patients who understand the rationale behind their prescribed medication, its intended effects, potential side effects, and safety considerations are better equipped to adhere to their treatment regimen and report any concerning symptoms promptly.
Comprehending the differences between Lenalidomide and Thalidomide is vital for healthcare professionals, patients, and caregivers. This knowledge supports informed decision-making, improves patient safety, facilitates appropriate treatment selection, and enhances overall treatment outcomes.
Thalidomide
Thalidomide could be a pharmaceutical that picked up a reputation within the late 1950s and early 1960s due to its awful teratogenic impacts. At first, presented as a narcotic and antiemetic sedate, it was afterward found to cause extreme birth abandons when taken by pregnant ladies. Despite its obliterating history, thalidomide has found new therapeutic applications as an immunomodulatory specialist and is presently utilized in the treatment of certain conditions.
Thalidomide’s instrument of activity isn’t completely caught on, but it shows immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and anti-angiogenic properties. These actions contribute to its therapeutic effects in various diseases.
Thalidomide is thought to apply its anti-tumor impacts through a few components. It improves the action of safe cells, counting T-cells and normal executioner (NK) cells, which play pivotal parts in safe reactions against cancer cells. Thalidomide moreover tweaks the generation of cytokines, such as tumor rot factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), which control resistant work and irritation.
Thalidomide shows anti-angiogenic impacts by hindering the arrangement of modern blood vessels. It meddles with the signaling pathways included in angiogenesis, counting vascular endothelial development figure (VEGF), in this manner diminishing the blood supply to tumors and obstructing their development.
Thalidomide is utilized in the treatment of other conditions as well. It has shown efficacy in managing erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL), a complication of leprosy characterized by painful skin nodules. Thalidomide’s anti-inflammatory properties help reduce the inflammation associated with ENL and alleviate symptoms.
Thalidomide is exceedingly teratogenic and can cause serious birth abandons when taken during pregnancy. It is contraindicated for use in pregnant women or women who may become pregnant unless under strict monitoring and adherence to specific pregnancy prevention programs. Thalidomide can moreover cause sedation and tiredness, fringe neuropathy (nerve harm driving to indications like deadness and shivering), stoppage, and skin responses. Regular monitoring and dose adjustments may be necessary to manage these side effects.
Due to thalidomide’s special history and potential dangers, its utilization is firmly controlled, and strict conventions are input to guarantee its secure organization. Physicians prescribing thalidomide are required to be part of specific risk management programs, and patients must adhere to rigorous pregnancy prevention measures.
Thalidomide serves as a cautionary tale in medicine, highlighting the importance of rigorous testing, safety monitoring, and informed prescribing practices to avoid the tragic consequences associated with its earlier use.
Conclusion
Lenalidomide and Thalidomide are unmistakable drugs with contrasts in their composition, mode of activity, security profiles, and treatment applications. Lenalidomide is utilized for the treatment of different myeloma, whereas Thalidomide finds applications in sickness administration as well. It is fundamental allude to”>to allude, healthcare experts, to decide the foremost fitting medicine for a particular condition, considering person components and potential dangers. Understanding the contrasts between Lenalidomide and Thalidomide is pivotal for making educated choices and guaranteeing the secure and viable utilization of these medicines.