Gynecomastia and chest fat are two distinct issues affecting the appearance of the chest. Gynecomastia involves the enlargement of glandular breast tissue, often due to hormonal imbalances, while chest fat is the accumulation of excess fat in the chest area, typically linked to lifestyle factors.
In this overview, we’ll explore the key differences between these conditions, their causes, and potential solutions, helping individuals better understand and address these concerns.
Brief overview of gynecomastia
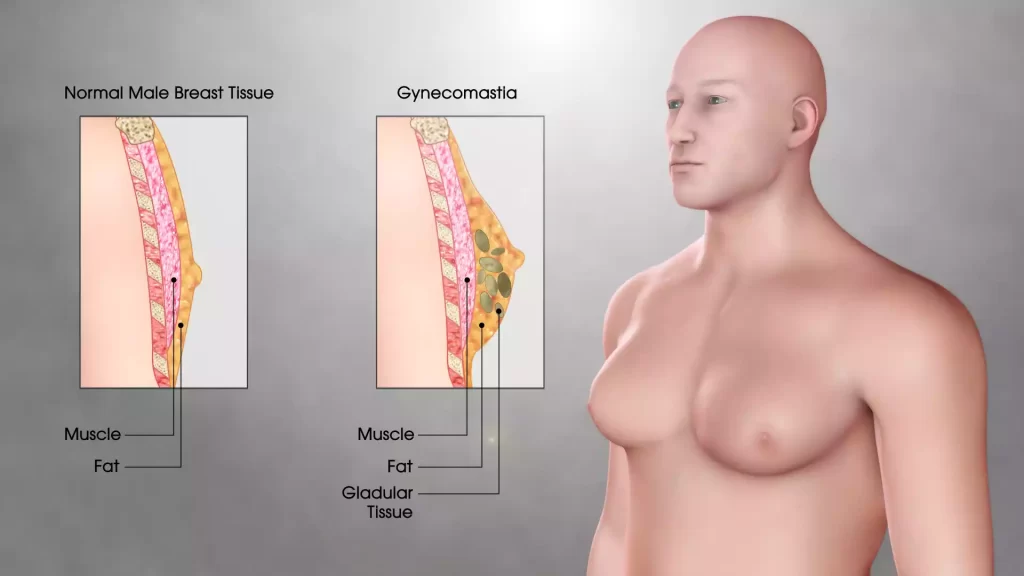
Gynecomastia refers to a medical condition that causes males to develop enlarged breast tissue. This is due to an imbalance of hormones. Typically, there is an increase in estrogen in relation to testosterone.
This imbalance may be caused by puberty or hormonal fluctuations as well as certain medical conditions. The breast tissue under the nipples is often firm, tender, and painful. The condition can affect people of any age, including adolescents and older adults.
The diagnosis involves a physical exam, imaging tests such as mammography or ultrasound, and blood tests in order to determine the cause. Treatment options can include non-surgical (observation and medication) or surgical interventions (liposuction, mastectomy), depending on the severity and the underlying cause.
Definition and Causes
Definition Gynecomastia, or breast-like breasts in men, is a medical condition that results from the enlargement of glandular breast tissue. The term is derived by combining the Greek words “gyne”, meaning woman, and “masters”, meaning breast. It refers to the physical changes.
Causes The main cause of gynecomastia, is an imbalance between sex hormones. This includes an increase in estrogen relative to testosterone.
- Puberty: Gynecomastia occurs frequently during puberty, when hormone levels fluctuate. It usually resolves itself as hormone levels stabilize.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: An imbalance in hormone levels caused by aging, certain medical conditions, or natural fluctuations may lead to gynecomastia.
- Medication: Certain medications, such as antipsychotics anti-androgens, and anabolic steroids, can cause gynecomastia by disrupting hormone balance.
- Medical Conditions: Medical conditions such as liver disease, kidney diseases, or tumors that affect hormone production and metabolism can cause gynecomastia.
