Definition of Tendonitis
Tendonitis, also known as tendinitis, is a medical condition characterized by the inflammation and irritation of a tendon. Tendons are thick cords of connective tissue that attach muscles to bones, allowing for the movement of joints.
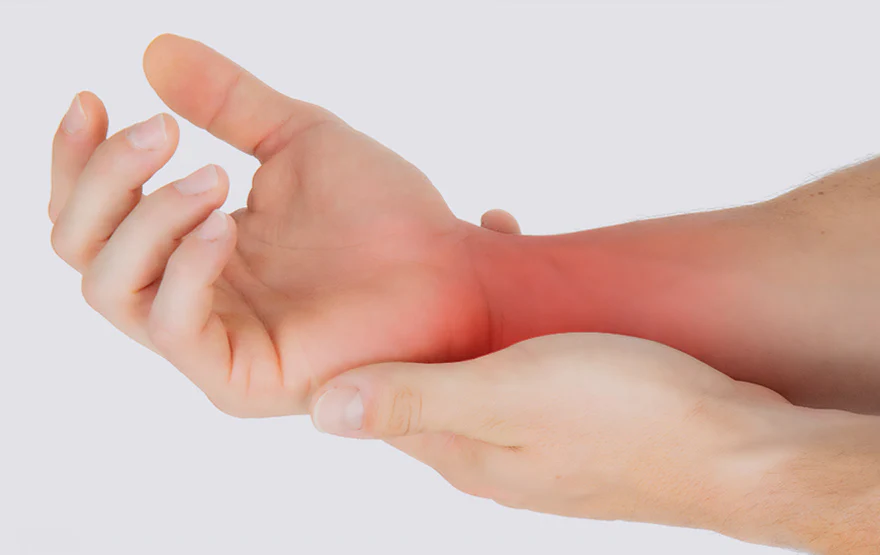
When a tendon becomes inflamed, it can cause pain, swelling, and discomfort in the affected area. Tendonitis often results from overuse, repetitive movements, injury, or aging, and it can occur in various parts of the body, including the shoulders, elbows, wrists, knees, and ankles. The condition can range from mild to severe, and timely treatment is essential to reduce pain, promote healing, and prevent further complications.
Definition of Arthritis
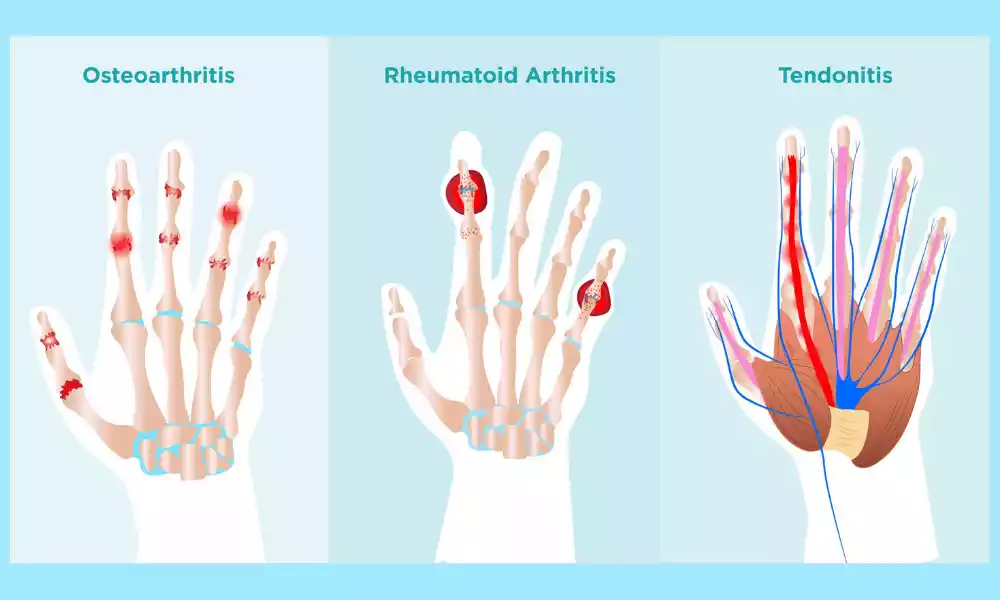
Arthritis is a broad medical term used to describe a group of more than 100 different inflammatory joint conditions that primarily affect the joints in the body. The most common types of arthritis include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis, among others.
