Petechiae, also known as Cherry Angioma, is a skin condition that appears in the form of red or purple spots. Understanding their differences, despite the fact that they have a similar appearance, is essential for an accurate diagnosis and treatment. This short overview will introduce the conditions and prepare you for a deeper exploration of their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Brief Explanation of Petechiae and Cherry Angioma
Petechiae:
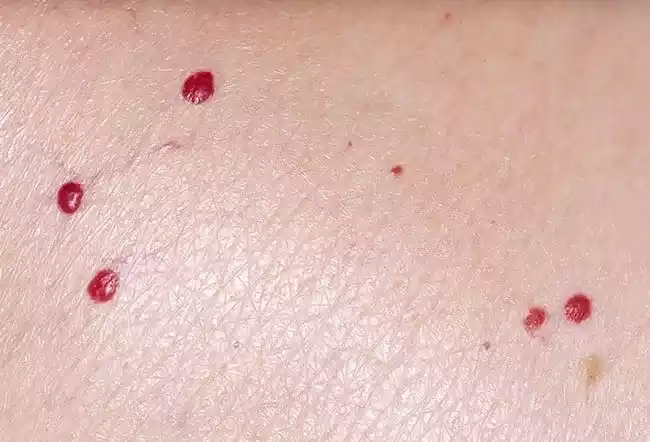
Petechiae appear as small red or purple spots on the skin and mucous membranes. These tiny hemorrhages are caused by capillary rupture. Petechiae are often caused by underlying medical conditions such as bleeding disorders, infections, or trauma.
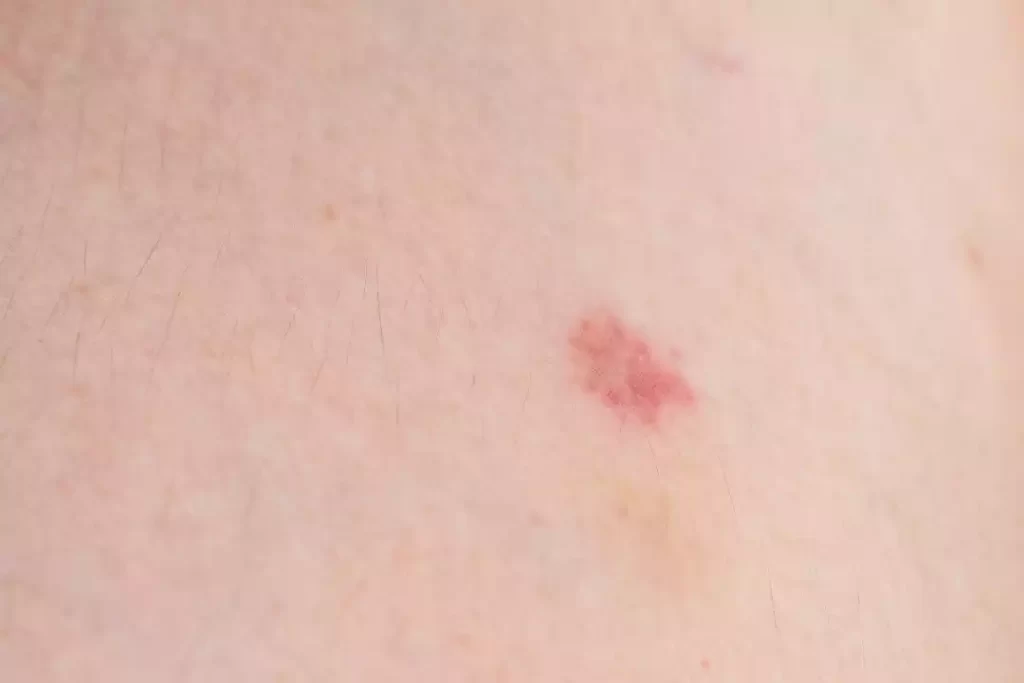
The spots are not affected by pressure and do not change color. This makes them distinct from other skin conditions. When petechiae appear, it is important to diagnose and treat the underlying condition.
Cherry Angioma:
Cherry angiomas are benign skin growths that appear as small red or cherry-red bumps. These growths can be round or oval in shape and vary in size between a tiny pinpoint and a few millimeters.
Cherry Angiomas develop as a result of the growth of blood vessels at the surface. They become more common as we age. Although they are generally painless and harmless, some people opt to remove them for cosmetic purposes or if they bleed or become irritated.
