These are three diverse body sorts that people have, and understanding their characteristics can give important bits of knowledge about wellness, sustenance, and general well-being. We’ll dig into the world of body sorts and investigate the key contrasts between Ectomorph Mesomorph and Endomorph. So, secure your seatbelts and get prepared to set out on an edifying journey!
Introduction of Ectomorph Mesomorph and Endomorph
Our bodies are one of a kind and come in different shapes and sizes. Whereas hereditary qualities play a noteworthy part in deciding our body sort, variables such as slimming down, workout, and way of life choices impact our physical make-up. The concept of body types originated from the somatotype theory developed by psychologist William H. Sheldon in the 1940s. According to Sheldon, people can be classified into three essential body sorts: Ectomorph Mesomorph and Endomorph.
Understanding your body sort can assist you tailor your fitness and sustenance regimen to attain the ideal comes about. Each body type has distinct characteristics, including metabolic rates, muscle mass, and fat distribution patterns. By recognizing your body sort, you’ll be able to make educated choices concerning your slim down, workout schedule, and general way of life choices.
Definition of Ectomorph Mesomorph and Endomorph
Ectomorph Mesomorph and Endomorph are terms used to describe three different body types based on physical characteristics and metabolic tendencies. These body types were originally introduced by psychologist William H. Sheldon in the 1940s and are still widely used today in the field of fitness and bodybuilding.
Here are the definitions of each body type:
1. Ectomorph:
• Ectomorphs are characterized by a lean and slender physique.
• They usually have a fast metabolism, which means they burn calories at a higher rate.
• Ectomorphs often find it challenging to gain weight and muscle mass.
• They typically have long limbs, narrow shoulders, thin bones, and small joints.
• Ectomorphs tend to have a low body fat percentage.
2. Mesomorph:
• Mesomorphs have an athletic and well-proportioned physique.
• They have a moderate metabolism and can maintain their weight relatively easily.
• Mesomorphs generally find it easier to gain muscle and lose fat compared to other body types.
• They typically have broad shoulders, a narrow waist, a muscular frame, and strong bones.
• Mesomorphs tend to have a low to moderate body fat percentage.
3. Endomorph:
• Endomorphs have a rounder and softer physique.
• They usually have a slower metabolism, making it easier for them to gain weight.
• Endomorphs often struggle with losing fat and building muscle.
• They typically have wider waists, wider hips, shorter limbs, and thicker bones.
• Endomorphs tend to have a higher body fat percentage.
It’s important to note that while these body types provide a general framework, most individuals fall somewhere on a spectrum rather than fitting perfectly into a single category. Many people have a combination of characteristics from different body types. Understanding your body type can help you tailor your fitness and nutrition approach to better support your goals and work with your unique physiology.
Importance of understanding body types
Understanding body types is important for several reasons:
1. Personalized Approach: Each body type has its unique characteristics and tendencies. By understanding your body sort, you’ll tailor your fitness and nutrition approach to adjust along with your particular needs and objectives. This personalized approach can optimize your results and make your efforts more effective.
2. Fitness Planning: Different body types respond differently to various types of exercise. Knowing your body sort can assist you decide the foremost appropriate workouts and preparing strategies for your physical makeup. For example, ectomorphs may benefit from focusing on strength training to build muscle, while endomorphs may need a combination of cardiovascular exercises and resistance training for fat loss.
3. Nutrition Optimization: Body types can also influence how your body responds to different diets and macronutrient ratios. Understanding your body type can guide you in making informed decisions about your nutrition plan. For instance, mesomorphs may require a balanced diet to maintain their physique, while endomorphs may need to focus on portion control and managing calorie intake.
4. Goal Setting: Knowing your body type can help you set realistic and achievable fitness goals. Each body sort has its possess qualities and challenges, and being mindful of these can assist you set objectives that are reasonable for your particular body sort. This can prevent frustration and disappointment and keep you motivated on your fitness journey.
5. Body Acceptance: Understanding body types can promote body acceptance and reduce comparison and unrealistic expectations. Recognizing that everyone has a unique body type can help foster a more positive body image and appreciation for the diversity of human physiques.
Understanding body types allows you to personalize your fitness and nutrition strategies, optimize your results, set realistic goals, and promote body acceptance. It could be a profitable apparatus for people looking to attain their wellness destinations in a way that adjusts to their interesting physiology.
What is Ectomorph?
Ectomorph refers to one of the three primary body types identified by psychologist William H. Sheldon.
Ectomorphs are characterized by certain physical traits and metabolic tendencies. Here are the key characteristics of an ectomorph:
1. Body Composition: Ectomorphs typically have a lean and slender body composition. They tend to have a moo body fat rate, making their muscles show up more characterized.
2. Fast Metabolism: Ectomorphs by and large have a quick metabolic rate, meaning they burn calories at the next rate compared to other body sorts. This can make it more challenging for them to gain weight, including both muscle and fat.
3. Difficulty Gaining Weight: Due to their fast metabolism, ectomorphs often find it more difficult to put on weight and build muscle mass. They may have a harder time gaining both size and strength compared to mesomorphs and endomorphs.
