Definition of Thrombolysis and Fibrinolysis
Thrombolysis: also known as thrombolysis, is a treatment in which medication is used to dissolve blood clots inside blood vessels. The fibrin strands that hold the blood clot together are broken down, allowing the blood to flow freely. This reduces the risk of serious complications like stroke, heart attacks, and pulmonary embolism.
Most commonly, thrombolysis is used to treat emergency situations such as acute ischemic strokes or myocardial ischemia.
Fibrinolysis: Also known as fibrinolysis in some countries, is a process that occurs naturally in the body. It involves the breakdown and removal of fibrin – a protein that forms blood clots. The body does this to prevent blood clots from getting too large and causing serious problems like strokes or heart attacks.
Fibrinolysis is triggered by plasminogen activators, enzymes that convert plasminogen into plasmin. This protein breaks down fibrin. Fibrinolysis is also induced artificially by medication. This can be used for conditions like deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
It is important to distinguish between thrombolysis and fibrinolysis
The two processes are similar in that they both involve the breaking down of blood clots but they differ in their mechanisms, indications, and complications. The use of medications to dissolve blood clots inside blood vessels is known as thrombolysis. It is usually used in emergencies such as acute strokes or myocardial ischemia.
Thrombolysis is only effective in a limited number of cases and can cause serious side effects, such as bleeding. It’s important to use thrombolysis only when it’s appropriate.
Fibrinolysis is a process that occurs naturally in the body. It involves the breakdown and removal of fibrin, which is a protein responsible for clots. The body does this to prevent blood clots from getting too large and causing serious problems like strokes or heart attacks.
Fibrinolysis may also be artificially induced using medications and can be used for conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism. Fibrinolysis does not carry significant bleeding risks, as thrombolysis does.
Healthcare professionals can select the best treatment by determining the difference between thrombolysis (clotting) and fibrinolysis (clotting). This will minimize the risk of complications, and maximize the benefits.
Thrombolysis
The use of medications to dissolve blood clots inside blood vessels is known as thrombolysis. It is usually used in emergencies such as acute strokes or myocardial ischemia.
The thrombolysis breaks down the fibrin fibers that hold a clot in place, allowing the blood to flow freely, and reducing serious complications like stroke, heart attacks, or pulmonary embolism.
It is best to administer thrombolysis as soon after symptoms have begun as possible. This is usually done through intravenous injections or a catheter placed directly in the blood vessel.
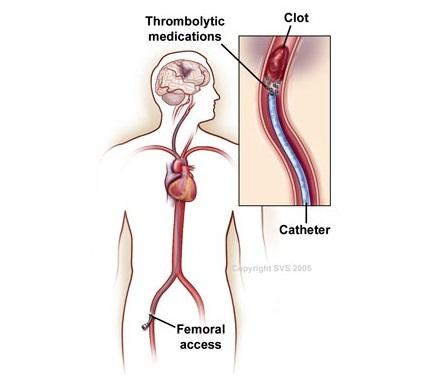
However, thrombolysis does not come without risk and can cause serious side effects, such as bleeding. It is therefore important to carefully weigh the benefits and risks associated with thrombolysis before administering the medication.
A history of bleeding disorders or recent surgery, uncontrolled hypertension, and recent trauma are all contraindications to thrombolysis.
These thrombolytic drugs include tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), as well as reteplase and tenecteplase. These medications are activated by the body’s plasminogen activators. They convert plasminogen into plasmin which breaks down the fibrin strands to dissolve the blood clot.
Fibrinolysis
It involves the breakdown and removal of fibrin – a protein that forms blood clots. The body does this to prevent blood clots from getting too large and causing serious problems like strokes or heart attacks.
You can induce fibrinolysis artificially by using medications. These can be used for conditions like deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
Fibrinolysis is achieved by activating plasminogen activators, which then convert plasminogen into plasmin. This protein breaks down fibrin. Plasmin can also break down fibrinogen, prothrombin, and other blood-clotting agents. This helps to prevent clots from forming.
Contrary to thrombolysis which is usually used in an emergency situation, fibrinolysis can be used prophylactically or as a preventative measure. Patients who are at a high risk of blood clots because of surgery or prolonged bedrest may receive medication that induces fibrinolysis to prevent the formation.
Contraindications to fibrinolysis can include bleeding disorders in the past, recent trauma or surgery, and uncontrolled high blood pressure. Fibrinolysis does not carry significant bleeding risks, as thrombolysis does.
Streptokinase is one of the fibrinolytics that can be used to induce fibrinolysis. Other fibrinolytics include urokinase and alteplase. These medications break down fibrin and prevent blood clots by activating plasminogen into plasmin.
Comparison chart
Here’s a comparison chart highlighting these differences:
| Aspect | Fibrinolysis | Thrombolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The natural process of clot breakdown | Medical intervention to dissolve clots |
| Mechanism | Involves the body’s own enzymes | Involves external agents (drugs) |
| Purpose | Maintains hemostasis and prevents clots | Dissolves existing pathological clots |
| Activation | Typically activated by tissue injury | Artificially induced by drugs or agents |
| Enzyme | Plasmin | Plasminogen activators (e.g., tPA) |
| Substrates | Fibrin and fibrinogen | Fibrin (the major target) |
| Role in the body | Essential for clot removal after healing | Emergency treatment for clot-related conditions |
| Regulation | Tightly regulated to prevent excessive bleeding | Controlled in a medical setting |
| Timeframe | Can occur over days or weeks | Rapid, within hours of intervention |
| Examples | Natural wound healing, prevention of excessive clotting | Treatment for acute myocardial infarction, stroke, pulmonary embolism |
Fibrinolysis is a natural process in the body that helps to maintain hemostasis and prevent excessive clotting. Thrombolysis, on the other hand, is a medical intervention that involves the use of drugs or other agents to dissolve existing pathological blood clots quickly. Thrombolysis is often used in emergencies to treat conditions like heart attacks, strokes, and pulmonary embolisms.
Convenience Thrombolysis and Fibrinolysis
Both thrombolysis and fibrinolysis can be used to treat certain medical conditions. They are effective in preventing serious complications and breaking down blood clots.
It is an excellent option for patients suffering from acute myocardial or ischemic strokes since it dissolves the clot quickly and restores blood flow. When thrombolysis is administered quickly, it can improve the patient’s outcome and reduce the risk of disability or death.
Fibrinolysis is also a good option for patients at risk of blood clots after surgery or long-term bed rest. Healthcare professionals can reduce the risk of complications like deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism by inducing fibrinolysis as a prophylactic measure.
It’s important to remember that thrombolysis or fibrinolysis is not suitable for everyone. Healthcare professionals should carefully weigh the risks and benefits before administering these treatments.
Patients who have a history of bleeding disorders, or have recently undergone surgery or been injured may not be good candidates for thrombolysis and fibrinolysis.
The use of thrombolysis and fibrinolysis is a convenient option for treating certain medical conditions. However, they should be used with caution and in the right way to achieve the best outcomes for patients.
The conclusion of the article
Both thrombolysis and fibrinolysis play an important role in the prevention and treatment of blood clots. Thrombolysis involves using medication to dissolve existing blood clots, while fibrinolysis breaks down fibrin – a protein responsible for clot formation in the blood.
Both thrombolysis (the breakdown of blood clots) and fibrinolysis (the breaking of fibrin) are used to break down blood clots. However, their mechanisms of action, indications, and timings, as well as the risks, differ.