Petechiae and Cherry Angioma in the comparison chart
Here is a comparison chart highlighting the differences between Petechiae and Cherry Angioma:
| Characteristic | Petechiae | Cherry Angioma |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Tiny red or purple spots | Small, red, or cherry-red bumps |
| Size | Pinpoint-sized | Varies from pinpoint to a few millimeters |
| Texture | Flat and non-raised | Raised, often dome-shaped |
| Causes | Rupture of capillaries due to underlying medical conditions, infections, bleeding disorders, or trauma | Benign and usually caused by an expansion of blood vessels near the skin’s surface |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, and blood tests to identify underlying causes | Clinical examination, dermoscopy |
| Treatment | Addressing underlying medical conditions, symptomatic relief | Removal for cosmetic reasons, or if they bleed, become painful, or are irritated |
| Medical Urgency | Seek medical attention, especially if sudden onset, severe, widespread, or associated with other concerning symptoms | Generally not urgent, but seek evaluation for changes in appearance, bleeding, or discomfort |
| Common Locations | Can occur anywhere on the skin or mucous membranes | Common on the trunk, arms, legs, and face |
| Blanching under Pressure | No blanching (spots do not fade when pressure is applied) | Typically do not blanch (may blanch slightly in some cases) |
| Prognosis | Depends on the underlying cause; and can be resolved with treatment | Usually benign and poses no significant health risks; may recur after removal |
| Recurrence | Recurrence is uncommon unless the underlying condition persists | May recur after removal, especially if genetic predisposition exists |
This chart is a general comparison of Petechiae vs. Cherry Angioma. However, each case may be different. It’s important to consult with a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
The importance of distinguishing between the two
There are several reasons why it is important to distinguish between Petechiae (Cherry Angioma) and Petechiae:
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Petechiae can be a sign of other medical conditions such as infections, bleeding disorders or autoimmune disease. It is important to identify and treat the underlying cause of petechiae in order to manage these conditions effectively. Cherry Angioma is a benign growth of the skin that is usually not linked to underlying health issues.
- Treatment Method: A proper diagnosis will ensure that the individual receives appropriate treatment. Petechiae are treated by addressing the underlying problem, which can include medications, lifestyle modifications, or other interventions that are specific to the health condition diagnosed. Cherry Angiomas may need to be treated if they become problematic because of bleeding, irritation or cosmetic concerns. The treatment is different.
- Medical Emergency: Petechiae may indicate a medical emergency, particularly if they are sudden, widespread or accompanied by additional symptoms of concern. In such cases, prompt medical attention is essential. While cherry angiomas may require medical attention for a variety of reasons, they are not generally considered an emergency.
- Cosmetic considerations: The removal of cherry angiomas is possible for cosmetic reasons, or if the angiomas cause pain, irritation, or bleeding. It is important to distinguish them from petechiae so that individuals can make an informed decision about whether they want the cherry angiomas removed.
- Peace of Mind and Reassurance: Understanding the difference between the two conditions can give individuals peace of mind. Knowing that a skin mark is a benign Cherry angioma and not petechiae linked to a serious medical condition can reduce unnecessary anxiety.
- Prevention: Early recognition of petechiae can help diagnose and manage underlying conditions. This could prevent further complications. Understanding Cherry Angiomas can also help people take preventive measures, or remove them if necessary.
It is important to distinguish between Petechiae (Cherry Angioma) and Petechiae in order to get an accurate diagnosis, the right treatment, and prompt intervention when necessary.
This allows people to identify underlying concerns, make informed choices about their skin’s health, and get the medical attention they need when dealing with potentially serious conditions.
Treatment of Petechiae and Cherry Angioma
The treatment for Petechiae varies depending on their causes and characteristics:
Treatment of Petechiae:
Treatment of petechiae is based on the underlying causes, which are often different. Here are some basic principles:
- Medical Assessment: Consult a healthcare professional if you notice petechiae. This is especially important if the symptoms are alarming or appear suddenly. The healthcare professional will examine your medical history and perform a physical examination. They may also order blood tests or any other diagnostic procedures.
- Treating the Underlying Condition: It is important to treat the condition that caused the petechiae. The treatment may include antibiotics to treat infections, adjustments in medications that affect blood clotting, or management of underlying medical conditions like autoimmune disorders or bleeding disorders.