4. Body Shape: Ectomorphs typically have a certain body shape and structure. They tend to have long appendages that limit shoulders, lean bones, and little joints. Their frame can sometimes appear “lanky” or “ectomorphic.”
5. Exercise Response: Ectomorphs may have a higher tolerance for endurance-based activities due to their fast metabolism. They regularly ought to center on resistance preparation and quality works out to construct muscle mass and include estimates in their outline.
6. Nutritional Considerations: Ectomorphs may require a higher calorie intake to support their fast metabolism and provide enough energy for their workouts. They frequently advantage of a slim down that incorporates an overflow of calories and the next extent of carbohydrates and protein to bolster muscle development.
It’s imperative to note that not everybody fits perfectly into a single-body sort category. Many individuals may exhibit a combination of characteristics from different body types. Understanding your body sort as an ectomorph can assist you create a custom-fitted wellness and nutrition plan that takes into consideration your particular needs and objectives.
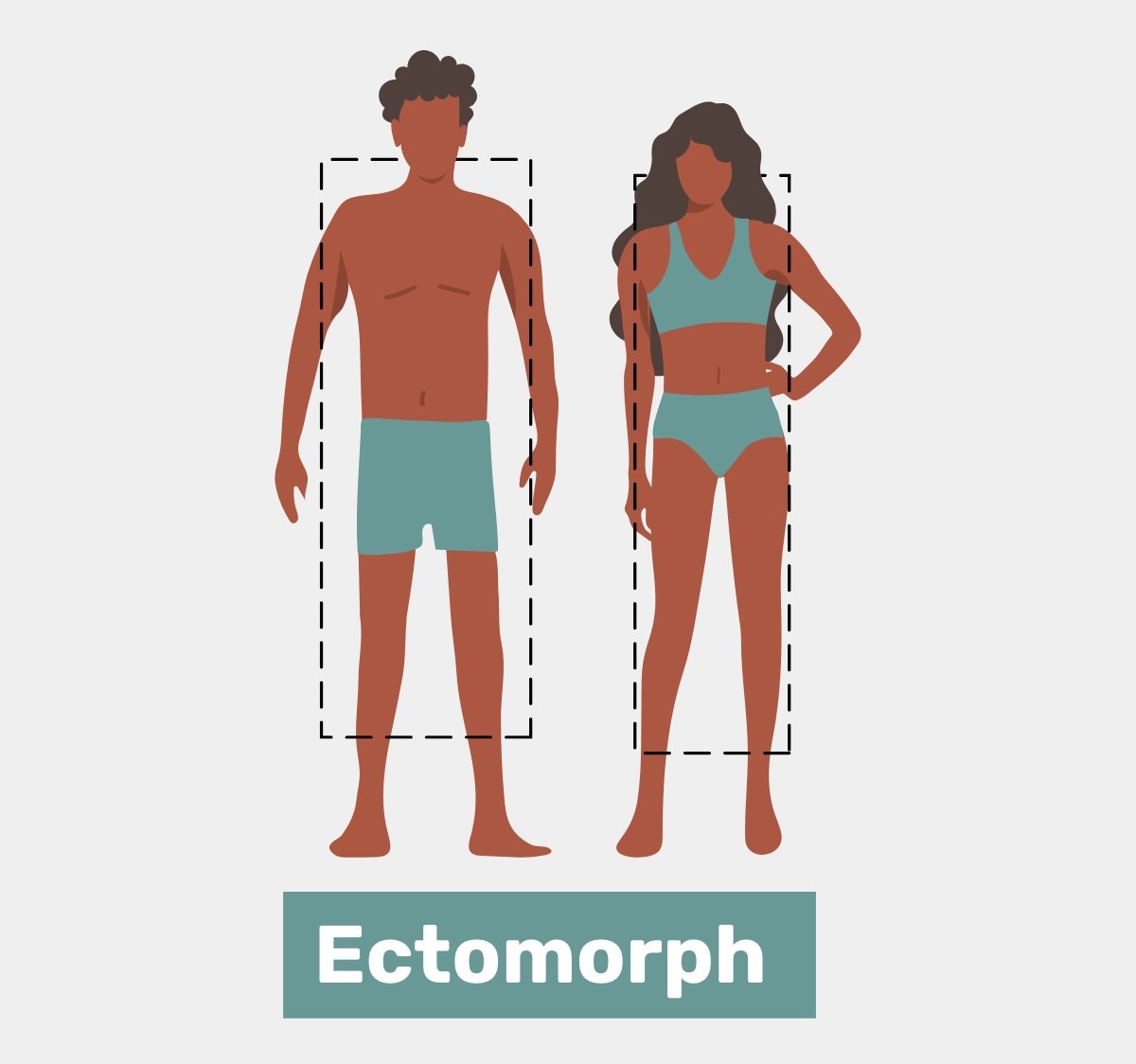
Ectomorph Body Type
The ectomorph body type is characterized by certain physical traits and metabolic tendencies.
