Immunoglobulins, commonly referred to as antibodies, are vital components of the immune system, offering protection against various pathogens and foreign substances. Among the diverse classes of immunoglobulins, IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD play distinct roles in immune defense mechanisms.
Understanding their unique structures, functions, and distributions within the body provides valuable insights into the complexity of the immune response and its defense strategies.
Important of igg igm iga ige and igd
Understanding the distinctions among IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD is vital to comprehending the specific roles that these immunoglobulins perform in the immunity system. IgG is the most prevalent antibody, and functions primarily in the long-term immune system and neutralization of pathogens.
IgM is the first response when an infection occurs, helps during the initial response to infection, and also activates the complement pathway. IgA is specifically focused on mucosal immune response and protects against pathogens on mucous membranes.
IgE is a key component in the immune system and helps protect against parasites. IgD is not fully understood but is a key factor in B cell’s maturation and activation.
Understanding these differences is essential for diagnosing immune-related conditions as well as in the development of targeted therapies and expanding our understanding of the immune system’s responses to various issues.
Igg
Igg is the most prevalent immunoglobulin class found in blood and accounts for 75%-80% of total immunoglobulins found within our bodies. It features four polypeptide chains with two heavy chains and two light chains connected by linkers. These chains are linked by disulfide bonds.
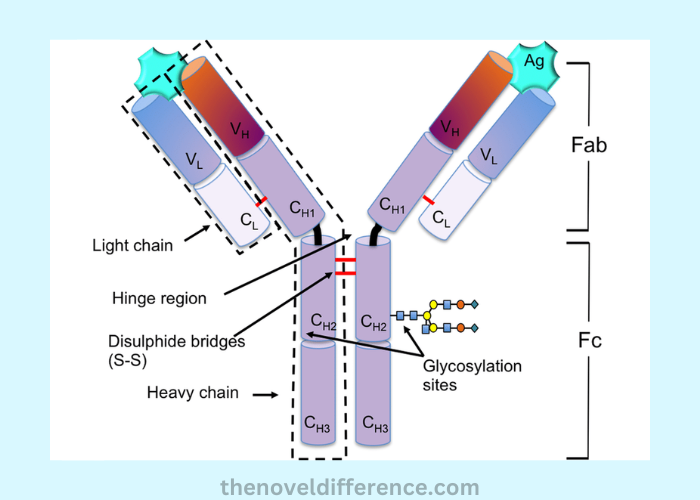
Igg antibodies are essential components of our immune systems, helping detect and neutralize pathogens like bacteria and viruses. Additionally, its cross-placental immunity enables pregnant mothers to pass along immunity during gestation. Igg proteins typically have a half-life of 21 days. This allows it to offer sustained protection against infection.
Igg is also important in the diagnosis and monitoring of diseases. Igg levels can be elevated to indicate chronic infections, autoimmune disorders, or immunodeficiency. Igg measurements are also helpful in monitoring treatment responses for certain diseases.
Igg plays an essential part in our immune system, protecting us against infections.
Igm
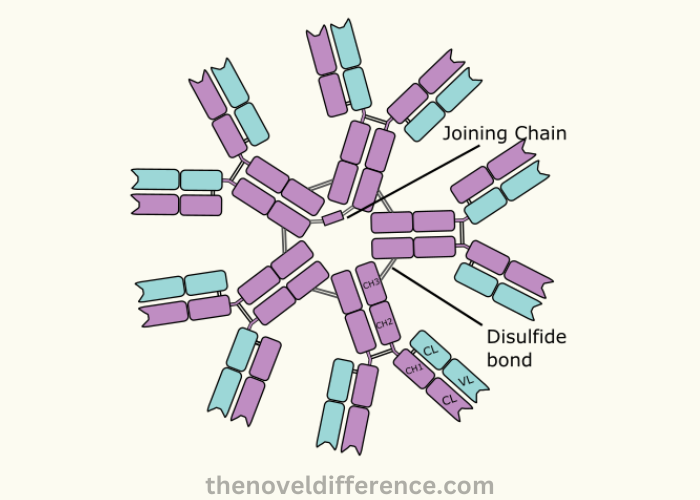
Igm, the largest immunoglobulin produced by the body in response to infection, is the first antibody. The pentameric shape is formed by five igm molecules linked together with a disulfide bond, giving it a star-like appearance. Each igm has two heavy and two lighter chains.
Igm is a critical component of the primary immune response. It acts as a first-line defense against pathogens that invade. It is especially effective in binding to and neutralizing bacteria and viruses. Igm plays a role in the clumping of microbes to make it easier for immune cells.
IgM is also useful for diagnosing and monitoring some diseases, just like igg. Igm levels that are elevated may indicate recent or ongoing infection, while lower levels could indicate immunodeficiency.
Igm plays a vital role in the first response to infection.
Iga
Iga is one of the second-most prevalent immunoglobulins and can be found in saliva, tears, and breast milk as well as mucosal tissues such as respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract mucosa.
It is a dimeric molecule consisting of two IgA molecules joined together by the j chain, and also contains a secretory component.
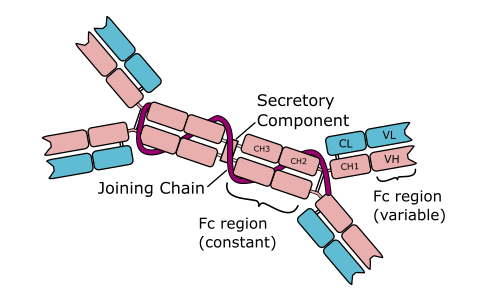
Iga is important in protecting against pathogens on mucosal surfaces, as these are the main entry points for infectious agents. It is a first line of defense, preventing pathogens from attaching to and penetrating epithelial cell surfaces.
