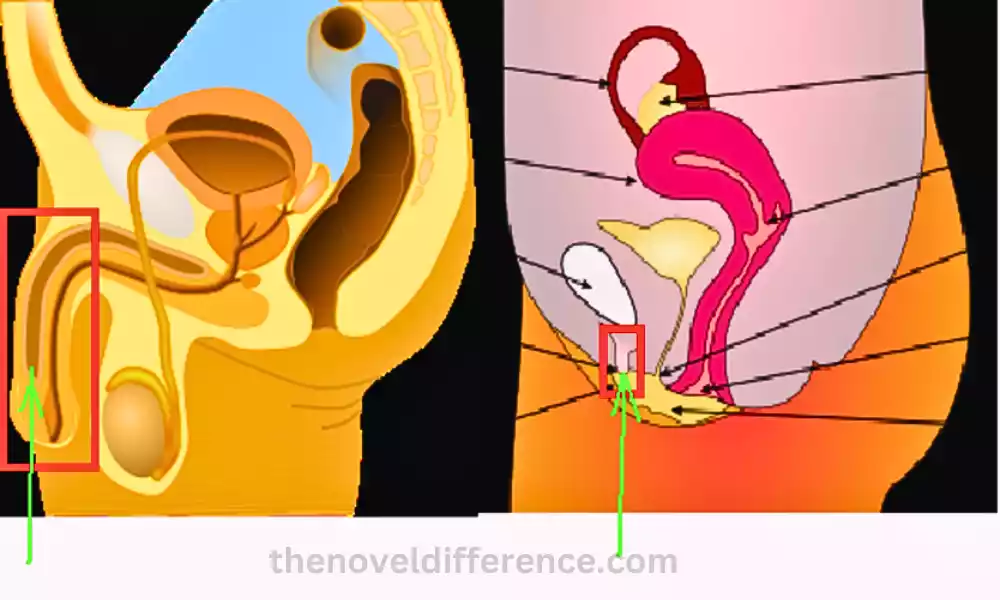
The difference between the corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum is that the corpus cavernosum is an erectile tissue of the penis that surrounds the urethra. While the corpus spongiosum forms an erectile tissue of the penis, it surrounds the lower part of the penis and the male urethra.
Corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum are two different types of erectile tissue in the male body that help in erection. Normally, this is why there are three erectile tissues in the body (two cavernosa and one spongiosum).
They are expandable, sponge-like structures that are involved in the process of penile erection. More blood accumulates to keep the corpus cavernosum properly erect. So the function of the corpus spongiosum is to protect the urethra from pinching off.
Importance of understanding the anatomy of the penis
Understanding the anatomy of the penis is important for a variety of reasons, from reproductive health to overall well-being.
Here are some key points that highlight the importance of understanding penile anatomy:
- Reproductive Health Education: Knowledge of penile anatomy is essential for both men and women to understand the reproductive process. This understanding helps make informed decisions about family planning, contraception, and sexual health.
- Early detection of abnormalities: Awareness of normal penile anatomy enables individuals to detect and identify any abnormalities or changes in the penis such as lumps, lesions or growths. Early detection can be important in diagnosing conditions such as penile cancer or sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Sexual health and function: Understanding the structures involved in sexual arousal, erection, and ejaculation helps individuals understand the mechanisms behind sexual function. This knowledge can contribute to healthy sexual experiences and improved communication with partners.
- Prevention and treatment of conditions: Familiarity with penile anatomy can prevent conditions such as erectile dysfunction, priapism (prolonged and painful erections), and Peyronie’s disease (penile curvature). It also helps to seek appropriate medical help if such problems arise.
- Informed Decision Making: Men considering surgical procedures such as circumcision, penile implants or corrective surgery can make more informed decisions when they have a clear understanding of penile anatomy and its implications.
- Effective communication with health care providers: When individuals can accurately describe their symptoms and understand treatment explanations, this promotes effective communication with health care professionals. This, in turn, leads to accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plans.
- Mental and emotional well-being: Adequate knowledge about penile anatomy can eliminate unnecessary anxiety or worry related to sexual health. Misinformation or lack of understanding can cause unnecessary stress or embarrassment.
- Promoting safe practices: A comprehensive knowledge of penile anatomy, which helps practice safe sex. Its function is to reduce the risk of unintended pregnancy, STIs and other sexual health complications.
Understanding the anatomy of the penis goes beyond basic knowledge—it empowers individuals to take control of their sexual and reproductive health, make informed decisions, and foster open discussions about sexual well-being. It plays a pivotal role in both individual health and public health initiatives.