Here are the key features of an ectomorph body type:
1. Lean and Slender Physique: Ectomorphs typically have a lean and slender body composition. They tend to have a moo body fat rate, which regularly comes about in a more characterized musculature.
2. Fast Metabolism: Ectomorphs generally have a fast metabolic rate, meaning their bodies efficiently burn calories at a higher rate compared to other body types. This can make it challenging for them to gain weight, including both muscle and fat.
3. Difficulty Gaining Weight: Due to their fast metabolism, ectomorphs often struggle to gain weight and build muscle mass. They may discover it more challenging to extend their estimate and quality compared to people with other body sorts.
4. Body Shape: Ectomorphs typically have a specific body shape and structure. They tend to have long appendages, contracted shoulders, lean bones, and little joints. Their frame may appear more “linear” or “ectomorphic” in nature.
5. Exercise Response: Ectomorphs may have a higher tolerance for endurance-based activities due to their fast metabolism. However, they often need to focus on resistance training and strength exercises to stimulate muscle growth and add size to their frame.
6. Nutritional Considerations: Ectomorphs often have higher calorie requirements to support their fast metabolism and provide adequate energy for their workouts. They may advantage of the count of calories that incorporates an overflow of calories and the next extent of carbohydrates and protein to back muscle development.
It’s vital to keep in mind that not everybody fits entirely into a single body sort category, and numerous people may display a combination of characteristics from distinctive body sorts. Understanding your body type as an ectomorph can assist you develop a customized wellness and sustenance arrangement that takes into consideration your particular needs and objectives.
Typical traits
Sure! Here are some typical traits associated with the ectomorph body type:
1. Long Limbs: Ectomorphs tend to have longer limbs in proportion to their bodies, including long arms, legs, and fingers.
2. Narrow Shoulders: Ectomorphs typically have narrower shoulders compared to individuals with other body types.
3. Thin Bones: Ectomorphs often have a smaller bone structure and thinner bones throughout their bodies.
4. Small Joints: Ectomorphs tend to have smaller joints, such as wrists and ankles.
5. Low Body Fat Percentage: Ectomorphs usually have a naturally low body fat percentage, which contributes to their lean and defined appearance.
6. Difficulty Gaining Weight: Ectomorphs often struggle to gain weight, including both muscle mass and fat. It can be challenging for them to add size and muscle to their frame.
7. Fast Metabolism: Ectomorphs generally have a fast metabolism, meaning their bodies efficiently burn calories at a higher rate compared to other body types.
8. Difficulty Building Muscle: Due to their fast metabolism and other genetic factors, ectomorphs may find it more difficult to build muscle mass compared to individuals with other body types.
Remember that these traits are not definitive and individuals can vary in their specific characteristics. It’s vital to grasp your interesting body and work with it to realize your well-being and wellness objectives.
Exercise and diet considerations
Exercise and diet considerations for individuals with an ectomorph body type are aimed at addressing their specific challenges and maximizing their potential for muscle growth and weight gain.
Here are some key considerations:
Exercise:
1. Focus on Resistance Training: Ectomorphs should prioritize resistance training exercises to stimulate muscle growth. This incorporates compound works out like squats, deadlifts, seat presses, and columns that target numerous muscle bunches.
2. Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the intensity, weight, or repetitions of your exercises over time to continuously challenge your muscles and promote muscle growth.
3. Frequency and Volume: Ectomorphs may benefit from higher training frequencies and volumes. Consider splitting your workouts into different muscle groups and incorporating multiple training sessions throughout the week.
4. Compound Movements: Emphasize compound exercises that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, as they provide a more efficient way to stimulate muscle growth.
5. Shorter Rest Periods: Reduce the rest periods between sets to keep the intensity high and promote hypertrophy (muscle growth).
Diet:
1. Caloric Surplus: Ectomorphs generally need to consume more calories than they burn to promote weight gain. Aim for a caloric surplus by consuming slightly more calories than your daily energy expenditure.
2. Macronutrient Balance: Ensure a balanced intake of macronutrients, including sufficient protein to support muscle repair and growth. Point for around 1.2-1.5 grams of protein per pound of body weight per day.
3. Frequent Meals: Consider eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day to meet your caloric and nutrient needs.
4. Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats in your diet, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, to provide additional calories and support overall health.
5. Carbohydrates: Prioritize complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to provide sustained energy for workouts and support muscle glycogen stores.
6. Adequate Hydration: Drink enough water to stay properly hydrated and support optimal bodily functions.
Remember that person varieties exist, and it’s basic to tune in to your body and make alterations based on your claim involvement and what comes about. Consulting with a registered dietitian or certified fitness professional can provide personalized guidance and help create an appropriate exercise and diet plan for your ectomorph body type.
What is Mesomorph?
Mesomorph refers to one of the three primary body types identified by psychologist William H. Sheldon. Mesomorphs are characterized by certain physical traits and metabolic tendencies.
Here are the key features of a mesomorph body type:
1. Athletic and Well-Proportioned Physique: Mesomorphs typically have an athletic and well-proportioned body composition. They tend to have a moderate body fat percentage, which allows for visible muscle definition.