- Substance Abuse: Drugs and substances such as marijuana, alcohol, and certain illegal drugs may increase the risk of developing gynecomastia.
- Genetics: A genetic predisposition can make certain individuals more susceptible to gynecomastia.
A Brief overview of chest fat
Chest Fat is the accumulation of excess fat tissue in the chest region. Chest fat is not a gynecomastia. This condition is usually caused by lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and genetics.
Chest fat can affect men and women. It is more common among individuals with higher body fat percentages. As there is no specific test for chest fat, the diagnosis relies primarily on physical examination and visual appearance.

The management and prevention of excess chest fat usually involves lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and a combination of aerobic and strength-training exercises. In some cases, cosmetic procedures such as liposuction are also considered.
Definition and Causes
Definition: Chest Fat is the accumulation of excess fat tissue in the chest region. Chest fat, unlike gynecomastia which is the accumulation of glandular breast tissue in the chest, is made up primarily of fat cells. This can cause a flabby or soft appearance to the chest, but it does not include the development of breastlike structures.
Causes: The main causes of chest fat include lifestyle factors and genetics.
- Diet: Unhealthy fats and calories can cause fat to accumulate in the chest.
- Lack Of Exercise: Sedentary living and inadequate physical activity can lead to increased body fat including chest fat.
- Genes: Genetics can affect the distribution of body fat, making certain individuals more likely to store excess fat around the chest.
- Hormonal factors: Although less significant than gynecomastia in terms of fat distribution, hormonal imbalances caused by stress or medical conditions may have an impact.
Gynecomastia and Chest Fat in the comparison chart
Here is a comparison chart highlighting the key differences between gynecomastia and chest fat:
| Aspect | Gynecomastia | Chest Fat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enlargement of glandular breast tissue in males. | Accumulation of excess fat in the chest area. |
| Causes | Hormonal imbalances, medications, and medical conditions. | Lifestyle factors (diet, exercise), genetics. |
| Symptoms | Breast tissue enlargement, and tenderness. | Excess fat in the chest area; no glandular tissue. |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, imaging (ultrasound, mammogram), blood tests. | Diagnosis is primarily based on appearance; no specific tests. |
| Prevalence | Affects individuals of all ages, more common in adolescents and older adults. | Individuals with higher body fat percentages tend to display these characteristics more often. |
| Treatment Options | Non-surgical (monitoring, medication) and surgical (liposuction, mastectomy). | Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise), cosmetic procedures (liposuction). |
| Psychological Impact | Can lead to body image issues and reduced self-esteem. | The impact varies based on individual perception; may affect self-esteem. |
| Prevention | Limited prevention due to hormonal and medical causes. | Preventable through lifestyle changes (diet, exercise). |
This chart provides a concise overview of the primary distinctions between gynecomastia and chest fat, helping individuals understand their differences and potential implications.
Explanation of the importance of discussing this topic
The importance of discussing gynecomastia (chest fat) and gynecomastia
There are several reasons why it is important to discuss gynecomastia.
- Health Awareness: By understanding the difference between gynecomastia, and chest fat, you can promote health awareness. People who notice changes in the appearance of their chest can determine if their concerns are primarily due to a medical condition, such as gynecomastia, or lifestyle factors. Early detection of health problems can be achieved by being aware.
- Mental Health: Gynecomastia as well as chest fat can cause significant emotional and psychological effects. When individuals are unhappy with the appearance of their chest, they may experience body image issues and low self-esteem. Discussions about these topics can reduce stigma, encourage individuals to seek help and solutions, and improve mental health.
- Proper Diagnosis: It is important to distinguish between gynecomastia (male breast tissue) and chest fat for an accurate diagnosis and the appropriate treatment. A misdiagnosis may lead to unnecessary or ineffective interventions that can cause physical or emotional stress. By educating individuals about the diagnostic process, they can make better-informed choices.
- Treatment options: Understanding the causes of chest problems is crucial to choosing the best treatment. Gynecomastia can be treated with medical procedures or surgery, but chest fat is often reduced by lifestyle changes. By discussing treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions tailored to their needs.
