Have you ever wondered about the various chemical reactions that occur around us every day? Chemical reactions are fascinating processes that involve the transformation of substances into new forms. Two types of reactions that are commonly encountered are metathesis and redox reactions. We will explore the differences between these two types of reactions in a simple and easy-to-understand manner.
Definition of Metathesis and Redox Reactions
Metathesis Reactions: Metathesis reactions, also known as double displacement reactions, involve the exchange of ions or compounds between two reactants. In simpler terms, it’s like a swapping game where the partners exchange places. The reaction occurs when the cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions) of the reactants switch positions, forming new compounds.
The reaction between sodium chloride (NaCl) and silver nitrate (AgNO3) forms sodium nitrate (NaNO3) and silver chloride (AgCl). In this case, the sodium ion (Na+) from sodium chloride combines with the nitrate ion (NO3-) from silver nitrate to form sodium nitrate, while the silver ion (Ag+) from silver nitrate combines with the chloride ion (Cl-) from sodium chloride to create silver chloride.
Metathesis reactions can also occur between compounds that are already dissolved in water. This type of reaction is commonly referred to as a precipitation reaction because one of the products formed is usually an insoluble solid (precipitate) that settles out of the solution.
Redox Reactions: Redox reactions, short for reduction-oxidation reactions, are all about the transfer of electrons between different chemical species. These reactions involve both a reduction process, where a species gains electrons, and an oxidation process, where a species loses electrons. This transfer of electrons is what drives the reaction and leads to the formation of new substances.
One of the most familiar examples of a redox reaction is the rusting of iron. When iron is exposed to oxygen and moisture, it undergoes oxidation, forming iron(III) oxide, commonly known as rust. In this process, the iron atoms lose electrons, while the oxygen molecules gain them.
Another classic example of a redox reaction is the combustion of a fuel, such as gasoline or wood. The fuel combines with oxygen, releasing energy in the form of heat and light. The fuel is oxidized, losing electrons, while oxygen is reduced, gaining those electrons.
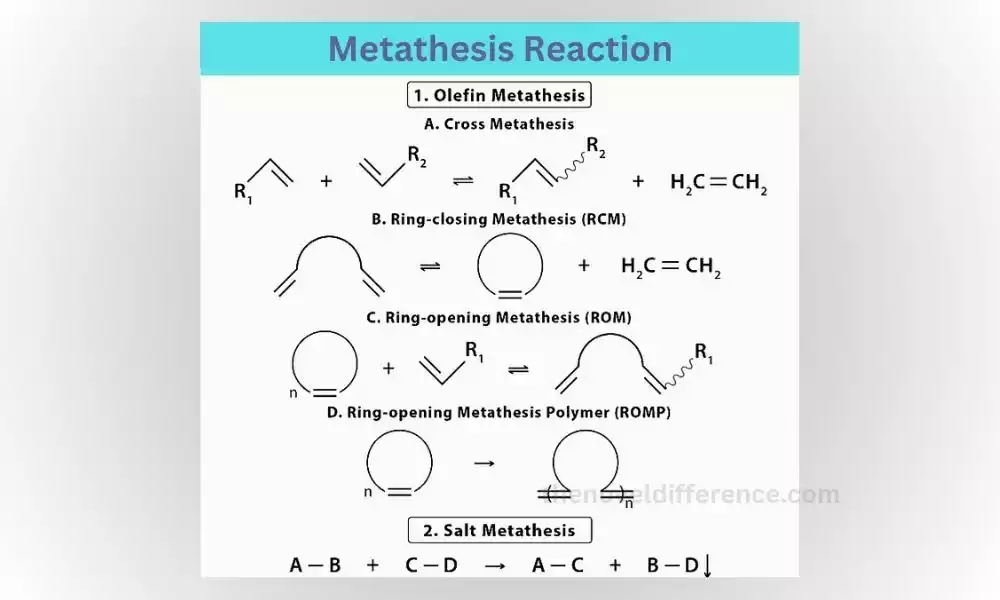
What is Metathesis Reaction?
Metathesis reactions, also known as double replacement reactions, occur when the positive and negative ions of two compounds exchange places with each other. This exchange of ions leads to the formation of two new compounds. A common example of a metathesis reaction is when two ionic compounds dissolve in water and the positive and negative ions swap partners.