2. Moderate Metabolism: Mesomorphs generally have a moderate metabolic rate, meaning their bodies efficiently burn calories at a balanced rate compared to other body types.
3. Easier Muscle Gain and Fat Loss: Due to their genetic predisposition, mesomorphs tend to have an easier time gaining muscle and losing fat compared to individuals with other body types. They can develop muscularity more quickly and efficiently.
4. Body Shape: Mesomorphs typically have a specific body shape and structure. They often exhibit broad shoulders, a narrow waist, and an overall balanced distribution of muscle mass.
5. Moderate Bone Structure: Mesomorphs usually have a moderate bone structure, neither as thin as ectomorphs nor as thick as endomorphs.
6. Exercise Response: Mesomorphs respond well to both resistance training and cardiovascular exercises. They have a natural tendency to build muscle and strength while maintaining overall fitness.
7. Nutritional Considerations: Mesomorphs can generally maintain a balanced diet without strict restrictions. They benefit from a well-rounded nutrition plan that provides adequate macronutrients and portion control to support their physique.
It’s important to note that while these traits are commonly associated with mesomorphs, not everyone fits strictly into a single body type category. Many individuals may exhibit a combination of characteristics from different body types. Understanding your body sort as a mesomorph can assist you create a customized wellness and nutrition plan that takes into consideration your particular needs and objectives.
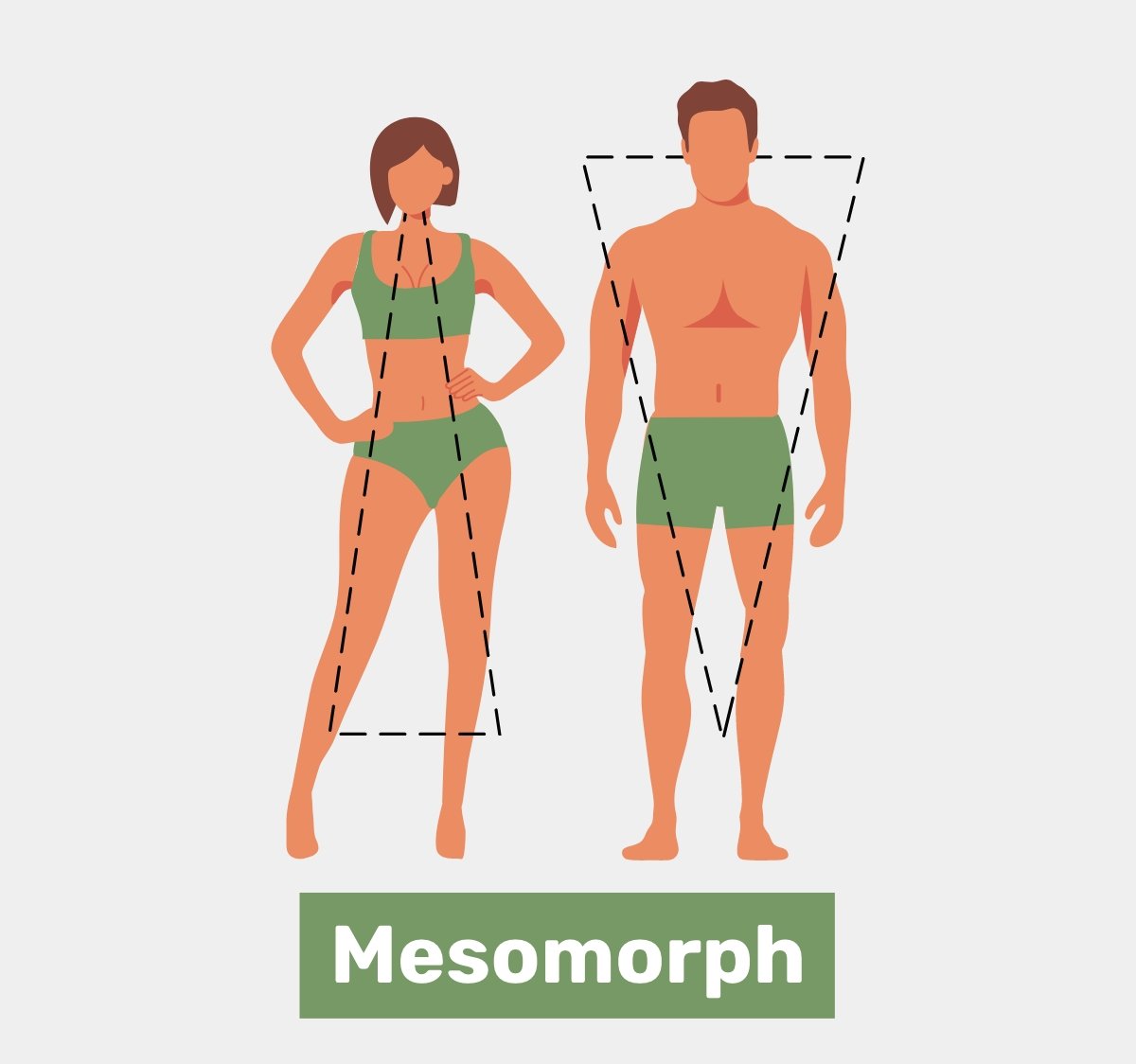
Mesomorph Body Type
The mesomorph body type is characterized by specific physical traits and metabolic tendencies.
