Definition and significance of heart attack and gastric pain
Definition and Significance of Heart Attack:
- Definition:
- An attack on the heart, medically referred to as a myocardial injury (MI) is a condition that occurs in the event of a sudden cut or reduction in the flow of blood to a part that is part of the muscle. It usually occurs due to obstruction by one or more coronary blood vessels which provide oxygen and nutrition to the heart.
- Significance:
- Heart attacks are a medical emergency and the leading cause of death across the globe.
- They can cause serious injury to heart muscles, impacting their ability to efficiently pump blood.
- Medical attention immediately is crucial to prevent injuries and save lives.
- Rapid treatment, which includes the use of medicines or medical procedures, can assist in enhancing outcomes and reducing the likelihood of developing future heart issues.
Definition and Significance of Gastric Pain:
- Definition:
- gastric pain also referred to as abdominal pain, is a sign of discomfort or pain that occurs in the region between the chest and pelvis, the area where the stomach as well as other organs of the abdomen are located. It may be caused by a variety of causes, such as digestive issues or inflammation, infections, or other medical issues.
- Significance:
- Gastric pain may vary in intensity and could be a sign of other health issues, like gastritis, peptic ulcers gastroesophageal reflux disorder (GERD) or IBS, or irritable bowel syndrome. (IBS).
- It could significantly affect the well-being and everyday activities.
- While gastric discomfort is typically not life-threatening, chronic or extreme abdominal pain must be assessed by a healthcare specialist to rule out the possibility of serious issues.
- A proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial to ease discomfort and treat the underlying cause.
A heart attack can be an emergency that is caused by a blockage of the flow of blood to the heart. In addition, gastric pain is an abdominal discomfort that can arise from many abdominal and digestive problems. Both have major medical consequences and require prompt assessment and treatment by medical professionals.
What is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack also known as a myocardial injury (MI) is a life-threatening and serious medical condition that develops when there is an abrupt cut or a decrease in blood flow to a particular part that is part of the muscle. It usually occurs because of the blockage of some or all coronary vessels that are responsible for providing an oxygen-rich bloodstream into the heart.
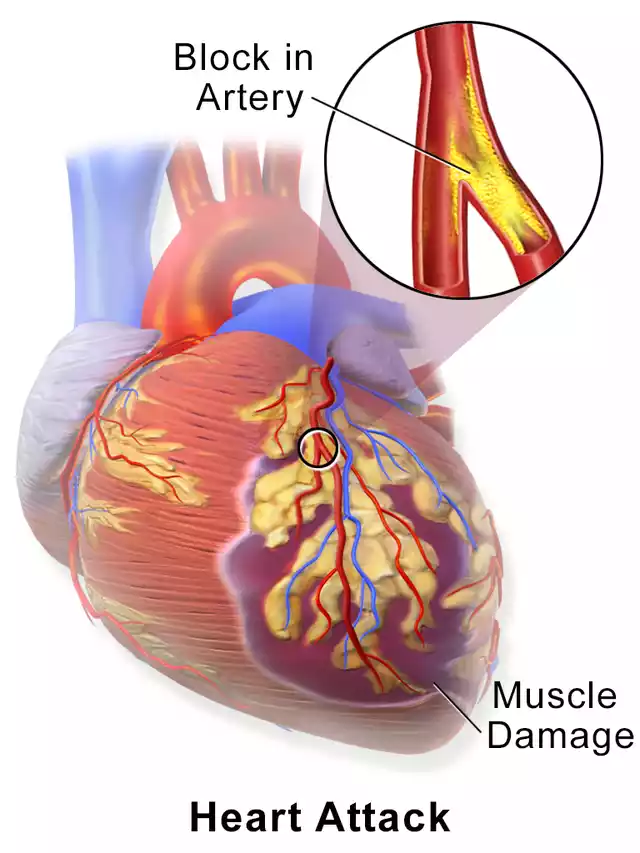
Here’s a fuller detail of the events that occur in a heart attack:
- coronary artery blockage: The majority of heart attacks occur when the coronary artery, which is the one that delivers an oxygenated flow of blood towards the heart muscle gets blocked or narrowed due to the accumulation of fat deposits known as plaque. It could be the result of atherosclerosis, which is a condition in which the walls of the arterial get thicker and less flexible.