Step-by-Step Explanation of a Metathesis Reaction:
1. Identify the reactants: You start with two compounds, each consisting of positive and negative ions.
2. Exchange of partners: The positive ion from one compound combines with the negative ion from the other compound, and vice versa.
3. Formulation of products: The result of this exchange is the formation of two new compounds, with the positive and negative ions now paired differently.
Let’s consider the reaction between silver nitrate (AgNO3) and sodium chloride (NaCl). The silver ion (Ag+) from silver nitrate combines with the chloride ion (Cl-) from sodium chloride, while the sodium ion (Na+) from sodium chloride pairs with the nitrate ion (NO3-) from silver nitrate. As a result, silver chloride (AgCl) and sodium nitrate (NaNO3) are formed.
Chemical Equations and Reaction Mechanisms
Have you ever wondered how chemicals react with each other to create amazing transformations? Well, it’s all thanks to chemical equations and reaction mechanisms. These magical tools help chemists understand and describe the complex dance of atoms and molecules in a way that even non-scientists can appreciate. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of chemical reactions together!
Chemical equations are like recipes for chemical reactions. They show us the ingredients (reactants) on the left side and the products on the right side. For example, the equation “2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O” represents the reaction between hydrogen gas and oxygen gas to produce water. See, it’s like a simple math equation, but with atoms and molecules instead of numbers.
Now, let’s talk about reaction mechanisms. Imagine you’re watching a movie. You see a hero fighting off villains, performing daring stunts, and saving the day. In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is like that behind-the-scenes footage that shows how the hero accomplishes all those amazing feats.
Reaction mechanisms reveal the step-by-step process of how a chemical reaction occurs. It’s like unraveling the mystery behind the magic trick. For example, in the combustion of methane (CH₄), the mechanism involves four steps: initiation, propagation, branching, and termination. Each step involves the breaking and forming of chemical bonds, and together, they transform methane and oxygen into carbon dioxide and water.
Understanding chemical equations and reaction mechanisms is crucial because they help us predict and control chemical reactions. They allow chemists to design new drugs, develop sustainable energy sources, and create materials with amazing properties. It’s like having the power to unlock the secrets of the universe on a molecular level!
So, next time you come across a chemical equation, don’t be intimidated. Remember that it’s just a simple way of representing the magical transformations happening at the atomic and molecular levels. And when you dig deeper into the reaction mechanism, you’ll discover the intricate steps that make it all happen.
Chemistry may seem like wizardry, but with chemical equations and reaction mechanisms as our spellbooks, we can unlock the mysteries and create wonders. So, let’s embrace the magic of chemistry and explore the incredible world of reactions together!
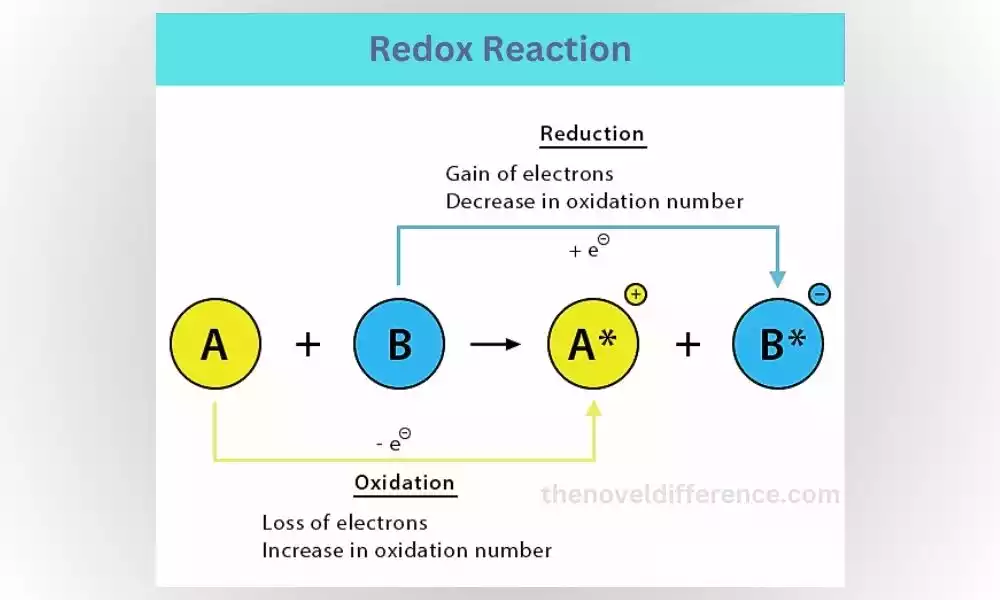
What is a Redox Reaction?