Here are the key features of a mesomorph body type:
1. Athletic and Muscular Build: Mesomorphs typically have a naturally muscular and athletic build. They often have well-defined musculature, with visible muscle definition and a balanced distribution of muscle mass throughout their body.
2. Moderate Metabolism: Mesomorphs tend to have a moderate metabolic rate, which means they can efficiently burn calories at a balanced rate. This permits them to preserve a sound body weight more effortlessly compared to other body sorts.
3. Easy Muscle Gain: Mesomorphs have a genetic advantage when it comes to building muscle. They tend to respond well to resistance training and can experience relatively faster muscle growth compared to other body types.
4. Proportionate Body Shape: Mesomorphs typically have an aesthetically pleasing body shape with broad shoulders, a narrow waist, and well-developed muscles. Their body proportions often give them a natural fit and athletic appearance.
5. Strong Bone Structure: Mesomorphs usually have a strong and dense bone structure, which contributes to their overall physical strength.
6. Exercise Response: Mesomorphs are generally well-suited for a wide range of physical activities. They have a great combination of quality, continuance, and nimbleness, permitting them to exceed expectations in different sorts of work out and sports.
7. Nutritional Considerations: Mesomorphs tend to have a more balanced approach to nutrition. They can generally tolerate a moderate intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats without significant issues. Mesomorphs must preserve an adjusted eat-less to bolster their general well-being and wellness objectives.
It’s important to remember that while mesomorphs have certain advantages when it comes to muscle gain and maintaining a fit physique, individual variations exist. Everyone’s body is unique, and factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and training habits can influence individual results. Understanding your body type as a mesomorph can provide insights into how to best leverage your natural advantages and tailor your fitness and nutrition approach accordingly.
Typical traits
Certainly! Here are some typical traits associated with the mesomorph body type:
1. Muscular Build: Mesomorphs tend to have a naturally muscular physique. They often have well-developed muscles and a visible muscle definition, even without extensive training.
2. Broad Shoulders: Mesomorphs typically have broad and well-defined shoulder muscles, which contribute to their athletic appearance.
3. V-Shaped Torso: Mesomorphs often have a V-shaped torso, with broader shoulders and a narrower waist, creating an attractive and symmetrical body shape.
4. Balanced Body Proportions: Mesomorphs usually have a balanced distribution of muscle mass throughout their bodies. Their arms, legs, and torso are proportionate, contributing to their athletic and well-built physique.
5. Efficient Metabolism: Mesomorphs tend to have a moderate metabolic rate. Their bodies efficiently utilize calories for energy, allowing them to maintain healthy body weight and easily manage body composition.
6. Easy Muscle Gain: Mesomorphs have a genetic advantage when it comes to building muscle. They typically respond well to resistance training and can gain muscle mass relatively easily compared to other body types.
7. Athletic Performance: Mesomorphs often excel in athletic activities due to their combination of strength, power, and agility. They have the potential to perform well in a wide run of sports and physical exercises.
8. Strong Bone Structure: Mesomorphs usually have a solid and sturdy bone structure. Their bones tend to be thicker and denser, providing a foundation for their muscularity and physical strength.
It’s imperative to note that not everybody fits entirely into a single body sort category, and there can be varieties inside the mesomorph body sort as well. Individuals may exhibit a combination of characteristics from different body types. Understanding your body sort as a mesomorph can assist you optimize your training and nutrition strategies to form the foremost of your hereditary preferences and accomplish your wellness objectives viably.
What is Endomorph?
Endomorph refers to one of the three primary body types identified by psychologist William H. Sheldon. Endomorphs are characterized by specific physical traits and metabolic tendencies.
Here are the key features of an endomorph body type:
1. Soft and Round Physique: Endomorphs typically have a soft and round body composition. They tend to have the next body fat rate and may carry an overabundance of weight, especially within the frame of fat, around the midriff, hips, and thighs.
2. Slower Metabolism: Endomorphs generally have a slower metabolic rate compared to other body types. This implies they burn calories at a slower rate, making it simpler for them to pick up weight and harder to lose it.
3. Difficulty Losing Weight: Due to their slower metabolism and genetic predisposition, endomorphs may find it more challenging to lose weight compared to individuals with other body types. They frequently got to put in extra exertion and make dietary and way-of-life alterations to realize their weight misfortune objectives.
4. Round Body Shape: Endomorphs typically have a rounder body shape with wider hips and a shorter, stockier build. They may have a propensity to store fat in their lower body, giving them a pear-shaped appearance.
5. Stronger Lower Body: Endomorphs often have strong lower body strength. They may naturally excel in exercises that engage the lower body, such as squats and lunges.
