“BPH and Prostatitis are two common conditions affecting the prostate gland in men, often causing discomfort and impacting urinary and sexual health.
While they both involve the prostate, they differ significantly in their nature, causes, and treatment approaches. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. Let’s delve into the distinctive aspects of BPH and Prostatitis to shed light on their unique characteristics and implications for men’s health.”
What is BPH?
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) refers to a benign enlargement of the prostate gland. which is a gland that’s the size of walnuts in males, located below the bladder and around the urinary tract.
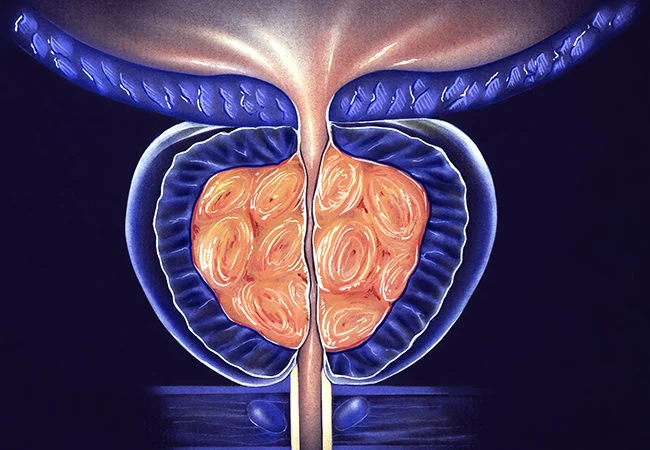
As people get older the prostate gland is prone to grow in size, which can lead to a compression of the urethra and subsequent urinary signs. BPH is a very common disease among older men and isn’t associated with the increased risk of prostate cancer.
However, it could impact urinary function and cause a variety of uncomfortable symptoms, such as a higher frequency of urination weak flow of urine in the bladder, insufficient emptying of the bladder, and even urinary retention.
What is Prostatitis?
Prostatitis is the term used to describe the swelling or inflammation that occurs in the prostate gland. It is generally caused by infection but other factors that aren’t infectious can cause it to develop.
Prostatitis can affect men of all ages, and can be classified into various types:
- Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: It is caused due to a bacterial infection it is characterized by acute and sudden symptoms that include chills, fever discomfort in the genital or groin area, difficulty in urinating, and frequent urine leaks.
- Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis: Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis is characterized by frequent urinary tract infections inside the prostate gland. The issue typically causes more mild symptoms that can last for a long time.
- Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS): Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS) is the most commonly encountered form of prostatitis. This kind is not bacterial and can be characterized by persistent discomfort in the pelvic region, pain when urinating, and sexual dysfunction. Its exact cause remains unclear.
- Asymptomatic Inflammatory Prostatitis: This kind does not present with obvious symptoms, but it is caused by inflammation of the prostate gland. It is often found out during medical exams for other ailments.
Prostatitis can greatly impact the quality of life as a result of its symptoms. Treatment differs based on the kind and the root cause including antibiotics for infections caused by bacteria anti-inflammatory medicines and alpha-blockers lifestyle adjustments and other specific therapies to reduce symptoms and inflammation.
Importance of the prostate gland in male health
Prostate glands play an important function in the male’s health and reproduction, assisting in different physiological functions.
- Functional Reproductive: The prostate gland produces a large part of the seminal fluid, which is a fluid that nourishes and shields the sperm. When you ejaculate, your prostate produces seminal fluid, which helps in the mobility of sperm and its viability.
- Urinary function: Just below the bladder and surrounded by the prostate gland the prostate gland has a role to play in controlling the flow of urine. It aids in the closing of the urethra in ejaculation to stop urine from entering the bladder. When it becomes the urethra is enlarged (as in BPH) it may block the urethra, which can lead to urinary problems.
- Hormonal Regulation: It is thought that the prostate can be sensitive to certain hormones, such as testosterone as well as dihydrotestosterone (DHT). These hormones impact the prostate’s growth and function in a way that affects its size and potential for conditions such as BPH.