- Ischemia: Blockage to the coronary blood vessel results in decreased blood flow to the heart muscle, which causes ischemia. Ischemia refers to a shortage of oxygen or nutrients circulating in the tissue of the heart.
- Cell Loss and Damage: When the heart muscle isn’t getting sufficient oxygen and nutrients over long periods, the affected heart muscle cells begin to become damaged, and eventually cease to function and die. This is the cause of the signs of a heart attack.
- Symptoms: The most common signs of a heart attack comprise:
- The discomfort or pain in the chest is usually described as a squeezing or crushing sensation.
- The pain could radiate into the left arm, neck, jaw, or back, and even the stomach.
- A shortness of breath.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- A feeling of fainting or lightheadedness.
- Diagnose: Doctors use various diagnostic tests to identify the presence of a heart attack. These tests include electrocardiograms (ECGs or EKGs) to determine the electrical activity of the heart blood tests to determine specific cardiac enzymes that are released if heart cells are damaged, and imaging tests such as angiography to see the coronary arteries.
- Treatment: The primary goal of the treatment of an attack on the heart is to bring blood flow back to the affected region of the heart, as fast as it is. The treatment options include:
- Drugs, such as antiplatelet drugs or clot-busting medications dissolve or stop blood clots.
- Stent and angioplasty placement to allow the arteries to be opened.
- Coronary bypass grafting (CABG) surgery is performed in some instances.
The need for prompt medical attention is vital in the case of an attack on the heart, to limit the injuries to your heart and increase the odds of a successful recovery. Lifestyle changes and long-term treatment are generally recommended to lower the likelihood of future heart-related problems.
What is a Gastric Pain?
Gastric pain, sometimes called abdominal pain or stomach pain, is a feeling of discomfort or pain that occurs in the area between your chest and pelvis, which is where the stomach and organs of the abdomen are.
Gastric pain is a variable thing in intensity and duration as well as the exact place within the abdominal area. It is a sign, not a medical condition that can arise from many root causes.
Here are a few important aspects of gastric pain:
- Causes: Gastric discomfort can be caused by many different reasons, including:
- Problems with digestion, for example, gastric indigestion.
- Gastrointestinal disorders, such as gastroenteritis.
- Inflammatory disorders, for example, gastritis (inflammation of the stomach and the stomach lining) and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD).
- These are ulcers that develop on the stomach’s lining or the duodenum (the initial part of the small intestinal tract).
- Gastroesophageal reflux disorder (GERD) that occurs when stomach acid is reabsorbed into the esophagus.
- Irritable intestinal syndrome (IBS) is a chronic, functional condition of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Gallstones or colic biliary.
- Food intolerances or allergies.
- Symptoms: The symptoms of gastric discomfort may vary based on the cause, but usually are:
- The sensation of cramps or itchiness can be felt in the abdomen area.
- Feelings of burning or gnawing.
- Feelings of fullness and bloating.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Constipation or diarrhea.
- Changes in the bowel habits.
- It can be painful and appear and disappear or remain over time.
- Diagnosis: The diagnosis of gastric discomfort typically is based on a medical history and physical examination and could require further tests, including:
- Endoscopy is a procedure in which the flexible tube that houses cameras can be used to see the stomach’s interior and the upper digestive tract.
- Imaging studies, like abdominal ultrasounds or CT scans.
- Tests of blood to determine inflammation, infection, or other indicators.
- Treatment: The treatment for gastric pain is dependent on the root cause, and can consist of:
- Lifestyle changes, like diet changes and managing stress.
- Medicines that relieve discomfort or treat the root of the disease (e.g. anti-acids, drugs to treat inflammation, antibiotics, or medications).
- In some instances, surgery is required may be necessary, like the removal of gallstones, or the severe complications of ulcers.
- Evaluation’s importance: While gastric pain is usually not life-threatening, severe or persistent abdominal pain must be assessed by a medical professional to rule out any serious issues and ensure that appropriate treatment is taken.
Gastric pain is one of the symptoms that is associated with many abdominal and gastrointestinal disorders and their treatment is dependent on the exact reason. If you are experiencing frequent or severe gastric pain, then it is advised to seek medical attention to identify the root of the problem and get proper treatment.
