Let’s Learn The Definition of Resin
Resin is a natural or chemical organic compound that is viscous liquid or solid at temperatures that are not too high. It is generally composed of a long chain of molecules, which can be made and molded into different dimensions and shapes.
Resin is an ideal material for a variety of applications like adhesives, coatings, composites, and ornamental objects. Resin is obtainable from many sources, like plants, and animals, as well as synthetic substances. Resin can also be altered to meet specific requirements for performance.
Definition of Vinyl Ester and Polyester Resin
Vinyl ester resin is one type of thermosetting polymer created by the reaction between the epoxy resin with an unaturated monocarboxylic acid generally methacrylic acid or acid. The result is an enhanced mechanical and chemical resistance when compared with traditional polyester resins. Vinyl esters are often employed in areas that require extreme resistance to corrosion, for example, pipes, chemical storage tanks, or marine structures.
Polyester resin is, on one other on the other hand, a thermosetting polymer, which is made by the esterification reaction of dicarboxylic acids (such as phthalic Anhydride) and diol (typically ethylene glycol). Polyester resins are extensively used in many industries, such as automotive, construction as well as marine applications like the reinforcement of fiberglass, composites, and casting. They have high mechanical durability, and weather resistance and are easy to process.
Types of Resin
There is various kinds of resins that can be used for different uses. The most commonly used types of resin include:
- Epoxy Resin A remarkably elastic and durable thermosetting resin commonly used for industrial and consumer applications, such as adhesives, coatings, and composite material.
- Polyester Resin – A thermosetting resin that is often used in fiberglass-reinforced composite applications, such as boat building, automotive parts, and corrosion-resistant tanks.
- Vinyl Ester Resin is one of the thermosetting resins that offers increased durability, strength, and chemical resistance compared to polyester resin. This makes it ideal for marine and industrial use.
- Phenolic Resin A kind of thermosetting resin that is impervious to temperatures of extremes and extensively used in coatings, insulation, and adhesives.
- Polyurethane Resin (PUR) is a multi-faceted and durable thermosetting resin that is used extensively in adhesives, coatings, and even foams.
- Silicone Resin is an extremely elastic and heat-resistant substance widely used in electronics, aerospace automobile, aerospace and automotive applications.
- Acrylic Resin Acrylic Resin is a type of thermoplastic resin that is commonly utilized in adhesives, coatings as well as in plastics.
- alkyd Resin A type of thermosetting resin used extensively in coatings and paints.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Resin can be described as a thermoplastic resin that is commonly employed for flooring, pipes, and medical devices.
- Melamine Resin is a type of thermosetting resin that is impervious to heat, chemicals, and water. This makes it the ideal material for tabletops, kitchenware, or laminate flooring.
These are just some of the many kinds of resins that are available on the market with each having distinct characteristics and characteristics that can be used for various applications.
What exactly is Vinyl Ester Resin?
Vinyl Ester Resin is a type of resin that is created through the esterification of epoxy resins with acrylic or methacrylic acid. In this particular structure, we use “vinyl” groups as the alternatives to the ester that are able to be polymerized.
It is therefore common to use an inhibitor to make this substance. After that, we can dissolve the diester substance in a reacted solvent (e.g. styrene) to trigger polymerization through free radicals that are formed due to ultraviolet radiation or peroxides.
Vinyl Ester Resin can be described as the thermosetting component of HTML0. It can be used as a substitute for polyester and epoxy substances. In this scenario, we can use this material to create a thermoset polymer matrix in Composite materials.
In these instances, the effectiveness and strength of the bulk cost are substantial. These properties are usually comparable to the properties of polyester and epoxy materials. Additionally, the density of vinyl ester is lower than polyester and epoxy.
There are a myriad of applications of vinyl esters. This includes their use as a precursor to create large classes of resins and also in the repair of various materials as well as in laminating due to their water-proofing properties, for the design of homemade aircrafts as well as in the construction of home-built aircrafts.
