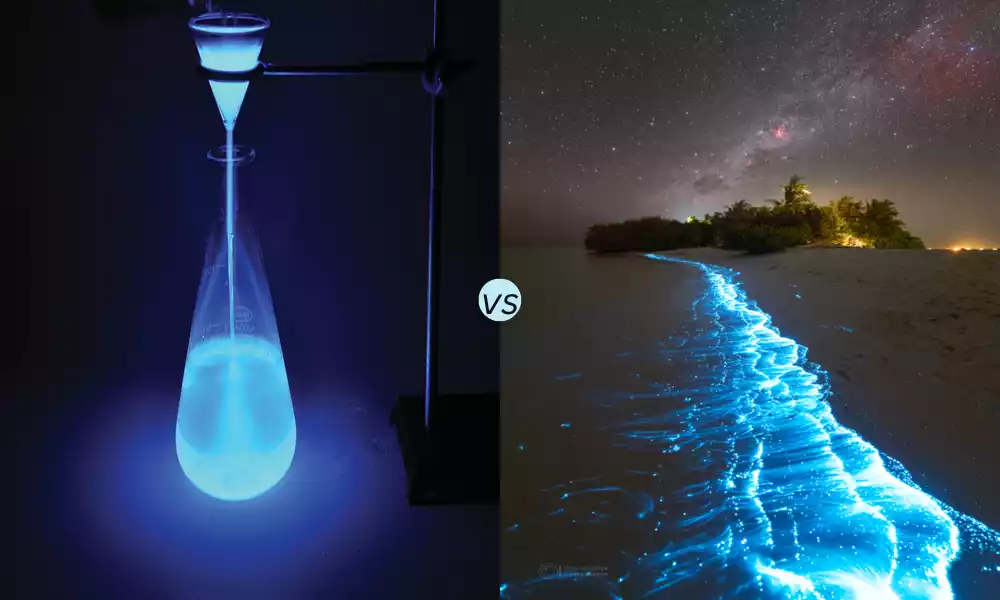
Introduction of Chemiluminescence and Bioluminescence
Chemiluminescence as well as bioluminescence are both fascinating natural processes that rely on emitting light, without being accompanied by heat. Chemiluminescence is a chemical reaction that produces light. bioluminescence is a biological process only found in certain species of organisms.
They both have their applications in technology, science, as well as the natural world. studying them can shed light on an interesting aspect of biological and physical sciences.
What is Chemiluminescence?
Chemiluminescence refers to a chemical reaction that creates visible light, without releasing heat. It happens when certain chemical compounds, also known as chemiluminescent substances or molecules undergo chemical reactions and release light energy as photons (light). This is a common phenomenon in a variety of practical applications where the production of light is needed without generating significant heat.
Some of the most important facts about Chemiluminescence are:
- Chemical Reaction: Chemiluminescence can be described as the result of a chemical interaction between certain molecules or compounds. The reaction is triggered by the excitation of electrons in molecules, and then returning them to their lower energy level and releasing energy through visible light.
- applications: Chemiluminescence has a variety of applications. It is often employed in glowing sticks, chemiluminescent tests in research (such as the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs)), and in certain kinds that use artificial light.
- Multipliability: Chemiluminescence can produce various hues of light, based on the chemical compounds that are involved in the reaction. This flexibility makes it suitable in a variety of situations in which different colors of light are required.
- Security: Because chemiluminescence doesn’t produce heat, it’s typically regarded as more secure than other types of light-producing processes like incandescence or combustion, which can generate extreme temperatures and cause risks of fire.
- Natural Occurrence: Chemiluminescence is also a phenomenon that occurs naturally. For instance, certain bioluminescent organisms like fireflies, emit light via the chemiluminescent process that involves certain enzymes and substrates inside their bodies.