Arthritis is characterized by inflammation, pain, stiffness, and swelling in one or more joints. This condition can affect people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds, but it is more common among older adults. Arthritis can vary in severity, from mild discomfort to severely limiting a person’s ability to perform daily activities.
The exact cause of arthritis depends on the specific type, but it often involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Some forms of arthritis are autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, including the joints.
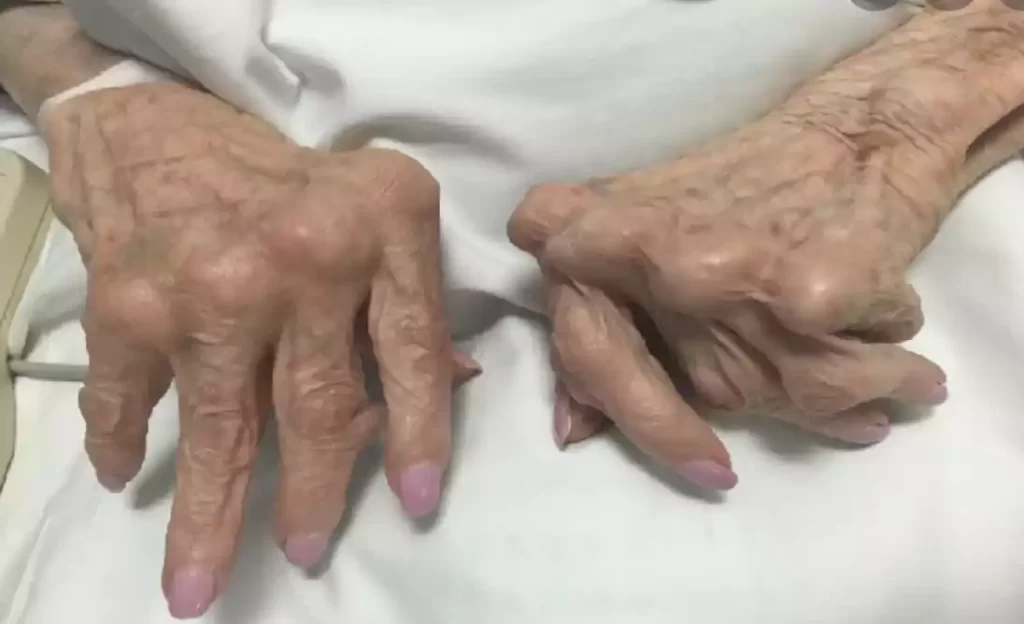
Arthritis is a chronic condition, meaning it typically persists over the long term. Management and treatment of arthritis may involve medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgical interventions to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and improve joint function. The goal of arthritis management is to enhance the quality of life for individuals living with this condition and to minimize its impact on their daily activities.
Symptoms and common signs
It is important to differentiate between arthritis and tendonitis of the thumb because the symptoms and signs can be similar.
Here are the symptoms and signs that each condition is associated with:
Tendonitis of the Thumb:
- Pain: Tendonitis of the thumb is often accompanied by localized pain along the tendon or at the base. Pain is often aggravated when thumb movements or activities are performed.
- Swelling: An inflammation of the tendon may cause swelling, which can be seen as a bump or puffiness.
- Stiffness: It may be difficult to move the thumb through its range of motion.
- Weakness: You may experience weakness of the thumb making it difficult to hold or grip objects.