- Prevention: By becoming aware of the factors that contribute to chest fat, individuals can adopt healthier lifestyles. Improved diets and regular exercise are lifestyle changes that can prevent chest fat and promote health. Preventing future health problems is essential.
- Reducing stigma: Discussing gynecomastia or chest fat openly reduces the stigma that is associated with this issue. Many suffer in silence out of embarrassment, or for fear of judgment. We can foster a supportive and empathetic atmosphere by normalizing the discussion.
Summary: It is important to discuss gynecomastia, chest fat, and other concerns in order to improve individual health and mental well-being. This includes proper diagnosis, treatment options, prevention, and the reduction of stigma. We can empower people to be in control of their own health by addressing this topic openly and with information.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Diagnosis and Symptoms of Gynecomastia :
Symptoms:
- Breast Enlargement: The main symptom of gynecomastia in men is an increase in glandular breast tissue. It can affect either one breast or both, and the size may vary.
- Tenderness: Gynecomastia is sometimes accompanied by tenderness in the breast tissue. This can be uncomfortable.
Diagnosis:
- Physical Exam: The healthcare provider will perform a physical exam to determine the size, shape, and consistency of breast tissue. They may also rule out any other conditions that could mimic gynecomastia.
- Medical history: Your medical provider will request information on your past health history. This includes medications, supplements, and underlying conditions.
- Blood Testing: Blood testing may be ordered in order to determine hormonal imbalances, such as testosterone and estrogen.
- Imaging Tests: Some imaging tests, such as mammography or ultrasound, may be recommended in order to determine the condition of the breast tissue.
Diagnosis and Symptoms of Chest Fat :
Symptoms:
- Excess fat: Chest adipose is the accumulation of excessive adipose tissues in the chest region, which results in a flabby or soft appearance.
- Lack of Breast Tissue: Because there is no glandular breast tissue in chest fat, it does not have breast-like features.
Diagnosis:
- Visual Exam: The diagnosis of chest fat is primarily based on visual assessment, either by a healthcare professional or by self-examination. It is usually obvious if there is excess fat in the chest region.
- Physical Exam: The healthcare provider can conduct a physical exam to determine the distribution of body fat, and rule out any other conditions.
- Lifestyle Assessment: Medical professionals can ask about diet, exercise habits, and overall health to determine the possible causes of chest fat.
- Body fat measurement: Techniques such as skinfold thickness measurements and body composition analyses can be used to determine the percentage of body fat or assess chest fat levels.
It is important to understand that gynecomastia has distinct symptoms, and the diagnostic approaches for both conditions are different. Gynecomastia is characterized by the development of glandular breast tissues and requires a comprehensive assessment of hormonal imbalances.
Chest fat, on the other hand, is characterized by excess fat and lifestyle factors. It is important to make an accurate diagnosis in order to determine the best treatment strategy.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Gynecomastia Prevalence and Risk factors:
Prevalence:
- Adolescents: Gynecomastia affects up to 70% of boys during puberty. It usually resolves by itself within a few weeks to a couple of years.
- Older adults: This condition is also common in older male adults, and the prevalence ranges from 24% to 65%. It’s often associated with hormonal changes that occur with age.
Risk Factors:
- Hormonal imbalances: The main risk factor for gynecomastia, is an imbalance in hormones. This includes an increase of estrogen relative to testosterone. This imbalance may occur during puberty or as a result of medical conditions, medication, or substance abuse.
- Medication: Certain medications such as anabolic steroids and antidepressants can increase your risk of developing gynecomastia.
- Medical Conditions: Underlying conditions such as liver disease, kidney diseases, or tumors that affect hormone production or metabolism are risk factors.
- Substance Abuse: The abuse of substances such as marijuana, alcohol, and certain illegal drugs may disrupt hormonal balance and increase your risk of developing gynecomastia.