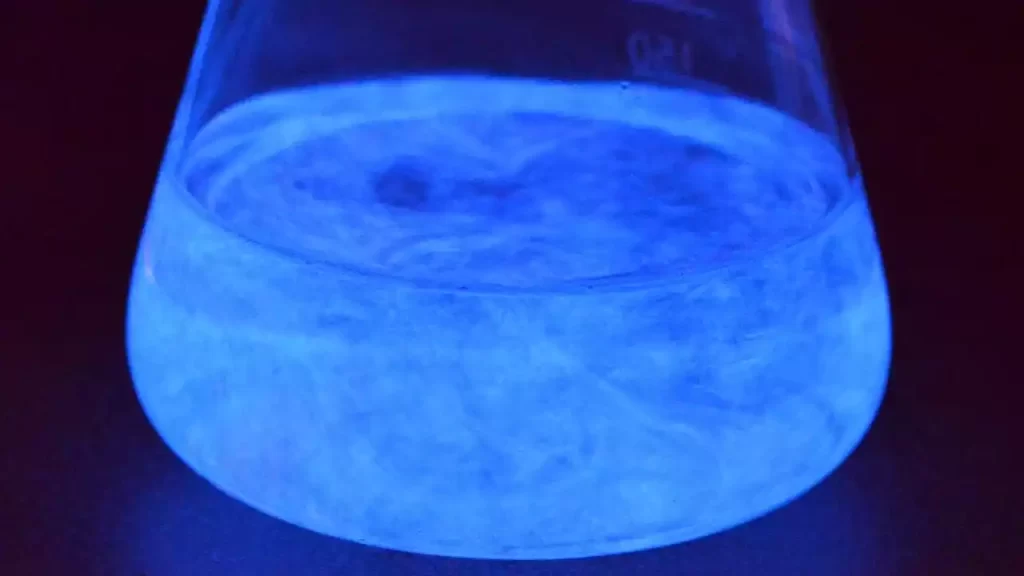
Chemiluminescence is a fascinating practical phenomenon that has a myriad of applications across a variety of areas, from entertainment to emergency lighting, to scientific studies and tests for diagnosing.
What is Bioluminescence?
Bioluminescence is a biological phenomenon where living organisms generate visible light by an enzymatic reaction inside their bodies. This process is unique to certain species of living organisms that are mainly found in the animal kingdom and it is used for various reasons for survival and ecology.
Below are some of the main characteristics of bioluminescence:
- Biochemical process: Bioluminescence is a biological process. It is a natural process that occurs in the living cells of some organisms. The chemical reaction is controlled with specific enzymes as well as substrates within these organisms.
- Enzymatic Reaction: The primary component of the bioluminescent process is an interaction between the enzymes involved, specifically Luciferases, with a light-emitting chemical called luciferin and other cofactors. The result is an emission of light visible.
- Organisms: The phenomenon of bioluminescence can be seen in a variety of marine creatures, including jellyfish of a certain variety of deep-sea and deep-sea species, as well as plankton. Fireflies, which are insect species are also famous for their bioluminescent ability. A few species of mushrooms and different fungi can be considered examples of bioluminescent organisms that are not part of the animal kingdom.
- Ecological functions: Bioluminescence serves multiple environmental purposes. This includes attracting partners for reproduction, dissuading predators by creating an illusion of unpalatableness, luring prey, hiding the animal from predators beneath, and communicating within the species.
- Color Variability: Bioluminescence can produce many shades of light. the exact colors that are produced depend on the kind of luciferase, Luciferin, and other elements that are involved in the process. Certain organisms have evolved to emit certain colors that fit their ecological functions.
- Natural as well as Artificial Studies: Bioluminescence is extensively studied in biology and has been an important topic for researchers who are interested in the biochemical, genetic, as well as ecological aspects of this phenomenon. It has also influenced artificial applications, like the creation of bioluminescent indicators for biotechnology as well as bioimaging.