- Redness and warmth: The affected area can appear red and warm due to an increased blood supply to the inflamed area.
- Tenderness: The area surrounding the affected tendon may be tender to touch or press.
- Crepitus: You may sometimes hear or feel a grating, creaking, or rattling sensation (crepitus) when you move your thumb.
Arthritis of the Thumb:
- Joint pain: Pain in the thumb joints caused by arthritis tends to be generalized, and can affect more than one joint. Pain is usually constant and gets worse with activity.
- Swelling: Thumb arthritis can cause swelling of the joints and make them look puffy.
- Stiffness: People with thumb arthritis experience stiffness, especially in the mornings or after periods of inactivity.
- Limited range of motion: Thumb arthritis can cause a reduced ability to move the finger, particularly in pinching and grasping motion.
- Joint Deformity: Arthritis can cause joint deformities such as the formation of a bump on the base of the finger known as “Heberden’s node” or a “thumb node.”
- Weakness: As arthritis progresses you may notice that your thumb is losing strength, making it harder to perform fine motor skills.
- Tenderness: The affected joints of the thumb may be tender.
Both conditions can cause swelling and stiffness. This can make it difficult to differentiate between them solely based on symptoms. A healthcare professional must perform a physical exam and, if needed, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs to properly diagnose the condition.
Tendonitis and Arthritis in Thumb in the Comparison Chart
Here’s a comparison chart outlining the key differences between thumb tendonitis and arthritis:
| Aspect | Thumb Tendonitis | Thumb Arthritis |
|---|---|---|
| Underlying Cause | Inflammation of tendons | Degeneration of joint cartilage |
| Primary Symptoms | Pain along tendons, swelling, limited range of motion | Joint pain, stiffness, bony nodules (Heberden’s nodes) |
| Inflammatory Response | Inflammation of tendons and surrounding tissues | Inflammation within the joint (synovitis) |
| Location of Symptoms | Along the path of affected tendons | Within the joint space |
| Age Group Affected | Can occur in individuals of various ages | More common in older adults |
| Movement Impact | Pain increases with specific thumb movements | Pain and stiffness with general thumb use |
| Imaging | May show swelling or inflammation in tendons on ultrasound | X-rays may reveal joint space narrowing and bone changes |
| Treatment Approaches | Rest, ice, anti-inflammatories, exercises | Pain relief medications, splinting, exercises, and possibly surgery |
| Response to Rest | Typically responds well to rest and conservative measures | Some relief with rest, but long-term management is often needed |
| Long-Term Outlook | Generally favorable with proper management and rest | Requires ongoing management and pain control |
| Complications | Rare, but untreated cases might lead to chronic issues | Joint deformities, loss of function if untreated |
| Preventive Measures | Ergonomics, exercises, balanced hand use | Ergonomics, joint-friendly movements |
| Key Emphasis | Inflammation, tendon care, early intervention | Joint health, pain management, maintaining function |
The importance of distinguishing the two conditions in thumb-related disorders
It is important to distinguish between thumb tendonitis (tendonitis of the thumb) and arthritis (arthritis of the thumb) for a number of reasons.
- Accurate Diagnose: Differentiating between the two conditions enables a precise diagnosis. It is important to distinguish between the two conditions because treatment, medication, and therapy for arthritis and tendonitis are very different. A correct diagnosis will ensure that the patient receives the best care possible.
- Effective Treatment: Thumb tendonitis has distinct causes and mechanisms. Tendonitis is caused by an inflamed tendon, while arthritis is caused by the joints. Understanding the condition helps healthcare providers customize treatment plans. While tendonitis might require rest, anti-inflammatory medication, and joint-specific intervention, arthritis may need pain management and joint-specific interventions.
- Preventing Mismanagement: A misdiagnosis can lead to the wrong treatment, which could worsen symptoms or cause unnecessary discomfort. Corticosteroids are often prescribed for tendonitis but may not be effective in treating arthritis.