6. Carbohydrate Sensitivity: Endomorphs may have a higher sensitivity to carbohydrates and a tendency to store them as fat. They must pay consideration to their carbohydrate admissions and select complex, nutrient-dense sources.
7. Focus on Weight Management: Endomorphs may need to focus on weight management strategies, including a balanced diet, portion control, regular exercise, and potential calorie restriction to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight.
It’s important to note that while these traits are commonly associated with endomorphs, not everyone fits strictly into a single body type category. Many individuals may exhibit a combination of characteristics from different body types. Understanding your body sort as an endomorph can assist you create a personalized wellness and nutrition plan that takes into consideration your particular needs and objectives, with a center on overseeing weight and body composition viably.
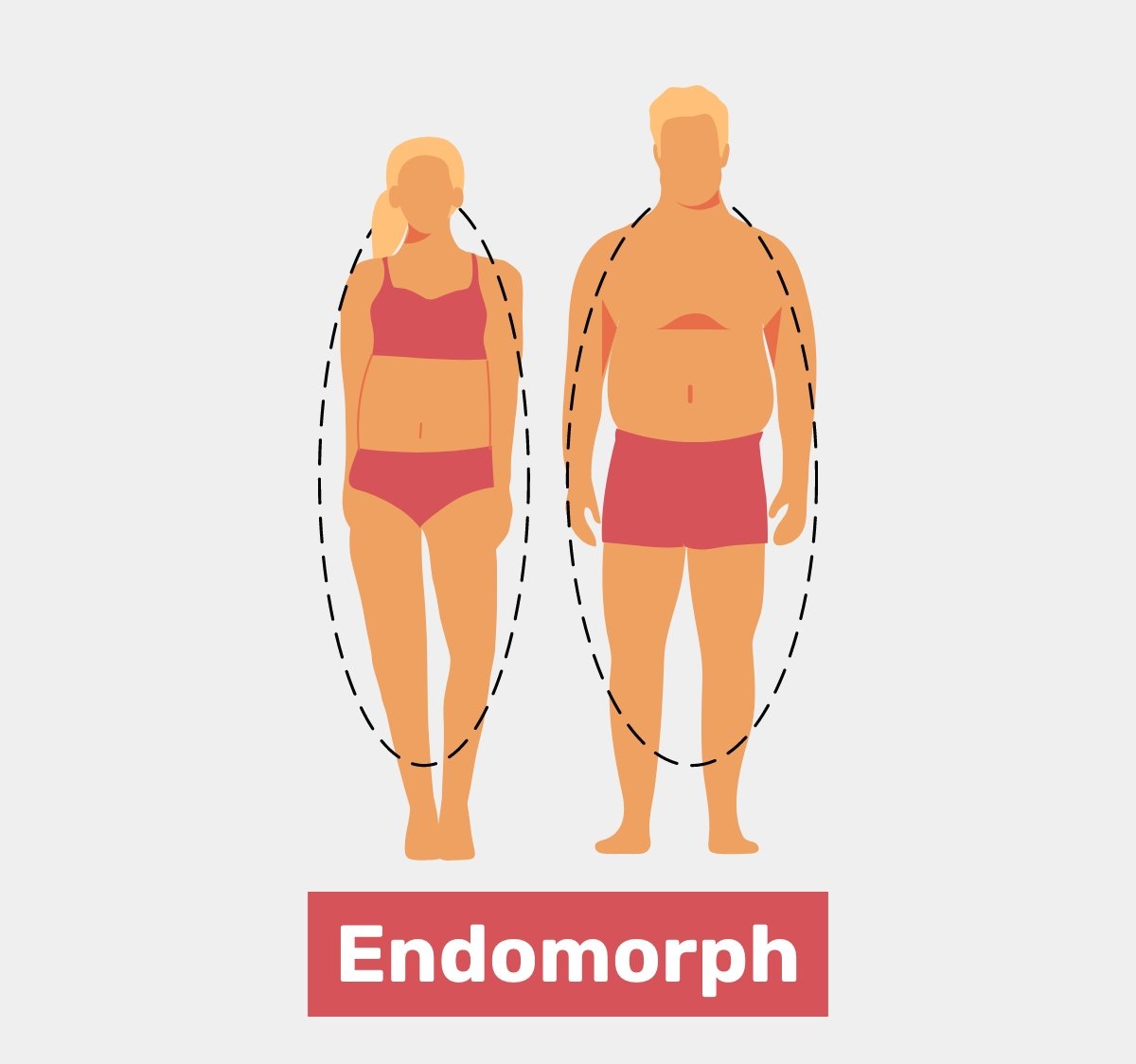
Endomorph Body Type
The endomorph body type is characterized by specific physical traits and metabolic tendencies.
Here are the key features of an endomorph body type:
1. Rounded and Soft Physique: Endomorphs typically have a rounded and softer body composition. They regularly have the next body fat rate and may have the propensity to carry an abundance of weight, particularly within the frame of fat, around the midsection, hips, and thighs.