- Symptomatic relief: Your healthcare provider may prescribe measures to alleviate discomfort or pain caused by petechiae while treating the underlying causes. Rest, pain relievers or topical treatments to reduce itching and irritation can be used.
Treatment of Cherry Angioma:
Cherry Angiomas tend to be benign and do not usually require treatment. Some people may choose to remove the angiomas for cosmetic reasons, or if they bleed, are painful or become irritated. Treatment options include:
- Cryotherapy: This is the freezing of Cherry Angioma using liquid nitrogen. It causes it to shrink, and then fall off.
- Electrocautery: A healthcare provider can use an electric current to heat up the angioma and cause it to coagulate, which will then disappear.
- Treatment with Lasers: Laser therapy can be used to eliminate angiomas by targeting the blood vessels.
- Shave excision: A healthcare provider uses a scalpel to remove the Cherry Angioma.
- Pulsed Dye laser (PDL) or Laser: Both methods are effective for angiomas that are larger and more prominent. They also target the blood vessels in the angioma with precision.
Consult a dermatologist before deciding on a treatment plan for Cherry Angioma. This will allow you to determine the best course of action while taking into account factors like size, location, and personal preferences. Cherry Angiomas can recur even after removal.
When to seek medical attention
It is important to know when to consult a doctor for petechiae or cherry angiomas to ensure a prompt diagnosis and treatment. These signs can be indicative of other health problems.
Guidelines for seeking medical attention for different conditions:
Petechiae:
- Sudden Onset: Seek medical attention immediately if you notice an unprovoked and sudden appearance of petechiae.
- Severe Petechiae or Widespread Petechiae: If you have petechiae that cover a large part of your body or spread rapidly, or if they are associated with any other symptoms, such as severe weakness altered consciousness, or bleeding at other sites, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
- Recurring or Persistent Petechiae: Consult a healthcare professional if you experience recurrent episodes or if they persist with no obvious cause.
- Conditions Underlying the Petechiae: In case you have a bleeding disorder or other medical condition that increases your risk of developing petechiae and notice any new petechiae or a worsening of existing ones, please contact your doctor to discuss how to manage them.
Cherry Angioma:
- Changes in Appearance and Symptoms: Although Cherry Angiomas tend to be harmless, you should seek medical advice if they change in appearance. This includes bleeding, rapid growth, or irritation.
- Cosmetic Concerns: If your Cherry Angiomas are bothering you from a cosmetic perspective, or they are in an area that causes discomfort, or they pose a bleeding risk due to friction, injury, or irritation, you should consult a dermatologist to discuss the removal options.
It’s important to keep in mind that healthcare professionals are able to provide accurate diagnoses based on the specifics of your situation. They can also recommend appropriate treatment options. Do not hesitate to contact a healthcare professional for advice and evaluation if you are concerned about any skin changes, spots or symptoms. Early intervention is crucial in preventing or treating underlying issues.
Similarities Between Petechiae and Cherry Angioma
Although Petechiae, Cherry Angioma, and other skin conditions are different and have their own causes and characteristics they share some similarities:
- Appearance in Red or Purple: Both Petechiae and Cherry Angioma appear as red or purplish spots on the skin. The similarity in color can lead to confusion as both are reddish-purplish.
- Dermatological Disorders: These two conditions are dermatological, which means they can affect the appearance of the skin and be seen with the naked eye.
- They can occur anywhere on the body: Petechiae or Cherry Angiomas can appear on different parts of the human body. They can occur anywhere on the body, regardless of their distribution or location.
Despite their similar appearances, Petechiae, Cherry Angioma, and other conditions have different causes and diagnostic criteria. They also require different treatment methods. Although recognizing the shared features of the two conditions can be useful, it is important to have a professional evaluate the condition in order to determine the best course of treatment.
Case Studies and Real-life Examples
Below are some case studies that illustrate both Petechiae (Cherry Angioma) and Petechiae:
Case Study 1: Petechiae
Patient Profile:
Jane, a woman of 35 years, went to see her primary physician because she was concerned about the multiple small red spots that appeared on her arms and leg. She said that the spots appeared suddenly, and they were not related to any injuries.
Diagnosis and Symptoms:
The physician examined Jane and found numerous red and purple pinpoint spots that did not blanch under pressure. No significant medical condition or trauma was present. She was given blood tests to determine her platelet counts. The results revealed that she suffered from thrombocytopenia. This condition is characterized by low platelet counts.