- Long-Term Planning and Prognosis: Understanding a specific condition can help in assessing a prognosis, and plan for long-term treatment. Rest and rehabilitation are often effective in treating tendonitis, while arthritis can require lifestyle changes and ongoing pain management. A correct diagnosis helps patients and healthcare professionals set realistic expectations about recovery.
- Prevent complications: Untreated or poorly managed, tendonitis or arthritis can cause joint deformities and loss of function.
- Quality of Life: It is important to distinguish between tendonitis (tendon inflammation) and arthritis in order to maintain or improve a patient’s life quality. Effective management strategies are able to alleviate pain and improve thumb function. This allows individuals to carry on with their daily lives.
It is important to distinguish between thumb tendonitis (also known as arthritis) and thumb tendonitis. This distinction has significant implications for accurate diagnosis, treatment effectiveness, and overall health. It is important to seek professional medical advice when you are experiencing thumb-related problems. This will ensure that the best possible care is provided and the best outcomes.
Similarities Between Tendonitis and Arthritis in the Thumb
They share many similarities that can make it difficult to distinguish between them. Here are some of the commonalities:
- Pain: Tendonitis or arthritis of the thumb can cause pain. The pain may be mild or severe and can interfere with everyday activities.
- Swelling: Inflammation, a feature common to both conditions, can lead to swelling of the affected area. Swelling may cause pain and discomfort.
- Stiffness: Both conditions may cause stiffness of the thumb particularly in the morning and after periods of inactivity. This stiffness may affect the thumb’s mobility and functionality.
- Tenderness: The affected areas in both tendonitis and arthritis can be tender and sensitive to touch. They become painful when pressure is exerted.
- Limited range of Motion: These conditions can restrict the thumb’s range of movement, making it hard to perform tasks or movements requiring thumb dexterity.
- Impact on Grip Strength: Arthritis and tendonitis can cause thumb muscle weakness, which affects grip strength.
- Symptom aggravation: Certain activities and movements involving the thumb may worsen symptoms for both conditions. Repetitive thumb usage or gripping with force can increase pain and discomfort.
- Risk factors: There are some risk factors that can lead to both tendonitis or arthritis, including aging, repetitive thumb movements, and previous thumb injuries.
- Diagnostic challenges: Due to these common symptoms and risk factors it can be difficult to differentiate between tendonitis or arthritis solely based on symptoms. A thorough medical evaluation may often be necessary for a correct diagnosis.
While there are similarities between tendonitis in the thumb and arthritis, the causes and treatment options for each condition differ. A healthcare professional’s diagnosis and the appropriate diagnostic tests such as blood tests or imaging studies are important for determining and treating the exact condition.
Prevention and Management
Prevention:
- Ergonomics: Use ergonomic tools and maintain proper hand position during tasks.
- Exercise: Strengthen and stretch your thumb muscles and joints regularly.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet. Avoid overusing.
- Rest: Allow your thumb to rest after repeated activities.
Management:
- Professional Advice: Consult your healthcare provider to diagnose and treat you.
- Immobilization and Rest: Use splints and braces when needed.
- Pain Management: Use medication as prescribed.
- Physical therapy: Use the therapist’s instructions to improve thumb mobility and strength.
- Surgery: If conservative treatments fail, consider surgery.
- Lifestyle Changes: Reduce thumb strain by modifying daily activities.
- Heat/Cold therapy: Use heat or cold packs to relieve pain.
- Complementary Therapies: Learn about acupuncture and massage under professional guidance.
- Emotional support: Ask for emotional support from family members, friends, or support groups.
Conclusion
Maintaining thumb health requires that you understand the difference between thumb tendonitis and arthritis. You should also take preventative measures. Consult a healthcare provider if you are experiencing symptoms for a timely diagnosis and tailored management. You can improve your quality of living by taking proactive measures and managing these conditions.