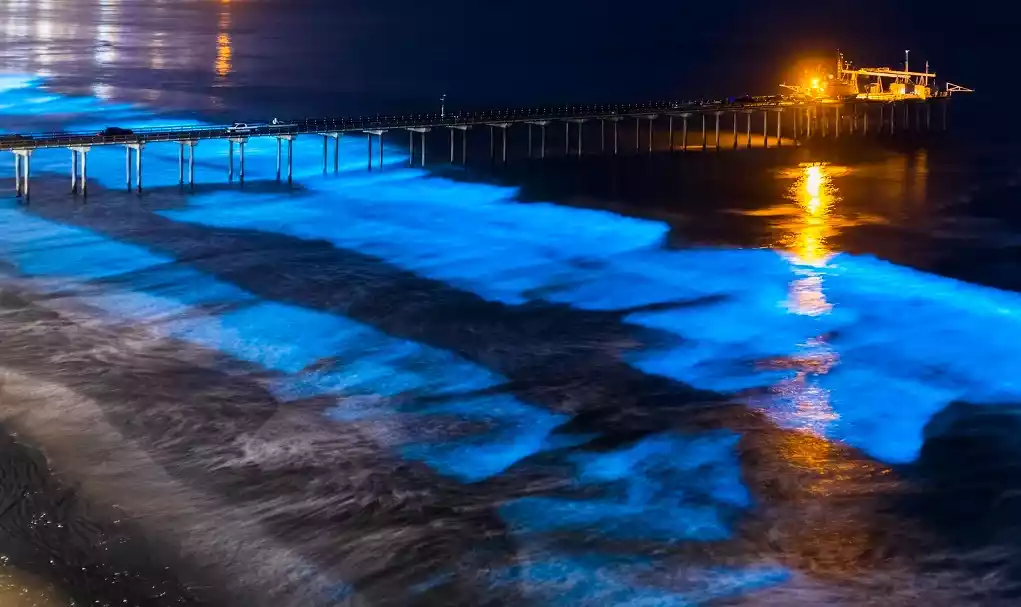

Bioluminescence is a fascinating, amazing adaptation within the animal kingdom. It evolved to serve a variety of purposes and allows organisms to communicate with their environment, fellow species, as well as members of their particular species. It is still the subject of scientific research and fascination.
Key Differences of Chemiluminescence and Bioluminescence
These are the most important distinctions between bioluminescence and chemiluminescence:
- Source:
- Chemiluminescence: The production of light is the result of a chemical reaction between certain molecules or compounds. It is possible to observe it in natural and artificial settings.
- bioluminescence: It is created through a process that occurs in living organisms that involves certain enzymes and substances. It is restricted to specific species of organisms, and it isn’t a chemical process that takes place outside of a living organism.
- Occurrence:
- Chemiluminescence: It can occur in natural and artificial settings. Some examples of the natural chemical chemistry comprise fireflies as well as some bioluminescent fungi.
- Bioluminescence: is an organic process that only occurs in living organisms, and is primarily found within the realm of animals. The most common examples are fireflies, jellyfish, creatures from deep seas, and a few species of mushrooms.
- Chemical Substrates:
- Chemiluminescence: It involves specific chemical substances or substrates which participate in the chemical reaction like luminol, or the reaction that occurs in glow sticks.
- Bioluminescence: Utilizes enzymes, like luciferases, together with other cofactors, such as oxygen to trigger the reaction that generates the light. It is dependent on certain biological components and processes.
- Color of Light:
- Chemiluminescence: Produces a wide spectrum of light colors dependent on the chemical components that are involved in the reaction. It’s extremely variable in terms of the color.
- bioluminescence Though bioluminescence may produce a variety of shades, it is typically restricted by special enzymes or substrates employed in the process, which results in an encapsulated spectrum of colors in comparison to chemiluminescence.
- Evolutionary Significance:
- Chemiluminescence: The evolutionary function and importance of chemiluminescence in non-biological settings are not as evident and could not be able to play a clear ecological significance.
- Bioluminescence: The bioluminescence of organisms has evolved to serve a variety of ecological functions, such as communication and predation, as well as attracting partners, and deterring predators.
These distinctions are a sign of the different methods of the source, applications, and sources of bioluminescence and chemiluminescence making them essential to recognize in ecological, scientific, and other practical settings.
Importance of understanding the differences
Understanding the difference between bioluminescence and chemiluminescence is crucial for a variety of reasons:
- Science Research: Understanding these mechanisms is essential to scientific research in areas like chemistry, biology, and ecology. Researchers must distinguish between chemiluminescence as well as bioluminescence to investigate the fundamental mechanisms as well as the ecological functions of these phenomena in different species and habitats.