2. Slower Metabolism: Endomorphs generally have a slower metabolic rate compared to other body types. This implies their bodies may burn calories at a slower rate, making it simpler for them to pick up weight and more challenging to lose it.
3. Difficulty Losing Weight: Due to their slower metabolism and genetic predisposition, endomorphs often face challenges when it comes to losing weight. They may discover it harder to shed body fat compared to people with other body sorts and may have to make additional endeavors to attain their weight misfortune objectives.
4. Round Body Shape: Endomorphs typically have a rounder body shape with a wider waist, fuller hips, and a larger bone structure. They may exhibit a more “curvy” or “pear-shaped” appearance.
5. Higher Body Fat Storage: Endomorphs have a natural tendency to store fat, particularly in the abdominal area. This can make it more challenging for them to achieve a lean and defined physique.
6. Stronger Lower Body: Endomorphs often have naturally stronger lower bodies, including their hips, thighs, and calves. They may find activities like squatting, lunging, and other lower-body exercises more manageable and may have an advantage in strength-related activities.
7. Carbohydrate Sensitivity: Endomorphs may have a higher sensitivity to carbohydrates and may be more prone to storing excess carbs as fat. It can be advantageous for them to center on an adjusted slim down that incorporates complex carbohydrates, fiber, incline proteins, and sound fats.
8. Focus on Fat Loss: Endomorphs often need to prioritize fat loss strategies, including a combination of regular exercise, calorie control, portion management, and potentially incorporating both cardiovascular activities and strength training to support weight management goals.
It’s important to remember that while endomorphs have certain challenges related to weight management, individual variations exist. Everyone’s body is unique, and factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and training habits can influence individual results. Understanding your body sort as an endomorph can give bits of knowledge into how to best approach your wellness and sustenance objectives, tailor your methodologies, and work together with your body to attain ideal wellbeing and well-being.
Wide waist and hips
Endomorphs often have a wider waist and hips as part of their body shape. This is one of the typical characteristics of the endomorph body type.
Here’s some additional information regarding the wider waist and hips in endomorphs:
1. Fat Distribution: Endomorphs have a genetic predisposition to store excess fat in the midsection, including the waist and abdominal area, as well as the hips and thighs. This can result in a wider waist and hips compared to other body types.
2. Pear-Shaped Body: The wider waist and hips contribute to a more pronounced pear-shaped body appearance in endomorphs. This body shape is characterized by a smaller upper body (shoulders and bust) and a more extensive lower body (midriff, hips, and thighs).
3. Estrogen Influence: The wider waist and hips in endomorphs can be influenced by hormonal factors, particularly estrogen. Estrogen tends to promote fat storage in the lower body, which can contribute to the wider hip and thigh area.
4. Structural Differences: Endomorphs may have a larger bone structure, including wider hip bones, which can contribute to the wider waist and hips. This structural difference is a natural part of their body type.
While the wider waist and hips are typical traits of the endomorph body type, it’s important to note that body shapes and proportions can vary among individuals. Not all endomorphs will have the same body measurements, and there can be variations within this body type category as well.
Understanding your body type as an endomorph can help you tailor your fitness and nutrition strategies to work with your unique body characteristics. It’s important to focus on overall health, body composition, and embracing your body shape while working towards your personal fitness goals.
Difference Between Ectomorph Mesomorph and Endomorph
The three essential body sorts, Ectomorph Mesomorph and Endomorph contrast in terms of physical characteristics, metabolic propensities, and reactions to work out and count calories.
Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between these body types:
1. Ectomorph:
• Physical Traits: Ectomorphs typically have a lean and slender body with a fast metabolism.
• Body Composition: Ectomorphs often have a low body fat percentage and may struggle to gain both muscle and fat.
• Metabolic Tendencies: Ectomorphs tend to have a fast metabolism, which means they burn calories quickly and may find it challenging to gain weight.
• Exercise Response: Ectomorphs may find it difficult to build muscle and may need to focus on resistance training and higher-calorie diets to support muscle growth.
• Diet Considerations: Ectomorphs may require a higher caloric intake, including a balanced mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats, to support their energy needs and promote muscle gain.
2. Mesomorph:
• Physical Traits: Mesomorphs typically have an athletic and well-proportioned physique with a moderate metabolism.
• Body Composition: Mesomorphs often have a balanced muscle-to-fat ratio and can gain and lose weight relatively easily.
• Metabolic Tendencies: Mesomorphs generally have a moderate metabolism, allowing them to manage their weight effectively.
• Exercise Response: Mesomorphs respond well to both resistance training and cardiovascular exercises, making it easier for them to build muscle and maintain overall fitness.
• Diet Considerations: Mesomorphs can generally maintain a balanced diet without strict restrictions but still need to focus on nutrition to support their fitness goals.
3. Endomorph:
• Physical Traits: Endomorphs typically have a rounder and softer physique, with a tendency to carry excess body fat.
• Body Composition: Endomorphs often have a higher body fat percentage and may struggle with weight management and losing fat.
• Metabolic Tendencies: Endomorphs generally have a slower metabolism, making it easier for them to gain weight and harder to lose it.