Heart Attack and Gastric pain in the comparison chart
here is a comparison chart highlighting the key differences between a heart attack and gastric pain:
| Aspect | Heart Attack | Gastric Pain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sudden interruption of blood flow to a portion of the heart muscle due to blocked coronary arteries. | Discomfort or pain in the abdominal region, typically originating in the stomach or surrounding organs. |
| Location of Pain | Chest, often radiating to the left arm, jaw, neck, or back. | Abdominal area, generally in the stomach region. |
| Nature of Pain | Often described as a crushing, squeezing, or heavy sensation in the chest. | Can vary from aching or cramping to burning or gnawing sensations. |
| Radiation of Pain | Typically radiates to the left arm, jaw, neck, back, or shoulder blades. | Usually stays within the abdominal area, and may not radiate. |
| Associated Symptoms | Shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, lightheadedness, cold sweats. | Bloating, belching, changes in bowel habits, nausea, and vomiting. |
| Risk Factors | High blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, family history, age, diabetes, obesity. | Diet, stress, infections, inflammatory conditions, food allergies, and more. |
| Diagnosis Methods | Electrocardiogram (ECG), blood tests (troponin levels), imaging (angiography). | Medical history, physical examination, endoscopy, imaging (ultrasound, CT), and blood tests. |
| Treatment | Immediate interventions (e.g., clot-busting drugs), angioplasty, medications, cardiac procedures (stents). | Lifestyle modifications (diet, stress management), medications (antacids, antibiotics), surgery (in severe cases). |
| Life-Threatening | Yes, a heart attack is a medical emergency and can be life-threatening. | Generally not life-threatening, but severe abdominal pain should be evaluated. |
| Urgency of Treatment | Immediate medical attention is crucial for the best outcomes. | Seek medical evaluation if pain is persistent, severe, or associated with concerning symptoms. |
It’s essential to recognize the differences between these two conditions, as they require different approaches to diagnosis and treatment. Heart attacks are a medical emergency and demand swift action, while gastric pain, although uncomfortable, is typically not life-threatening but should still be assessed by a healthcare professional when severe or persistent.
Importance of understanding the differences between the two conditions
Understanding the distinctions between heart attacks as well as gastric pain is of vital importance for several reasons:
- Life-saving Knowledge: Knowing the distinctions between these two diseases can be the difference between life and death. Heart attacks are a health emergency that requires urgent intervention to prevent any damage done to your heart and to save the lives of people. Incorrect or delayed recognition of symptoms of a heart attack can result in the death of a patient.
- appropriate action: Understanding the differences allows individuals and other people to decide on the best course of action whenever someone is experiencing symptoms. If someone is experiencing an attack on their heart and is experiencing symptoms, they should seek urgent medical help immediately. If they are experiencing gastric discomfort an earlier intervention may be necessary however, a medical examination is necessary in the case of severe and persistent signs.
- Preventing unnecessary anxiety: Recognizing gastric pain as distinct from a heart attack may reduce anxiety and stress. A lot of people feel abdominal pain at any time in their lives, but not all of them are an indication of heart problems. Knowing the signs and symptoms of each illness can offer some peace of mind and lessen the anxiety.
- Quick Treatment: Distinguishing between two conditions guarantees that appropriate as well as timely treatments are provided. For heart attacks, there are specific treatments such as clot-busting medicines or cardiac procedures, whereas gastric pain can be controlled by taking medications, making dietary adjustments, or other treatments.
- Cutting down on Healthcare Costs: The avoidance of unnecessary visits to the emergency department for gastric pain could aid in reducing healthcare costs for both healthcare providers and individuals. Knowing when to seek medical care and when it’s not urgent will result in better utilization of healthcare services.
- Better Health Results: A timely diagnosis and accurate treatment for gastric pain and heart attacks result in healthier outcomes for health. Rapid intervention in the event of an attack will reduce the damage to heart muscles as well and early treatment of gastric pain could prevent complications and increase the quality of life.
- Educational and Preventive: Information about these diseases can help individuals adopt lifestyle changes that reduce the risk factors that can lead to coronary heart diseases (e.g. stopping smoking, ensuring the healthiest food regimen) and digestive problems (e.g. managing stress and diet adjustments) that can aid in preventing both conditions.
Understanding the distinctions between heart attacks and gastric pain is crucial for your well-being and that of those around you. It helps people react appropriately to emergencies to avoid stress and ensure that the appropriate treatments are implemented promptly. This information helps improve health outcomes, lower healthcare expenses, and better overall health.