- Environmental studies: The distinction between bioluminescence and chemiluminescence is crucial to studying ecology and monitoring. Bioluminescence in marine organisms for example, is utilized for studies on marine health as well as predator-prey dynamics. It is also used in investigating the effects of climate change and pollution.
- Application for Diagnostic and Medical Use: In the field of biotechnology and medical diagnostics Chemiluminescence is widely used to test and assays. Knowing the distinctions can help in the designing and interpreting of tests and experiments.
- Bioimaging: The use of bioluminescence in the field is to show biological processes occurring in living organisms. Researchers employ bioluminescent markers to monitor specific cell activities as well as gene expression. Understanding how bioluminescence works is essential for precise imaging and interpretation of data.
- Conservation as well as Biodiversity: Understanding bioluminescence is crucial to the conservation of bioluminescent species. By knowing what causes and how certain organisms generate light conservationists can safeguard their habitats and avoid the pollution of light that can affect their natural behaviors.
- Technology and Innovation Technology: Differentiating between these processes can spur creativity. For instance, the study of bioluminescence has led to the creation of more sustainable and efficient lighting techniques and possible applications in medicine and biotechnology.
- Educational and Awareness: Informing the general public on the differences between bioluminescence and chemiluminescence could increase their appreciation of the natural world as well as the scientific concepts that drive these phenomena. It could also help in promoting conservation efforts to protect bioluminescent species and their habitats.
Understanding the differences between chemiluminescence as well as bioluminescence can have wide-ranging implications for research in science and medical applications, environmental studies conservation, technology development education, as well as public education. It increases our understanding of the natural world as well as its applications to various areas, ultimately resulting in technological advancements and a better knowledge of the environment that surrounds us.
Similarities between Chemiluminescence and Bioluminescence
While chemiluminescence as well as bioluminescence have distinct characteristics, the two do have several similarities:
- Light Emission: Both bioluminescence and chemiluminescence make use of emitting visible light. They are distinct in that they emit light that does not generate heat, which makes them extremely useful in a myriad of ways.
- Chemical Reactions: Each process is triggered via chemical reactions. In chemiluminescence, certain chemical compounds can react and produce light. In bioluminescence, enzymes in the body catalyze the chemical reaction, which results in luminescence.
- The release of energy: In both chemiluminescence and bioluminescence, energy gets discharged when electrons that are excited revert to their grounded state, resulting in emitting photons (light). This release of energy is the primary reason for the similarity in both processes.
- applications: Both phenomena have practical applications. Chemiluminescence is utilized in chemiluminescent tests and lighting systems, and bioluminescence is utilized for bioimaging research, scientific research, and natural environments to serve ecological purposes.
- Diverse Colors: Both bioluminescence as well as chemiluminescence can create a variety of colors in light. The precise colors are determined by chemical components or biological elements that are involved in the reaction.
- Ecological Significance: Although they have different reasons in the natural world, both chemiluminescence as well as bioluminescence share ecological significance. Chemiluminescent chemicals are found in marine organisms and bioluminescence is an omnipresent feature of a variety of deep-sea marine creatures.
These resemblances are significant However, it’s crucial to understand that the main differences are in their source (chemical as opposed to. biological) the chemical reactions involved, and the substrates and the evolutionary functions that they perform in living organisms that exhibit them.
Applications and Advancements
Both bioluminescence and chemiluminescence have been used in a multitude of ways and have witnessed advancements in a variety of areas. Here are a few major applications and developments for each
Chemiluminescence:
- Chemiluminescent Assays: Chemiluminescence is extensively used in diagnostics and research. Chemiluminescent tests, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent tests (ELISAs) are crucial to detect biomolecules (e.g. proteins, proteins, or nucleic acids) in biotechnological and medical applications. The latest developments include more sensitive assays and high-throughput tests.
- Glow Sticks: Chemiluminescent substances are utilized in glow sticks as well as different emergency light devices. They are very popular for entertainment and safety for entertainment and safety.
- Artificial lighting: Researchers have explored the possibility of using chemiluminescent materials to create artificial lighting systems which include emergency lighting, signs, and lighting for decorative purposes. Improvements aim to increase efficiency and reduce the environmental impact.