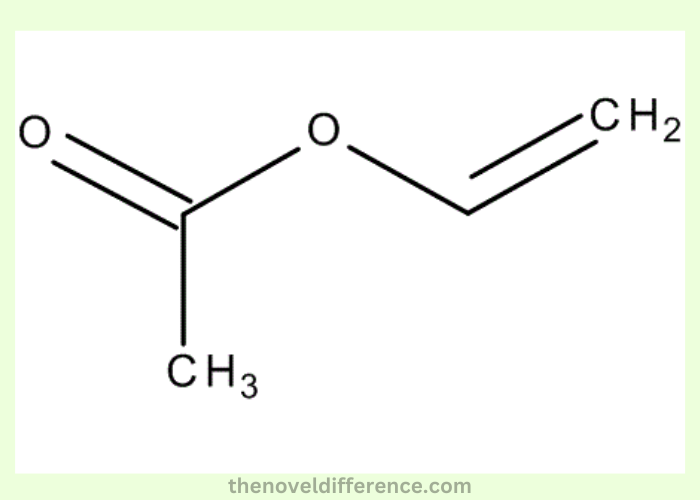
What’s Polyester Resin?
Polyester resin form of resin created through the reaction between dibasic organic acids and Polyhydric alcohol. It is an organic form, but an artificial one. Generally speaking, maleic anhydride can be used as a raw material if it is found in an environment with dibasic functionality within unsaturated polyester resins.
The resins of polyester listed are not saturated. They can be used in sheet molding compounds, bulk molding compounds as well as in the case of laser printers, toner.
Furthermore, we can make use of panels made from Polyester resins and strengthened by fiberglass to make bathrooms, kitchens, restaurants, and other areas that require low-maintenance, easy-clean wall surfaces. Furthermore, it is suitable for pipe applications which cure-in-place.
Analyzing the chemical structure and structure of Polyester resins is a type of polymer where the functional repeats of the ester group are found within chains. Additionally, they are polymers that grow incrementally. In this process of making polyester resins, difunctional acid or acyl halide reacts with difunctional alcohol.

The Differences Between Vinyl Ester and Polyester Resin
Polyester resin and vinyl ester resins are two thermosetting resins often employed to form composite materials such as fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) and carbon fiber-reinforced plastic (CFRP). Although both resins share the same properties and use, however.
It has some key distinctions between them:
- Chemical Differences: Vinyl is created through the reaction of epoxy resin with an unsaturated monocarboxylic acid, in contrast to the polyester resin, created through a reaction between dibasic acids with polyol and monool. Vinyl ester resin has the ability to attain higher cross-linking it is also more robust to chemical corrosion than polyester resin.
- Physical differences: Vinyl esters are less viscose and have greater reactivity than polyester. This makes it easier to work with and allows for faster drying times. It also provides higher moisture and thermal resistance than polyester resin.
- Mechanical distinctions: Vinyl is a resin with more elongation and tension at break than polyester resin, making it suitable for high-stress conditions. Polyester resin is, however, stronger in its capacity to compress than vinyl resin.
- The performance differences are: Vinyl Ester Resin is stronger and more resistant to water, chemical and chemical elements, and UV radiation in comparison to Polyester resin. This is the reason it is an ideal option for outdoor and marine projects. Polyester resin is less expensive and easier to work with as compared to vinyl ester.
- Cost Variations: Cost Differences for Vinyl Ester Resin can be more costly than polyester resin because of its higher quality and higher performance.
The decision to use both is based on the requirements specific to the particular use. In cases where durability strength and chemical resistance are crucial and long-lasting vinyl ester resin might be the most suitable choice. For applications that are not as demanding, and where simplicity of use is more crucial, polyester resin might be a better option.
Conclusion
Vinyl esters, as well as Polyester resins, are distinct kinds of thermosetting resins commonly used to create composites. Although both resins have the same characteristics and functions, there are a few significant differences between the two in terms of chemical, physical mechanical performance, and price.
The choice between vinyl esters and polyester resins will depend on the requirements specific to the specific application and purpose, with vinyl ester resin the best choice for high-stress and outdoor applications, and polyester resin the better option for applications that are less demanding where cost and ease of use are the most important factors.