• Exercise Response: Endomorphs may need to focus on a combination of cardiovascular exercise and strength training to manage body weight and improve body composition.
• Diet Considerations: Endomorphs may have a higher sensitivity to carbohydrates and may need to be mindful of their calorie intake and choose nutrient-dense foods to support weight management.
It’s important to note that while these body types provide a general framework, many individuals may exhibit characteristics from multiple body types or fall somewhere between them. Each individual is interesting, and components such as hereditary qualities, way of life, and person varieties can impact body composition and reaction to working out and eating less. Understanding your body sort can serve as a beginning point for fitting your wellness and sustenance approach to your particular needs and objectives.
Comparison Chart
Certainly! Here’s a comparison chart highlighting the key characteristics of the Ectomorph Mesomorph and Endomorph body types:
| Characteristic | Ectomorph | Mesomorph | Endomorph |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Traits | Lean and slender | Athletic and well-proportioned | Rounder and softer physique |
| Body Composition | Low body fat percentage | Balanced muscle-to-fat ratio | Higher body fat percentage |
| Metabolic Tendencies | Fast metabolism | Moderate metabolism | Slow metabolism |
| Weight Gain/Loss | Difficult to gain both muscle and fat | Can gain and lose weight relatively easily | Tendency to gain weight and struggle with fat loss |
| Exercise Response | Difficulty building muscle | Builds muscle and maintains fitness easily | Focus on a combination of cardio and strength training |
| Diet Considerations | Higher caloric intake, balanced nutrients | A balanced diet, moderate calorie intake | Calorie control, nutrient-dense foods, carbohydrate sensitivity |
| Body Shape | Long, lean limbs | Athletic and well-proportioned | Rounder body shape, wider waist, and hips |
| Strengths | Good endurance, lean physique | Well-built, responds well to exercise | Strong lower body, the potential for strength |
| Challenges | Difficulty gaining muscle and weight | Need to maintain balance, may gain weight easily | Weight management, fat loss |
It’s important to note that this is a general comparison and individual variations exist within each body type category. People may display a combination of traits from different body types, and other factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and training habits can also impact individual characteristics.
Understanding your body type provides a starting point for developing a personalized fitness and nutrition plan, but it’s essential to consider your unique circumstances and consult with professionals for personalized guidance.
Understanding Your Body Type
Understanding your body type is valuable for several reasons. It can give experiences into how your body reacts to working out and slimming down, assist you set practical objectives, and direct you in making a personalized wellness and nourishment arrangement.
Here are some key reasons why understanding your body type is important:
1. Tailored Exercise Programs: Different body types may respond differently to various forms of exercise. Knowing your body sort can assist you recognize the sorts of works out and preparing strategies that are most viable for your body. For case, ectomorphs may advantage from centering on quality preparation to construct muscle, whereas endomorphs may advantage from a combination of cardiovascular workout and resistance preparation for weight administration.
2. Effective Diet and Nutrition Strategies: Your body type can influence how your body metabolizes and responds to different nutrients. Understanding your body type can guide you in selecting the appropriate macronutrient ratios and food choices that support your goals. Ectomorphs may require higher caloric admissions, mesomorphs may advantage from an adjusted slim down, and endomorphs may have to be careful of carbohydrate admissions.
3. Realistic Goal Setting: Knowing your body type can help you set realistic and attainable goals. It permits you to have a distant better; a much better; a higher; a stronger; an improved”>an improved understanding of what your body is inclined to and what you’ll anticipate in terms of muscle pick up, fat misfortune, or body composition changes. This helps prevent setting unrealistic expectations and promotes a healthier and more sustainable approach to reaching your desired outcomes.
4. Motivation and Confidence: Understanding your body type can help you embrace and appreciate your unique characteristics. It permits you to center on upgrading your qualities and working towards your objectives, instead of comparing yourself to others with different body sorts. This will boost your inspiration, self-confidence, and general body picture.
5. Personalized Approach: Each body type has its unique traits and challenges. By understanding your body type, you can personalize your approach to fitness and nutrition. This incorporates customizing your workout schedules, altering your macronutrient proportions, and selecting appropriate procedures to optimize your advance and accomplish the leading conceivable comes about for your body.
Remember that body type is just one aspect of your overall health and fitness journey. It’s important to consider other factors such as individual genetics, lifestyle, and preferences when creating a comprehensive plan. Counseling with a healthcare proficient, nutritionist, or certified wellness coach can moreover give important direction and back in understanding your body sort and creating a custom-fitted approach to your wellness and sustenance objectives.
Conclusion
Understanding the contrast between Ectomorph Mesomorph and Endomorph can engage you to form educated choices concerning your wellness objectives, dietary choices, and workout schedules. Keep in mind that whereas body sorts give a system for understanding your physical make-up, it is vital to tune in to your body’s one-of-a-kind needs and adjust your way of life appropriately.
So, embrace your body type, appreciate its strengths, and work towards achieving a balanced and healthy lifestyle. By combining the right exercise, nutrition, and mindset, you can unlock your full potential and thrive in your fitness journey.