Chest fat prevalence and risk factors:
Prevalence:
- Overweight or Obesity: Chest Fat is more common in overweight and obese individuals since excess body fat tends to accumulate throughout the entire body, including chest fat.
- Variations by gender: Although chest fat affects both men and women, its prevalence can vary due to hormonal influences and variations in body fat distribution.
Risk Factors:
- Diet: A high-calorie diet that is rich in unhealthy fats and sweets can lead to an increase in body fat, including the accumulation of chest fat.
- Lack Of Exercise: An inactive lifestyle and insufficient physical activity may lead to an increase in body fat including chest fat.
- Genes: Genetics can play a part in determining the location of fat storage, making some people more susceptible to chest fat.
- Factors affecting fat distribution: Stress and medical conditions, while not the main cause of abdominal fat, can affect fat distribution.
It is important to understand that gynecomastia has a different risk factor and prevalence pattern than chest fat. Gynecomastia primarily results from hormonal imbalances, while chest fat is closely related to lifestyle factors and body fat levels.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for gynecomastia :
- Observation & Monitoring: A healthcare provider might recommend waiting and watching in cases of mild gynecomastia. This is especially true during puberty. Gynecomastia usually resolves itself within a year or two.
- Medications:
- Hormone Treatment: Medicines such as tamoxifen and raloxifene can be prescribed to balance hormone levels, reduce breast tissue growth, or both.
- Aromatase-inhibitors: In certain cases, aromatase-inhibitors like anastrozole can be used to block estrogen conversion.
- Surgery:
- Liposuction: The procedure is performed to remove excessive fat in the chest, particularly when gynecomastia results from fatty tissue.
- Mastectomy: In severe cases, the surgical removal of glandular tissue from the breast (mastectomy), may be required. It’s usually done in conjunction with liposuction.
- Psychological counseling: Individuals suffering from gynecomastia can benefit from counseling to help them with any emotional or psychological issues related to their body image or self-esteem.
Treatment options for Chest Fat:
- Lifestyle changes:
- Diet modification: A balanced diet that includes a reduced intake of calories, healthy fats, and fiber can reduce overall body fat including chest fat.
- Regular Exercise: By engaging in regular strength and aerobic training, you can lose weight and burn calories.
- Cosmetic Procedures
- Liposuction: The procedure can be used for cosmetic reasons to remove excess chest fat. This is not a treatment to treat gynecomastia, but it can reduce chest fat.
- Consultation With a Healthcare Professional: When lifestyle changes are not working, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional or fitness professional to get personalized advice and recommendations.
The choice of treatment depends on a number of factors, including the severity of the condition and the individual’s preferences. Consultation with a medical professional or healthcare provider is crucial to determine the best treatment. Adopting a healthy diet and exercising regularly can also help prevent and manage chest fat.
Psychological and Emotional Impact
The Psychological and Emotional Effects of Gynecomastia :
The psychological and emotional effects of gynecomastia are significant.
- Body image issues: The presence of breast-like tissue can lead to concerns about body image and dissatisfaction with one’s appearance. It is possible that the presence of breast tissue can make people feel self-conscious and avoid doing activities such as swimming or changing clothes in public spaces.
- Lowered Self-Esteem: Many people with gynecomastia have low self-esteem. Due to embarrassment and inadequacy, they may withdraw from intimate relationships and social interactions.
- Depression & Anxiety: Gynecomastia may cause depression or anxiety symptoms. The emotional distress caused by the condition can have a negative impact on mental health.
- Social isolation: Some people isolate themselves from others to avoid judgment or scrutiny. This can exacerbate loneliness and feelings of isolation.
- Impact of Gynecomastia on Quality of Life: The condition can have a negative impact on many aspects of your life including your relationships, career prospects, and quality of life.
- Stigmatization: Due to a lack of awareness, gynecomastia can be stigmatized, or the subject of teasing, or derogatory remarks, further impacting an individual’s health.
The Psychological and Emotional Effects of Chest Fat:
Chest fat can have emotional effects, although not as severe as gynecomastia.