- Chemiluminescent Tracers: In the fields of environmental research and fluid dynamics, chemical tracers are employed to study airflow as well as water currents. They can aid in understanding the dispersion of pollutants, airflow patterns as well and ocean flow.
Bioluminescence:
- Bioluminescent Markers: Bioluminescent proteins, such as Luciferase have been engineered genetically to function as markers for a variety of biological processes. They are extensively used in molecular biology. They allow researchers to examine gene expression, protein localization, as well as cell signaling. Innovations include the development of more powerful and stable bioluminescent markers.
- Bioimaging: The use of bioluminescence in biology is to show and analyze biological processes in living organisms. Bioluminescent imaging advances allow researchers to track molecular and cellular activities in real time.
- Biologyluminescent Organisms As Models: Organisms that are bioluminescent, like fish and fireflies, continue to be useful models for ecology as well as environmental sciences. They aid researchers in studying predator-prey interactions, species interactions, and the effects of climate change and pollution.
- Conservation as well as Ecotourism: Bioluminescent organisms like glow-in-the-dark mushrooms, and bioluminescent bays are a popular attraction in ecotourism. The study and preservation of these unique ecosystems is becoming increasingly crucial.
- Marine Research: The advancements made in the exploration of deep seas technologies have enabled researchers to study and discover new bioluminescent species that are found in the deep ocean. These discoveries help us to improve our understanding of diversity as well as adaptation to extreme environments.
In both bioluminescence and chemiluminescence, the ongoing technological advances and research allow them to continue expanding their applications and increase their effectiveness in terms of sensitivity, sensitivity, and usability across a variety of areas, from research and diagnostics to lighting and environmental conservation.
Real-Life Examples
Here are real-world examples of chemiluminescence as well as bioluminescence:
Chemiluminescence:
- Glow Sticks: The glow sticks typically used for events, parties, or emergencies, are made of chemically luminescent substances. When you twist and shake the glowing stick it cracks the vial in its interior, allowing two chemicals to mix and create bright light, without heating.
- Chemiluminescent Assays: In both biological and medical research, chemiluminescent test kits can be used to identify and quantify biomolecules that are specific to them. For example, chemiluminescence-based ELISAs are used to measure proteins or antibodies in diagnostic tests.
- fireflies: They are an excellent instance of chemiluminescence in the course of their actions. The light they emit comes through a chemical reaction in their bodies. They attract partners and act as an indicator of communication during their mating rituals.
- LEDs that emit light (LEDs): Some chemicals that are chemiluminescent are used to make chemical LEDs. They are electrical lighting sources. They have been studied to be used in applications such as lighting for signage and other decorative purposes.
Bioluminescence:
- fireflies: Fireflies are among the famous examples of bioluminescence that we can find in the natural world. They make use of their bioluminescent light to attract their mates and communicate with each other.
- Deep-Sea Creatures: A variety of deep-sea animals like anglerfish, as well as certain jellyfish species, employ bioluminescence as a method of camouflage and predation and even communication in the dark depths of the ocean.
- Bioluminescent Algae: Certain kinds of bioluminescent algae like Noctiluca scintillans produce spectacular bioluminescence displays when moved by waves or movements. The phenomenon is commonly described as “sea sparkle” and can be observed in the oceans of the globe.
- Bioluminescent Mushrooms: Certain species of mushrooms like”foxfire,” for instance “foxfire” fungus, exhibit bioluminescence. They emit a gentle greenish glow. They can be located in forests, especially in wood that is decaying.
- Bioluminescent Bays: Particular bays such as Mosquito Bay in Vieques, Puerto Rico, and Mosquito Bay in Vieques, Puerto Rico, are famous for their bioluminescent water. Bioluminescent microorganisms living in the waters emit light when disturbed, resulting in spectacular natural illumination.
- Bioluminescent Insects as well as Arachnids: Apart from fireflies, many insects and arachnids such as glowworms of various types and click beetles display bioluminescence. They utilize it for courtship as well as predation and defense.