Redox reactions, short for reduction-oxidation reactions, involve the transfer of electrons between different reactants. One reactant is oxidized, meaning it loses electrons, while the other reactant is reduced, gaining those electrons. These reactions are crucial for various biological processes and are responsible for energy production in our bodies.
Step-by-Step Explanation of a Redox Reaction:
1. Identify the reactants: A redox reaction involves two reactants, one that gets oxidized and another that gets reduced.
2. Electron transfer: Electrons are transferred from the oxidized reactant to the reduced reactant.
3. Formation of products: As electrons are transferred, new compounds are formed.
To illustrate, let’s consider the reaction between iron (Fe) and oxygen (O2) to form iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3). In this reaction, iron loses electrons, while oxygen gains those electrons. The iron atoms are oxidized from a neutral state (Fe) to a positively charged state (Fe3+), while the oxygen molecules are reduced from a neutral state (O2) to negatively charged ions (O2-). As a result, iron(III) oxide is formed.
The Difference Between Metathesis and Redox Reactions
Now that we understand the basic concepts behind metathesis and redox reactions.
Let’s highlight their key differences:
1. Exchange of ions vs. electron transfer: Metathesis reactions involve the exchange of positive and negative ions between reactants, while redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons.
2. Changes in oxidation state: Metathesis reactions do not result in changes in oxidation state, as the ions merely exchange partners. On the other hand, redox reactions involve changes in the oxidation state of the reactants.
3. Formation of new compounds: Metathesis reactions lead to the formation of two new compounds, whereas redox reactions result in the formation of compounds through the transfer of electrons.
Understanding the Nature of Reactants and Products in Chemistry
I want to talk to you about the fascinating world of chemistry and specifically dive into the nature of reactants and products in chemical reactions. Don’t worry, I’ll keep things simple and easy to understand!
Chemical reactions are like a magical dance between different substances. You have the reactants, which are the ingredients that come together, and the products, which are the new substances formed as a result. Let’s explore their nature and how they differ.
When it comes to reactants, two types take the spotlight: ionic compounds or ions. These can be things like sodium chloride (table salt) or potassium hydroxide (caustic soda). They are like puzzle pieces, each with its unique charge. When they mix, they can exchange partners and form new compounds through a process called metathesis reaction. It’s like couples switching partners at a dance, resulting in new pairs being formed.
The reactants are elements or compounds that undergo oxidation or reduction. You might have heard of oxidation in rusting metal, right? Well, in redox reactions, it’s all about the transfer of electrons between substances. Imagine it as a game of electron hot potato! Some substances lose electrons (oxidation) while others gain them (reduction), resulting in a change in their chemical makeup.
Now, let’s move on to the products. The products are new compounds that are formed when the reactants exchange ions. This can lead to the formation of precipitates (solid particles), gases, or even neutral compounds. It’s like a chemical recipe where the reactants mix and a brand-new dish is created!
The products are also new compounds, but their formation is driven by the transfer of electrons. The reactants that underwent oxidation and reduction give birth to fresh substances with different properties. It’s like a transformative makeover!
Understanding the nature of reactants and products is crucial in chemistry. It allows us to predict and explain the outcome of various reactions, making it like solving puzzles and uncovering the secrets of matter.
So, whether it’s the intricate dance of ions in metathesis reactions or the electron shuffle of redox reactions, chemistry never ceases to amaze. The next time you witness a chemical reaction, take a moment to appreciate the fascinating nature of the reactants and the incredible products they create.
Conclusion
Chemical reactions are vital to understanding the world around us, and two important types of reactions are metathesis and redox reactions. Metathesis reactions involve the exchange of positive and negative ions between compounds, while redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons. In metathesis reactions, two compounds swap partners, forming two new compounds. In redox reactions, one reactant gets oxidized by losing electrons, while the other gets reduced by gaining those electrons.
Understanding the differences between metathesis and redox reactions can help us grasp the fundamental principles of chemistry. Metathesis reactions are all about ion swapping, whereas redox reactions focus on electron transfer. Both types of reactions play important roles in various chemical processes, ranging from everyday occurrences to biological functions.