- Sexual Health: The health of the prostate gland could affect sexual function. Prostate-related conditions like prostatitis or BPH may cause pain or discomfort when sexually active, which can lead to erectile dysfunction and other issues with sexuality.
With its many roles in reproductive function the urinary system, reproduction, as well as hormonal control, keeping an active prostate is vital to overall male health. Regular screenings, healthy lifestyle practices, and prompt medical attention for any symptoms that may be troubling greatly improve the health of the prostate, and consequently, the health of males generally.
Comparison Table of BPH and Prostatitis
Certainly, here’s a comparison table highlighting the key differences between BPH (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia) and Prostatitis:
| Aspect | BPH (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia) | Prostatitis |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland | Inflammation or infection of the prostate gland |
| Causes | Age-related hormonal changes | Bacterial infection (acute/chronic), non-bacterial factors |
| Symptoms | Increased urinary frequency – Weak urine flow – Incomplete bladder emptying – Urinary retention | Varies based on type: – Acute: Fever, pain, difficulty urinating – Chronic: Recurrent urinary tract infections – Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS): Pelvic pain, discomfort during urination – Asymptomatic: Typically no noticeable symptoms |
| Diagnosis | Digital rectal examination – Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test – Transrectal ultrasound – Uroflowmetry | Medical history and physical examination – Urine tests (for bacteria or inflammation) – Prostate fluid or tissue analysis – Cultures for bacterial identification |
| Treatment | Watchful waiting for mild symptoms – Medications (alpha-blockers, 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors) – Minimally invasive procedures (TURP, laser therapy) – Surgery (prostatectomy) | Antibiotics for bacterial infections – Alpha-blockers, pain medications – Anti-inflammatory drugs – Lifestyle changes and home remedies |
| Impact on Quality of Life | Urinary symptoms affecting daily activities – Potential impact on sexual health – Psychological stress | Varies based on type: – Acute: Sudden and severe symptoms – Chronic: Recurrent infections, discomfort – CPPS: Long-term pelvic pain, potential sexual dysfunction |
This table provides a comparative overview of the nature, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and impact on quality of life between BPH and Prostatitis, highlighting their distinct characteristics and differences.
Similarities Between BPH and Prostatitis
Certainly! Although BPH (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia) and Prostatitis differ in significant ways there are a few similarities between the two conditions:
- Urinary Symptoms: Both BPH and certain kinds of prostatitis can trigger urinary symptoms. They may be accompanied by increased frequency of urination, a feeling of urgency, and weak flow of urine as well as difficulty initiating urination and the feeling of a lack of bladder emptying. These symptoms may make it difficult to differentiate between the two types of conditions without a proper diagnosis.
- Impact on the quality of your life: Both conditions have the potential to significantly impact the quality of a man’s life. The symptoms of urinary incontinence discomfort, discomfort, and discomfort associated with either BPH or prostatitis may result in disruptions in everyday activities, discomfort when it comes to the urination process, as well as psychological stress.
- Potentially impact on sexual Health: Both BPH and prostatitis could affect sexual health. Although the effects may differ the discomfort or pain that occurs around the pelvic area changes in libido and issues in sexual functioning can be experienced due to either condition and affect sexual satisfaction.
- A need for medical attention: In both cases seeking medical advice and the correct diagnosis is essential. Although they differ in sources and treatment options each BPH or prostatitis requires medical treatment to treat symptoms efficiently and avoid complications.
But it’s important to recognize the fact that BPH as well as prostatitis can be separate diseases with distinct reasons and treatments. A proper diagnosis by a healthcare expert is vital to establish the condition in question and tailor the treatment to suit it.
Conclusion
Although both BPH (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia) and Prostatitis have some common urinary symptoms and can affect men’s health. they are distinct diseases with distinct causes and treatments.
Understanding the distinctions between them is vital to a correct diagnosis and proper treatment. Getting medical attention for an accurate evaluation and a customized treatment is crucial to effectively deal with these issues related to the prostate and ensure overall health for men’s health.