These real-world examples illustrate the numerous applications and environmental applications of chemiluminescence and bioluminescence throughout the natural world and in research and development, as well as various kinds of illumination.
Benefits and Limitations
Bioluminescence and Chemiluminescence come with distinct advantages and limitations, dependent on their contexts and applications:
Benefits of Chemiluminescence:
- safety: Chemiluminescence is often considered to be more secure than other forms of light-producing technology because it doesn’t produce heat. It is utilized in situations in which heat may pose risks for instance, in the case of glow sticks.
- Flexibility: Chemiluminescence can produce an array of colors based on the chemical substances that are involved in the reaction. This allows it to be adapted to various uses.
- Durability: Chemically active materials can provide light for a longer time without the need for an external source of power. This makes them ideal for emergency lighting as well as outdoor activities.
- Simple: Chemiluminescent light sources are typically simple and easy to use, which makes them suitable for a broad array of uses.
Limitations of Chemiluminescence:
- Chemical Waste: A few chemiluminescent reactions may produce waste chemicals that can cause problems with environmental impact and disposal.
- Applications Limited: Chemiluminescence is primarily employed for applications that require short periods of light emission like glow sticks, and is not suitable for continuous light emission.
Benefits of Bioluminescence:
- Eco-friendly: Bioluminescence is an ecologically friendly light source because it doesn’t produce heat and does not rely on electricity. It consumes a low amount of energy.
- Natural Adaptations: Bioluminescence has evolved in many organisms to fulfill specific ecological reasons and is a fascinating research topic for understanding natural adaptations.
- Science Research: Organisms and bioluminescent markers are essential in scientific research to visualize and investigate biological processes and dynamic processes in real-time.
- Marine exploration: Biologyluminescence can be described as an essential element of the deep-sea marine environment and its research has led to a myriad of discoveries of new species as well as insights into the ocean ecosystem.
Limitations of Bioluminescence:
- Limited Color Spectrum: Bioluminescence often produces the same colors but with a smaller range in comparison to chemiluminescence, due to its specific substrates, enzymes, and proteins that are used.
- The complexity: In research and biotechnology working with bioluminescent living organisms and markers may be more complicated and require special equipment and experience.
- Limited to Live Organisms: Bioluminescence is only available to living organisms and is not suitable for artificial lighting systems or applications that do not employ living organisms.
Both bioluminescence and chemiluminescence have distinct advantages and drawbacks, which makes them suitable for various scenarios and situations. Chemiluminescence is typically utilized to create artificial lighting, security, and versatility, whereas bioluminescence is mostly found in nature and has applications in research and green lighting.
Understanding the Science
The science that underlies bioluminescence and chemiluminescence requires studying the biological and chemical processes that result in an emission of light. Here’s a quick overview of the fundamental scientific concepts of both of these phenomena:
Chemiluminescence:
- Chemical Reaction: Chemiluminescence can be triggered by a chemical reaction. Chemical compounds that are specific to a particular chemical, commonly called chemiluminescent substrates are involved during this chemical reaction.
- Energy Levels: Chemiluminescent process electrons within the molecules are stimulated to higher levels of energy. When the exuberant electrons go back to the original state and release energy, it is through light particles (light).
- Color Variability: the specific hue of light emitted depends on the characteristics that the chemical chemistry substrate that is involved. Different chemicals produce different colors that can be helpful in many applications.
- Security: Chemiluminescence is considered safe since it doesn’t produce heat. This property makes it ideal for applications where heat might be a safety risk.
- applications: Chemiluminescence is utilized in a variety of applications, such as glowing sticks, glow lamps, tests in research and scientific studies, as well as various artificial lighting systems.
Bioluminescence:
- Biochemical Process: It is an innate biological phenomenon that is only found in certain species, mostly within animals. It requires specialized enzymes like luciferases, with a molecule that emits light known as luciferin, oxygen along other cofactors.
- Enzymatic Reaction: The heart of the bioluminescent process is an enzyme reaction. Luciferases are enzymes that catalyze the oxidation process of luciferin. This produces electrons in the form of light particles (light).