Similarities Between Heart Attack and Gastric Pain
Although heart attacks (myocardial infarctions) and gastric pain are medical conditions that have distinct effects and causes There are some commonalities between the two. It is important to remember that these resemblances can confuse as some symptoms may be similar.
Here are a few similarities:
- Chest Discomfort: Both gastric pain and heart attacks may cause pain or discomfort in the chest. This is the most obvious similarity which can make it difficult to differentiate between them by merely observing this symptom.
- Nausea and vomiting: Both conditions can result in nausea or vomiting. Patients who suffer from either an attack on the heart or severe gastric pain can experience nausea and vomiting as a reaction to the pain.
- Radiotherapy of Pain: While pain from a heart attack generally extends down the left side of your body or neck, jaw, or back the pain of gastric ulcers can sometimes radiate to regions in the abdomen, upper or chest, and perhaps the lower back. This could further lead to confusion when diagnosing.
- Shortness of Breath: Heart attacks as well as extreme gastric pain may be linked to shortness of breath. If you suffer from an attack on the heart, the reduced circulation of blood to heart muscles may cause oxygen deprivation, which can cause breathlessness. Gastric pain can result in discomfort that can affect breathing patterns.
- Stress and anxiety: The sensation of experiencing severe discomfort or pain in the abdominal or chest area can trigger stress and anxiety in people. The emotional reaction can be identical to heart attacks as well as extreme gastric pain.
It’s crucial to stress that while there are some similarities, there are significant distinctions between the two types of conditions, as discussed earlier. These similarities emphasize the need for medical attention and evaluation by a doctor in the event of chest discomfort or abdominal pain that is severe. A precise diagnosis and the right treatment are crucial to ensure the proper condition is treated quickly.
When to Seek Medical Attention
The right time it is appropriate to get medical assistance is vital for heart attacks and extreme gastric discomfort.
Here are some guidelines on the best time to seek medical assistance for each condition:
Heart Attack:
- The chest is painful: If you or someone else suffers from severe chest pain or achy feeling that persists for more than a few minutes, or is absent take immediate medical attention. This is especially important when the pain is described as crushing, squeezing, or a hefty sensation.
- Pain radiating: If the chest pain extends to the left arm jaw neck, back, or shoulder blades It could be a sign of an attack on the heart. Seek medical help right away.
- Breath Shortness: Trouble breathing, in conjunction the chest pain could be an indication of a heart attack. If you are unable to breathe Do not delay and call emergency help.
- Other symptoms: Additional symptoms like nausea or vomiting, lightheadedness cold sweats, or a sense of imminent danger could be indicators of an attack on the heart. Be aware of these signs and dial 911 or your emergency number right away.
Severe Gastric Pain:
- Persistent Pain: If you suffer from chronic abdominal discomfort that fails to ease or get worse over time it is important to seek medical care. This is particularly important when the pain is severe uncontrollable, painful, or interferes with your everyday activities.
- The Associated symptoms: If your abdominal pain is followed by symptoms like vomiting, high fever blood, bloody stool extreme diarrhea, or symptoms that you are dehydrated (e.g. excessive thirst dry mouth, decreased urine output) It is recommended to seek medical attention immediately.
- Previous conditions: If you have an underlying history of digestive issues, including diverticulitis, peptic ulcers, or inflammatory bowel disease and you notice the symptoms are getting worse or a new, intense pain, you should consult a healthcare expert immediately.
- The changes that occur in your pain: If you notice that your abdominal pain is not similar to your normal gastrointestinal discomfort or if there’s a doubt about the reason it’s best to be on the safe side and get a medical examination.
- The signs of shock: Symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, breathing, and confusion as well as fainting can indicate an issue that needs immediate medical treatment.
If you aren’t sure if your symptoms are indicative of an attack on your heart or gastric pain, it’s better to seek medical assistance. A medical professional can conduct the required tests and assessments to identify the root of your symptoms and offer the appropriate treatment. Take note that quick action could be lifesaving in the event in the event of heart attacks. It will help avoid complications that are associated with severe abdominal pain.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between heart attacks and gastric discomfort is crucial to prompt and effective medical treatment. Being aware of the signs seeking medical attention promptly and recognizing the difference between the two conditions could help save lives, ease anxiety, and improve results for health.