- Body image concerns: Chest fatty tissue can cause dissatisfaction and body image problems, particularly when people desire a more defined chest.
- Self-Esteem: Individuals with excess chest fat can experience a lower sense of self-esteem, especially when compared to social ideals and expectations.
- Avoidance behaviors: Similar in nature to gynecomastia (chest fat), individuals with chest fatty tissue may avoid certain activities and clothing choices so as to conceal their chest. This can limit their participation in social or physical activities.
- Social Impact: Chest Fat can affect social interactions and relationships. This could lead to anxiety or self-imposed restrictions in certain situations.
- Motivation to Change: Chest fat is a motivator for some people to adopt a healthier lifestyle through diet and physical activity to reduce their fat levels and to improve the appearance of their body.
Both gynecomastia and chest fat, have psychological and emotional components. It is important to address these aspects. Support from professionals in the medical field, counseling, and support groups are all beneficial to coping with concerns like these, as well as improving mental health. Open conversations about these topics can also help to reduce stigma and promote a more understanding and empathetic society.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes and prevention for gynecomastia :
It may not be possible to prevent gynecomastia, especially if it’s due to hormonal imbalances and medical conditions. There are lifestyle changes you can make to help reduce or manage the risk.
- Medication Reviews: Consult your healthcare provider if you have gynecomastia listed as a possible side effect of a medication. You may also want to consider alternative medications or treatments.
- Substances: Avoiding or minimizing the use of substances that are known to increase the risks of gynecomastia such as alcohol, marijuana, and some illegal drugs.
- Healthy diet: Maintain a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, lean protein, and whole grains. Reduce the intake of high-calorie and high-fat food to help you manage your weight.
- Exercise Regularly: Participate in regular physical activities, including cardiovascular and strength training exercises. Exercise can maintain a healthy composition of the body and help reduce body fat.
Lifestyle changes and prevention of chest fat:
Lifestyle changes are the most effective way to reduce and prevent chest fat:
- Dietary changes: Adopting a balanced diet, which includes foods rich in nutrients and limits the consumption of processed foods, sweetened beverages, and excess calories. To promote weight loss, monitor portion sizes and maintain an overall calorie deficit.
- Regular Exercise: Include regular aerobic exercise (such as cycling, swimming, or running) and strength-training exercises (such as weightlifting) in your fitness routine. These activities burn calories, promote fat loss, and build muscle.
- Strength Exercises: By strengthening the chest muscles, you can tone up the area and reduce the appearance of chest fat.
- Cardiovascular Exercise: Increase calorie expenditure by engaging in cardiovascular exercises to promote fat loss.
- Stress management: High levels of stress can lead to weight gain or fat accumulation. Include stress-reduction methods like mindfulness, meditation, and yoga in your daily routine.
- Adequate sleep: Make sure you sleep well, as a lack of sleep can affect hormones that are related to your appetite and fat storage.
- Hydration: Keep hydrated, as dehydration affects metabolism and energy levels.
Note that spot reduction, which targets fat loss in certain areas such as the chest, is not effective. As a result, fat loss is experienced throughout the entire body. Adopting a holistic approach to lifestyle change, including diet, exercise, and other factors, is crucial to maintaining your overall health and managing chest fat.
Consult your healthcare provider or a fitness professional before beginning any new exercise or diet program, particularly if you suffer from underlying medical conditions.
Conclusion
For individuals who are concerned about the appearance of their chest, it is important to understand the difference between gynecomastia (enlarged glandular breast tissue) and chest fat.
Gynecomastia is a condition that involves enlargement of the glandular breast tissue and requires medical treatment. Chest fat, however, is a result of lifestyle factors. It can be treated through diet and physical activity.
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments available for these conditions allows individuals to make informed decisions for their mental and physical well-being.
Take proactive steps to improve your health and confidence, whether you’re seeking medical advice to treat gynecomastia, or adopting healthier habits to reduce chest fat.