Treatment:
Jane was referred by her doctor to a hematologist, who would further evaluate and manage the situation. She was diagnosed as having immune thrombocytopenia (an autoimmune disorder causing a drop in platelets). Her treatment options included medication to suppress her immunity and raise her platelet counts.
Case Study 2: Cherry Angioma
Patient Profile:
Mark, a man of 50, noticed that he had a small raised cherry-red bump. It grew slightly larger and more noticeable over time.
Diagnosis and Symptoms:
Mark’s dermatologist identified the lesion as a Cherry Angioma. Dermoscopy confirmed that the bump contained dilated vessels. Mark experienced no pain, bleeding or discomfort as a result of the lesion.
Treatment:
The dermatologist suggested Mark remove the Cherry Angioma because it was in an obvious area of his chest. The angioma could be safely and efficiently removed using electrocautery during an outpatient procedure. Mark felt minimal discomfort and is pleased with the outcome.
Real-life Example:
Sarah, 65, was concerned when she noticed small red bumps on her abdomen. She was worried about the appearance of these bumps, but they did not cause her any pain or discomfort. Sarah went to a dermatologist.
Diagnosis:
Cherry Angiomas were identified by the dermatologist. Sarah had several angiomas in her abdomen. They all exhibited the typical benign characteristics. Sarah’s dermatologist told her that, while the angiomas were benign and harmless, they could be removed for cosmetic reasons.
Treatment:
Sarah chose to remove some of her larger Cherry Angiomas using laser therapy as a cosmetic procedure. Sarah was happy with the outcome of the procedure, which was done in her dermatologist’s clinic. The angiomas are no longer visible.
These real-life case studies and examples illustrate the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment options of both Petechiae (Cherry Angioma) and Petechiae. Remember that each case is unique and that healthcare professionals are crucial in assessing, managing, and treating these conditions according to the individual circumstances of each patient.
Prevention and Self-Care
It is important to maintain skin health by using prevention and self-care techniques for Petechiae as well as Cherry Angioma. Here are some prevention and self care tips for each condition.
Self-Care and Prevention for Petechiae :
- Management of the underlying condition: Work closely with your healthcare provider if you have a medical problem or are taking medications that can increase your risk for petechiae.
- Infection prevention: To prevent infection-related petechiae from occurring, it is important to practice good hygiene and wash your hands regularly.
- Prevent Trauma: Take care to avoid injuries that may lead to petechiae. Avoid excessive vomiting, coughing or straining as these can lead to small blood vessels ruptures.
- Medication Reviews: Discuss your medications with your doctor and make sure you follow his or her recommendations.
- Protect your skin: Wear protective clothing and use sunscreen to protect yourself from skin damage.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle will support the skin’s and vascular health.
Self-Care for Cherry Angioma and Prevention:
- Sun protection: Protect yourself from sun exposure as it can lead to Cherry Angiomas. Wear protective clothing and use sunscreen, especially in hot climates.
- Avoid Skin Injury: Prevent Physical Irritation or Injury to Cherry Angiomas. Avoid picking or scratching them as this may cause discomfort or bleeding.
- Cosmetic removal: Consult a dermatologist to discuss your options if you are bothered by Cherry Angiomas from a cosmetic perspective.
- Skin Checks: Conduct regular skin checks to monitor the appearance and any changes in your skin.
- Consult a dermatologist: If there are any changes in the appearance or symptoms of Cherry Angiomas such as bleeding, rapid expansion, or irritation, you should consult a dermatologist to get an evaluation and advice.
- Genetic predisposition: You may be at a higher risk of developing Cherry Angiomas if you have a history in your family. Consider regular skin checks and early removal.
While these self-care and prevention tips can reduce the risk of Petechiae or Cherry Angiomas, individual cases and risks may vary. A dermatologist or healthcare provider is the best source for an accurate diagnosis and personalized advice. They can also provide you with treatment options that are specific to your case.
Conclusion of Petechiae and Cherry Angioma
Petechiae are two distinct skin conditions. They both have a reddish color, but they differ in their diagnosis and treatment. Petechiae are often signs of underlying medical conditions and need to be evaluated immediately, whereas Cherry Angioma tends to be benign but can still be removed cosmetically or for symptomatic purposes. A professional diagnosis is crucial for the appropriate treatment of these skin conditions and for peace of mind.