- Ecological Functions: Bioluminescence in nature plays diverse ecological purposes, such as attracting partners, deterring predators, the lure of prey, camouflaging, and even intraspecific communication. Different organisms have developed bioluminescence to serve specific functions.
- Color Variability: the color and intensity of light that is emitted by bioluminescence may be different, but it is typically controlled by the particular enzymes or substrates utilized by organisms.
- Science Research: It is frequently utilized in research conducted by scientists to aid in investigating and analyzing biological processes. Bioluminescent markers help observe cellular activity as well as gene expression and much more.
- Environmental Conservation: The bioluminescent species are essential in ecological research and efforts to conserve marine ecosystems since their behavior and presence could provide indicators for the condition of ecosystems that are dominated by water.
The science of chemiluminescence as well as bioluminescence is a matter of understanding the biological and chemical processes that are involved, as well as their practical application as well and their ecological importance. Both are the subject of research and awe in a variety of fields.
Importance in Research
Bioluminescence as well as chemiluminescence are crucial to research in various fields of science. This is how they can be useful in research:
Chemiluminescence in Research:
- Molecular and Cellular Biology: Chemiluminescence-based assays are commonly used in molecular and cellular biology to detect and quantify specific biomolecules like proteins, nucleic acids, and enzymes. They are crucial instruments in methods such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent tests (ELISAs), Western blotting, and assays for reporter genes.
- The HTML0 format is used for drug Discovery: Chemiluminescent assays are utilized in high-throughput screens (HTS) to discover new drugs that allow researchers to evaluate the effects of chemicals in biologically relevant targets. This is essential in identifying potential drugs that could be candidates for development.
- Environmental Monitoring: Chemiluminescence can be used in environmental monitoring, specifically in the field of analytical chemistry and environmental science to identify and measure small amounts of pollutants toxicants, and analytes found in the air, water, and soil.
- imaging: Chemiluminescence imaging is an important tool for biomedical and biological research. It lets researchers see and observe the location of particular molecules, like tumor markers for cancer research or the expression of genes in developmental biology.
Bioluminescence in Research:
- Molecular as well as Cellular Biology: Bioluminescent markers, typically taken from the genetics of organisms that produce bioluminescence are extensively utilized in cellular and molecular biology research. They permit the visualization and analysis of protein expression, gene expression localization, and cellular functions in real-time.
- Ecology as well as Marine Biology: Bioluminescent organisms that live in marine ecosystems act as indicators of environmental health as well as ecological interactions. The study of bioluminescence can help scientists learn about predator-prey relationships and species behavior, as well as adapting to extreme environments.
- Deep-Sea Exploration: Bioluminescence is a key element when it comes to deep-sea research. It assists in the identification of the existence of novel species as well as the study of biodiversity in deep seas, and understanding the organisms’ adaptations to extreme environments.
- Conservation: Monitoring the numbers and behavior of bioluminescent species is essential in conservation efforts in the marine environment. The patterns of bioluminescence could be a sign of the effects of disturbances to our environment.
- Neuroscience: The bioluminescent marker can be utilized as part of neuroscience research to investigate neural activity and the role of neurons in living organisms. They shed the light on brain functions.
- Biosensors: Recent advances in the field of bioluminescence have led to the development of bioluminescent sensors. They can identify certain molecules or conditions within living organisms, which makes them useful in fields such as health as well as environmental surveillance.
Bioluminescence and chemiluminescence are an array of powerful tools for researchers working in a wide range of areas, allowing them to examine biological processes, interactions with nature, or environmental variables with superior accuracy and sensitivity. Their non-invasiveness and capability to offer real-time information make these instruments invaluable in the advancement of research and answering a variety of research issues.
Conclusion
Bioluminescence and Chemiluminescence can be fascinating and natural phenomena that have significant applications in research and practical application. Chemiluminescence is the emission of light through chemical reactions, while bioluminescence can be described as an exclusive biological process that is only found in certain species of organisms.
Understanding the distinctions in science, technology, and applications to these phenomena is crucial in a myriad of fields, ranging from molecular biology and environmental science to marine conservation and technology. Bioluminescence and chemiluminescence both continue to spur research, invention, and a greater appreciation of the world around us.