Iga is also important in diagnosing and monitoring diseases. Iga levels that are elevated may be indicative of certain autoimmune conditions, infections or inflammations, while low levels could indicate immunodeficiency.
Iga plays a vital role in the immune system by protecting the mucosal surface against infection.
Ige
Ige, the least abundant of the immunoglobulins in the body, is involved primarily in allergic reactions and the defense against parasites. It is y-shaped, similar to igg. Two heavy chains and two lighter chains are linked by a disulfide bond.
Ige is a key player in the immune response against allergies. It binds to allergens such as food proteins or pollen and triggers the release of histamine from mast cells. Allergies are characterized by symptoms such as itchiness, swelling, and breathing problems.
Ige also plays a role in the immune response against parasitic infections. It binds parasites and releases toxins that kill them.
Increased levels of ige can indicate allergies or a parasitic infection, while lower levels could indicate immunodeficiency.
Ige is a specific type of iga that plays an essential role in our immune systems. It’s important for the protection against parasitic and allergic infections.
Igd
Igd, the least-understood immunoglobulin of the body, and its role in the immune response are not fully understood. It is y-shaped, similar to igg or ige. Two heavy chains and two lighter chains are linked by a disulfide bond.
Igd can be found on the surface b cells where it functions as an antigen receptor. The b cell is activated when an antigen binds with the igd-receptor. This causes it to become plasma cells that secrete antibodies.
Uncertainty surrounds the IGD’s precise role in the immune system; however, it may help regulate the immune response.
In clinical practice, igd is rarely measured. However, a decrease in levels can indicate immunodeficiency.
Though igd remains poorly understood, its role in the immune system and regulation of antibody production remains widely accepted.
Comparison chart of Igg, igm iga, ige, and igd
Here’s a comparison chart of key differences between IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD:
| Characteristics | IgG | IgM | IgA | IgE | IgD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Y-shaped monomer | Pentameric, can be monomeric | Monomeric or dimeric | Monomeric | Monomeric |
| Quantity | Abundant in serum | The first antibody produced in response | Predominant in mucosal surfaces | Relatively low levels in serum | Relatively low levels in serum |
| Function | Long-term immunity, neutralization | Primary immune response activates complement | Mucosal immunity neutralizes pathogens | Allergic reactions defend against parasites | B cell activation, role in immune regulation |
| Complement Activation | Yes | Yes | Yes | Limited | Limited |
| Location | Blood, and tissues, cross the placenta | Blood, initial response in infections | Mucosal surfaces, secretions | Mast cells, basophils | B cells, unclear tissue presence |
| Role in Immune Response | Secondary response to infections | Primary response to infections | Defense at mucosal surfaces | Allergic reactions, parasitic defense | B cell activation, unclear role |
Gg igm iga ige and igd: what’s the main difference?
The type of heavy chains in each antibody. Igg is a type g heavy chain while igm is a type m heavy chain. Iga, ige, and igd all have a heavy chain type.
In higher-level animals, antibody production occurs in response to antigens as part of activating the adaptive immune system.
The interactions between antibodies and antigens lead to reactions like agglutination, neutralization, opsonization, and complement activation. These reactions are all part of an immune response against a foreign body. The structural and functional characteristics of antibodies vary.
What are the benefits of igg igm iga ige igd?
IgG gives long-term immunity through neutralizing pathogens enhancing the phagocytosis process, and supplying protection to the fetus by the placenta. It’s essential to fight recurring infections and is an essential element of the process of generating immunity through vaccination.
IgM as the initial responder to an immune reaction IgM aids in the quick identification of pathogens and activates immune system pathways to remove them. It acts as the primary defense in initial infections and plays a crucial role in eliminating pathogens from the bloodstream.
IgA protects mucosal surfaces that prevent pathogens from entering your body. Its presence in various secretions such as tears, saliva, as well as breast milk protects against infections of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts, thereby granting localized immunity.
IgE: Despite being found in comparatively low quantities, IgE is crucial in reactions to allergens, facilitating the process of reactivity against allergens. It also aids in the fight against parasites by activating immune cells to combat parasites and remove them from the body.
Though its exact functions are not yet fully comprehended, IgD is associated with maturation and activation of B cells which contributes to the control of the immune response. It is believed to play a role in the process of immune surveillance and modulation but further research is required to fully understand the benefits.
What are the similarities among igg, igm, iga, ige, and igd antibodies?
Structure: All five immunoglobulins (IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD) belong to the antibody family and share a basic Y-shaped structure composed of two heavy and two light chains.
Origination: They are produced by B cells as part of the adaptive immune response against pathogens and foreign substances.
Recognition: Each antibody class recognizes specific antigens, contributing to the immune system’s ability to identify and neutralize threats.
Variable Regions: They all possess variable regions that enable them to bind to diverse antigens, thereby facilitating targeted immune responses.
Immunoglobulin Classes: While they vary in their functions and distributions, IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE, and IgD are all classes of immunoglobulins present in the human body, each serving distinct roles in immune defense.
The conclusion of the article
Immunoglobulins are an essential part of our immune response and serve a critical function in protecting against infections and foreign invaders. Understanding igg, igm, iga, ige, and igd distinctions when diagnosing or monitoring diseases is of vital importance when diagnosing and monitoring diseases or conditions.
Each immunoglobulin is unique in its structure, abundance, and half-life. Its location and function are also distinct. Measuring their levels can give important information about immune response and health. It will take more research to understand the roles of igd and all immunoglobulins in the immune system.