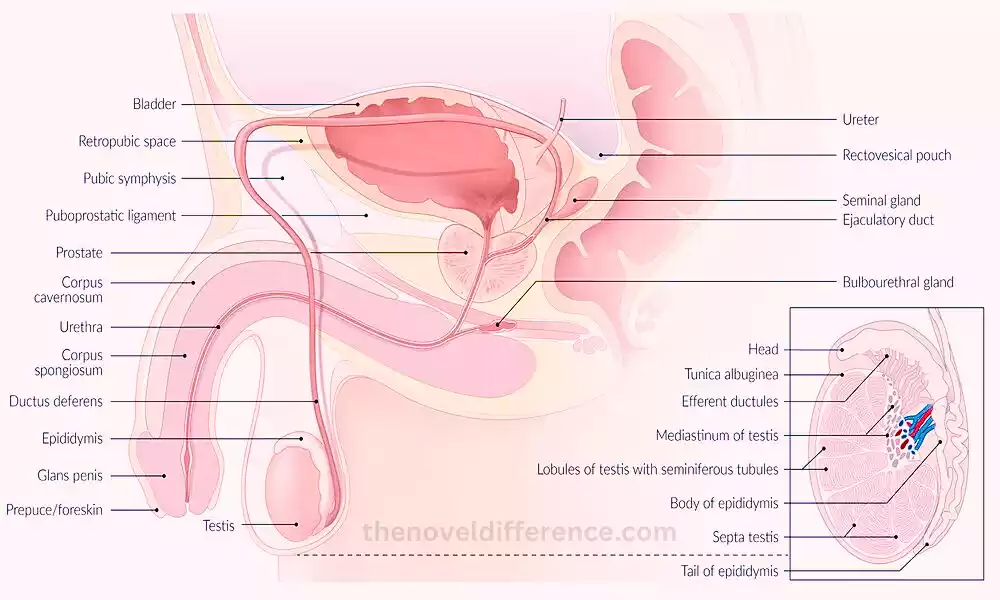
What is Corpus Cavernosum?
Corpus cavernosum refers to a paired structure of the male reproductive system that plays an important role in producing penial erection. It forms a spongy tissue inside the blood vessels that makes the penis rigid.
It fills with blood during erection. During erection, approximately 90% of the blood fills the corpus cavernosum. Therefore, this spongy tissue helps to make the penis very hard to enter the vagina. Thus, the muscle tissue helps during contraction which facilitates the movement of spermatozoa from the tip of the penis.
The corpus cavernosum is made up of smooth muscle and structures called intracavernosal strut. Some of the common conditions affecting the corpus cavernosum are penile cancer, thrombosis, erectile dysfunction, penile fracture, ejaculation disorder, priapism, Peyronie’s disease, and cellulitis.
Things to focus on to check the health of the corpus cavernosum include medical history, physical exam, ultrasound, x-ray, CT scan, and MRI. Sutra, common treatments for affecting the corpus cavernosum include drugs (antibiotics and pain relievers), surgery, and chemotherapy.
What is Corpus Spongiosum?
The corpus spongiosum is a spongy erectile tissue that surrounds the male urethra inside the penis. The corpus spongiosum plays an important role in the rise of the urinary tract by avoiding obstructions in the urinary tract.
This helps preserve the urethra as a reasonably open channel for ejaculation. Additionally, the corpus spongiosum also contributes to the general flexibility and shape of the penis during an erection. Corpus spongiosum is composed of smooth muscle, collagen, and elastic fibers.
Some common conditions that affect the corpus spongiosum are erectile dysfunction and urethral strictures. Common tests to check the health of the corpus spongiosum include a sexual history, a mental health or physical exam, and imaging tests such as X-rays and MRIs.
In addition, common treatments for conditions affecting the corpus spongiosum may include medication (sildenafil), augmentation, urethrotomy, and open surgery.
Comparison table of Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum
Here’s a comparison table of the Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum based on their anatomical and functional characteristics:
| Characteristic | Corpus Cavernosum | Corpus Spongiosum |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Paired structures on the sides of the penis, dorsal to the urethra | Surrounds the urethra, located on the ventral side of the penis |
| Composition | Composed of erectile tissue | Composed of erectile tissue |
| Blood Supply | Receives blood from the deep arteries of the penis | Receives blood from the bulbourethral artery and branches of the internal pudendal artery |
| Erectile Function | Responsible for most of the erectile response during arousal | Keeps the urethra open and allows for the passage of semen during ejaculation |
| Filling Mechanism | Fills with blood during sexual arousal, leading to erection | Fills with blood during sexual arousal, contributing to maintaining the shape of the penis and preventing compression of the urethra |
| Role in Erection | Major contributor to penile rigidity | Supports the structural integrity of the penis during erection |
| Anatomical Differences | Divided into left and right corpora cavernosa; larger in size | Surrounds the urethra as a single structure; smaller in size compared to corpora cavernosa |
| Role in Ejaculation | Not directly involved in the process of ejaculation | Contracts rhythmically during ejaculation to propel semen out of the urethra |
| Sensation | Less sensitive compared to the glans penis | Contains sensitive nerve endings and contributes to sexual pleasure |
| Pathology | Impairment can lead to erectile dysfunction | Impairment can affect urination and potentially impact ejaculation |
It’s important to note that while this comparison table highlights the general characteristics of the Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum, individual variations can exist among different individuals. This information is accurate up until September 2021, and there may have been further developments or research since that time.
Similarities Between Corpus Cavernosum and Corpus Spongiosum?
- The corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum are two diverse sorts of erectile tissues in male life systems.
- Both are spongy erectile tissues.
- They are found within the penis.
- Both of them erectile tissues are made up of smooth muscle cells.
- They help erection and reproduction.
- Both of them erectile tissues are affected by different conditions.
- Conditions influencing these erectile tissues can be analyzed through physical examination and imaging tests.
- conditions influencing these erectile tissues can be treated through drugs and surgeries.
Summary – Corpus Cavernosum vs. Corpus Spongiosum
Corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum are two diverse sorts of erectile tissue in male life structures. Males have two corpus cavernosum and only one corpus spongiosum in the penis. both of them tissues help in erection and reproduction.
The corpus cavernosum helps to properly evacuate blood, while the corpus spongiosum helps maintain the urethra as an effective open channel for ejaculation. The corpus cavernosum is a spongy erectile tissue that lies on either side of the urethra in the penis.
while the corpus spongiosum is a spongy erectile tissue that surrounds the male urethra in the penis. Thus, this summarizes the difference between corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum.
